Endocrine system
-
Upload
dina-ghoraba -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
206 -
download
0
Transcript of Endocrine system

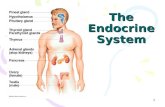
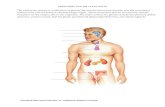
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
BY
DINA ABDEL-AZIM GHAZY GHORABA
LECTURER OF MEDICAL SCIENCE

Body GlandsEndocrine Glands Exocrine Glands
Produce and secrete their hormones directly into the bloodstream
Send their chemical substances into ducts and out of the body

Endocrine Glands
Hormone
BloodstreamTarget Organ Or Tissue
Binds to Its Receptor
Produce Their Effect

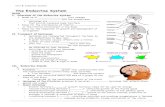
1-Thyroid gland 2-Parathyroid glands (four glands) 3- Adrenal glands (one pair) 4- Pancreas(islets of Langerhans) 5- Pituitary gland 6- Ovaries in female (one pair) 7- Testes in male (one pair) 8- Pineal gland9- Thymus gland(Thymosin)

Howstuffworks Endocrine System.url

[1] Thyroid Gland
1-Thyroid Gland 2- Trachea3- Thyroid Cartilage4- Isthmus

Function:

[2] Parathyroid Gland Epiglottis
Pharynx
Thyroid Gland
Parathyroid Glands
Esophagus Trachia

Function:
Parathyroid Hormone PTH

[2] Adrenal Glands Adrenal Cortex Adrenal Medulla
Kidney
Ureter
Blood Vessels

Function:Adrenal Cortex
Corticosteroids
Glucocorticoid Mineralcorticoid Sex Corticoid
Increase Salt
(Na+)reabsorption

Function:Adrenal Medulla
Catecholamines

[3] Pancreas
Liver
Tail of the
pancreas
Duodenum Stomach head of pancreasThe pancreas Islets of
langerhans DuctExocrine gland cell

Function: Pancreas (islet cells)
Lowers blood sugar Raises blood Sugar
(Glucose to glycogen) (Glycogen to Glucose)

1- Anterior lobe cerebrum
(adenohypophysis)
2-Posterior lobe(Neurohypophysis)
3-Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
[4] Pituitary Gland

HYPOTHALAMUS HYPOTHALAMUS
secretes releasing and inhibiting factors secretes hormones directly to
Via blood
To
anterior pituitary(adenohypophysis) posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
Secretes hormones Stores and releases hormones

Function:Anterior pituitary
Increases water
Stimulates Labor reabsorption

Function:Anterior pituitary
(7 HORMONES)
Adrenocorticotropin Gonadotropin Gonadotropin
Adrenocorlicotropic Follicle-stimulating
hormone (ACTH) hormone (FSH)
(MSH)
Stimulate Ovaries
And testes
PromotesOvulation Stimulate
Testes
Luteinizinghormone
(LH)
Melanocyte Stimulating hormone

Function:Anterior pituitary
(7 HORMONES)
Stomatotropin ThyrotrpinGrowth hormone Thyroid Stimulating
(GH) hormone (TSH))
Stimulates Thyroid Gland
StimulatesMilk
Production
StimulatesGrowth
Prolactin(PRL)

Ovaries
[5] Ovaries
Maintains Pregnancy
Female Sexual
Characteristic

Testes
[5]Testes

Abnormal ConditionsEnlargement =Goiter
1. Endemic in certain regions due to deficiency of iodine in the diet
Treatment :to increase the supply of iodine in the diet.
2. Hyperplasia: Treatment : thyroid hormone
to suppress the normal thyroid functioning

Hypersecretion=Hyperthyroidism
=Graves diseaseWith Exophthalmos (protrusion of the eyeballs) occurs as a result of the swelling of tissue behind the
eyeball.
Treatment• Thyroidectomy, • Antithyroid drugs• Administration of radioactive iodine

Hyposecretion=Hypothyroidism
= Graves disease1. Myxedema
adulthood result in
blood lipid(Atherosclerosis)Edema because of the
collection of mucus-like (myx/o means, mucus) material under the skin
Treatment by
thyroid hormone

3. Cretinism: In Childhood leads to a lack of normal physical and mental growth

Neoplasm = Thyroid Carcinoma
• Some tumors are very slow growing, and others may metastasize widely. Adenomas (benign growths) can be distinguished from carcinomas (malignant growths) by radioactive iodine tracer scans.