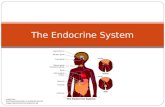
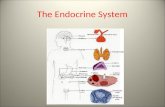
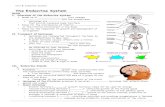
The Endocrine System Image from: mages-system/endocrine-system-01.gif.
Endocrine System
-
Upload
aurorabiologia -
Category
Education
-
view
510 -
download
0
Transcript of Endocrine System

Unit 4. B: Endocrine System

Index
1. Introduction2. How Parathormone Works3. Main Hormones 4.Regulation of the Hormones’ Production5. How Pancreas Works6. Differences between Nervous System and Endocrine System7. Ilnesses related to the Endocrine System

1. IntroductionThe endocrine system is a coordination system, that is, it regulates the functioningof the organism, allowing to keep the internal equilibrium (homeostasis)
Endocrine systemEndocrine glands
releaseHormones
•Thyroid gland•Parathyroid gland•Adrenal glands
•Pancreas•Testes•Ovaries
•Thyroxine and calcitonine•Parathyroid hormone•Cortisol, adrenaline and noradrenaline•Insulin and glucagon•Testosterone•Estrogens and progesterone
contains

Hormones are chemical messengers which act on specific cells in our body.These cells are called target cells. Endocrine glands release hormones into the blood. The target cells recognise the hormone because they have specific receptors for their regulating hormones.
Video: EndocrineSytemGeneral

2. How Parathormone Works
The function of the parathormone is to control the amount of calcium in the blood.It is released by the parathyroid gland.
The target organs of the parathormone are:
•Intestine
•Kidneys
•Bones
When the target organs detect the arrival of the parathormone, they begin to release calcium to the blood.

3. Main HormonesMain human hormones
Gland Hormone Function
Neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary)
OxitocineUterine contraction and lactation
Antidiuretic hormoneIt reduces the production of urine
Adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary)
Growth hormone It stimulates growth
ProlactinIt stimulates production of milk
Tropic hormones They regulate other glands
Thyroid
ThyroxineIt activates the cellular metabolism
CacitoninIt avoids the calcium loss in bones
Parathyroid ParathormoneIt increases the level of calcium in the blood


Main human hormones
Gland Hormone Function
Suprarrenal glandsAdrenaline and noradrenaline
They prepare the organism for physical effort
PancreasInsulin
It decreases the level of glucose in the blood, favouring its entry into the cells
GlucagonIt increases the level of glucose in the blood

Main human hormones
Gland Hormone Function
Testicles TestosteroneDevelopment of masculine sexual characteristics
OvariesEstrogens
Development of female sexual characteristics and control of the ovulation cycles
ProgesteroneUterus’ preparation for the pregnancy

3. Regulation of the hormones’ production
The hypothalamus relates the two coordination systems (endocrine and nervous)
The hypothalamus releases hormones, which control the adenohypophysis. And the adenohypophysis releases tropic hormones which control other glands

An endocrine gland begins to secrete its hormone when it receives a stimulus.Once the stimulus desappears the production of the hormone stops:
when the amount of hormone in the blood is high (FEED BACK)
Feed back
when the stimulus stops Video: Pituitary Gland Regulation
Activity 2 and 3 page 105

4. How Pancreas Works
Pancreas releases insulin and glucagon
Insulin It decreases the level of glucose in the blood, favouring its entry into the cells
Glucagon It increases the level of glucose in the blood
The combination of these hormones keeps the glucose levels in the blood

5. Differences between Nervous System and Endocrine System
Nervous Endocrine
Type of cells Neurons Glands
Type of messengers
Electrical impulses
Chemical messengers (hormones)
Way of transporting
Nerves Blood
Type of answers Fast and short Slow and maintained

Diabetes
It can be caused:
by a lack of insulin Type 1 Diabetes
because the cells do not recognise the insulin Type 2 DiabetesThe result is an increase in the level of glucose in the blood. This is called hyperglycemia
7. Ilnesses related to the Endocrine System
Video: Diabetes1