DNA and RNA Chapter 12. Types of Nucleic Acids DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) RNA (Ribose Nucleic...
-
Upload
dylan-bailey -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
0
Transcript of DNA and RNA Chapter 12. Types of Nucleic Acids DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) RNA (Ribose Nucleic...

DNA and
RNA
Chapter 12

Types of Nucleic Acids
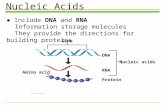
• DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid)
• RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid)

DNA Structure
•DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix.
•A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of tiny subunits called Nucleotides.

Nucleotides are composed of:1. A sugar 2. A phosphate group3. A nitrogenous base

Nucleotides
Phosphate
Pentose
Sugar
Nitrogenous
Base

Nucleotides• The phosphate and sugar form the
backbone of the DNA molecule, whereas the bases form the “rungs”.
• There are four types of nitrogenous bases.

Nucleotides
A
Adenine
T
Thymine
G
Guanine
C
Cytosine

Nucleotides
• Each base will only bond with one other specific base.
• Adenine (A)• Thymine (T)
• Cytosine (C)• Guanine (G)
Form a base pair.
Form a base pair.

DNA is a molecule of nucleic acid that stores and transfers genetic information.
Nitrogenous Bases
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)

Chargaff’s Rule
• Percentages of guanine and cytosine and percentages of adenine and thymine are almost equal in any sample of DNA.
• A = T and C = G

Question
If 32% of the bases in a certain sample of DNA were thymine, what would be the percentages of adenine, cytosine and guanine?

DNA Replication
• DNA duplicating before a cell divides• A pairs with T and G pairs with C
In the diagram, the complementary strand would be:
GTAGGC

G
G
A
T
T
A
A
C
T
G
C
A
T
C

RNA• A messenger between DNA and
ribosomes
• “Decodes” the genetic message contained in the DNA molecule

3 Types of RNA:
• Messenger RNA (mRNA) - copies information from DNA and carries it to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm
• Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - makes up the major part of the ribosomes
• Transfer RNA (tRNA) - carries amino acids to the ribosomes where the amino acids are joined to form a polypeptide

Transcription
• Information in a DNA molecule is transferred to an mRNA molecule (DNA RNA).
• Guanine pairs with Cytosine
• Adenine pairs with Uracil
• Thymine pairs with Adenine

Practice Transcribing DNA
CUAGGA

Translation
• Decoding mRNA into a chain of amino acids (RNA proteins)
• Groups of 3 RNA nucleotides, called codons are “decoded” into amino acids

TranslationSection 12-3

TranslationSection 12-3

DNA RNA
• Deoxyribose (sugar)• Double stranded• Nitrogenous bases:
– Guanine– Cytosine– Adenine– Thymine
• Ribose (sugar)• Single stranded• Nitrogenous bases:
– Guanine– Cytosine– Adenine– Uracil

Codon
• Three-nucleotide sequence on mRNA that codes for a single amino acid

The Genetic Code

The Genetic Code

Mutation
• Change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information

Blueprint
• DNA is the blueprint of an organism
• DNA tells an organisms how to construct it self

Genetic Mutations
• Point Mutations – change involving one or a few nucleotides– Substitution of one base for another– Insertion or deletion of a base
• Frameshift Mutations – shifts the reading of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide

Substitution InsertionDeletion
Genetic Mutations: Substitutions, Insertions, Deletions
Section 12-4

Chromosomal Mutationsinvolve a change in the number or structure
• Deletion – loss of chromosome
• Duplication – produce extra copies of parts
• Inversions – reverse direction of parts
• Translocations – part breaks off and attaches to another part

Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Translocation
Chromosomal MutationsSection 12-4