Endocrine System Part 1. Endocrine System The endocrine system is the “other” control system of…
Endocrine System
-
Upload
dana-tuazon -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
2.847 -
download
5
Transcript of Endocrine System

THE ENDOCRINE
SYSTEM

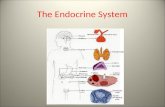
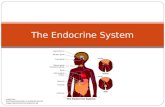
The endocrine system consists of a collection of small glands that regulates a number of vital functions of our body.
Includes all the glands in the body.
endocrine system is instrumental in regulating mood, growth and development, tissue function, metabolism, and sexual function and reproductive processes.
endocrine system is in charge of body processes that happen slowly, such as cell growth. Faster processes like breathing and body movement are controlled by the nervous system. But even though the nervous system and endocrine system are separate systems, they often work together to help the body function properly.
DEFINITION OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM

1) To maintain a stable environment within the body or homeostasis.
Ex: Maintaining the blood sugar levels according to changes occurring in the body is homeostasis
2) Promoting the structural changes of the body.
Ex: The permanent changes occurring in the body over the period of time like height, development of sexual organs, etc. is a part of the structural changes.
FUNCTIONS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM

1) HORMONES Body's chemical messengers. Transfer information and instructions from one set of
cells to another.
2) GLANDS Group of cells that produces and secretes, or gives off,
chemicals. Selects and removes materials from the blood,
processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body.
Some types of glands release their secretions in specific areas. For instance, exocrine glands, such as the sweat and salivary glands, release secretions in the skin or inside the mouth. Endocrine glands, on the other hand, release more than 20 major hormones directly into the bloodstream where they can be transported to cells in other parts of the body.
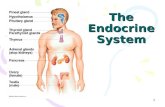
FOUNDATION OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM

1. Hypothalamus2. Pituitary gland3. Parathyroid gland4. Thyroid gland5. Adrenal glands6. Pancreas7. Ovaries (in female body)8. Testes (in male body)
8 MAJOR GLANDS THAT HELPS IN THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM TO
FUNCTION

a collection of specialized cells that is located in the lower central part of the brain, it is the main link between the endocrine and nervous systems. The nerve cells of the hypothalamus control the pituitary gland by stimulating or suppressing the hormone secretions.
1. HYPOTHALAMUS

It is an endocrine gland about the size of a pea and weighing 0.5 g (0.02 oz.), in humans
Most important part in the endocrine system
The pituitary gland secrete hormones on the basis of the emotional and seasonal changes
Pituitary gland is divided into two parts: the anterior lobe and the posterior lobe
2. PITUITARY GLAND

These are four tiny glands that are attached to the thyroid gland.
They release the parathyroid hormone that helps in regulating the level of calcium in blood along with another hormone produced by thyroid called as calcitinin.
3. PARATHYROID GLAND

The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls how sensitive the body should be to other hormones.
It also plays a role in bone growth and development of the brain and nervous system in children.
4. THYROID GLAND

The adrenal glands are triangular-shaped glands located on top of each kidney.
The adrenal glands are made up of two parts. The outer part is called the adrenal cortex, and the inner part is called the adrenal medulla. The outer part produces hormones called corticosteroids, which regulate the body's metabolism, the balance of salt and water in the body, the immune system, and sexual function. The adrenal medulla, produces hormones called catecholamines (ex: adrenaline). These hormones help the body cope with physical and emotional stress by increasing the heart rate and blood pressure.
5. ADRENAL GLANDS

Click icon to add picture

The pancreas is an elongated organ located toward the back of the abdomen behind the stomach.
The pancreas has digestive and hormonal functions. One part of the pancreas, the exocrine pancreas, secretes digestive enzymes. The other part of the pancreas, the endocrine pancreas, secretes hormones called insulin and glucagon. These hormones regulate the level of glucose (sugar) in the blood.
6. PANCREAS

The female gonads, or ovaries, secrete the female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone, which help in stimulating the production of eggs. Moreover, they are also responsible for the physical changes that occur during puberty, besides regulating the menstrual cycle.
7. OVARIES (IN FEMALE BODY)

The male gonads, called the testes, are located in the scrotum.
The male sex hormones influence changes related to physical and sexual development, and the male secondary sex characteristics like growth of pubic and facial hair, change in voice, etc. Testosterone also assists in sperm production.
8. TESTES (IN MALE BODY)

There are almost 30 hormones on our body that are being produced by various glands of the endocrine system.
The sense of thirst and hunger is triggered in our body by the hypothalamus gland.
The pineal gland induces sleep in our body. It produces a hormone named melatonin which controls the sleep cycle of our body.
The behavior and the characteristic of a person is largely influenced by the endocrine system.
DID YOU KNOW THAT …

- THE END -
-Created by Ai-Ni Bautista

GROUP MEMBERS :
Jazmine Bianca de Guzman
Ai-Ni Bautista
Jeanne Pauline Tejoso
Norhaina Oranon
Dave Gallarte
GROUP 1