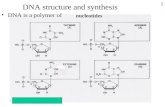
DNA Replication. Genes as Information Transfer A gene is the sequence of nucleotides within a...
-
Upload
eustace-hoover -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
description
Transcript of DNA Replication. Genes as Information Transfer A gene is the sequence of nucleotides within a...

DNA ReplicationDNA Replication

Genes as Information TransferGenes as Information Transfer
A A genegene is the sequence of nucleotides is the sequence of nucleotides within a portion of DNA that codes for a within a portion of DNA that codes for a peptide or a functional RNApeptide or a functional RNA
Sum of all genes = Sum of all genes = genomegenome

DNA Replication is DNA Replication is SemiconservativeSemiconservative
Each strand of the parent DNA is used as a Each strand of the parent DNA is used as a templatetemplate to make the new daughter strand to make the new daughter strand
DNA replication makes 2 new complete double DNA replication makes 2 new complete double helices each with 1 old and 1 new strandhelices each with 1 old and 1 new strand

Steps in DNA Replication
1. DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds holding bases together.
2. DNA polymerase adds new complementary nucleotides to each original strand from 5’ to 3’.
3. Each new DNA molecule is identical to the parent DNA molecule and is composed of an original strand and a new strand.