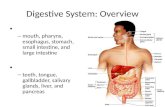
Digestive system organs Alimentary canal or GI tract 1. mouth 2. pharynx 3. esophagus 4. stomach 5....
-
Upload
chad-james -
Category
Documents
-
view
382 -
download
6
Transcript of Digestive system organs Alimentary canal or GI tract 1. mouth 2. pharynx 3. esophagus 4. stomach 5....

Digestive system organs
• Alimentary canal or GI tract
1. mouth
2. pharynx
3. esophagus
4. stomach
5. small intestine
6. large intestine



Digestive system organs
• Accessory glands and organs
1. teeth
2. tongue
3. salivary glands
4. gallbladder
5. pancreas
6. liver








Anatomy of the organs of the alimentary canal (GI tract)
From the esophagus to the anal canal, the walls of every organ are made up of 4 basic tunics from the lumen outward these layers are : 1.mucosa
2. submucosa
3. muscularis externa
4. serosa (or adventitia)


Anatomy of the organs of the alimentary canal (GI tract)
MucosaThe mucosa consists of 3 layers
1. surface epithelium
2. lamina propia
3. muscularis mucosa
The surface epithelium, typically simple columnar epithelia rich in mucus secreting cells goblet cells.



Anatomy of the organs of the alimentary canal (GI tract)
Underlain the surface epithlium there is a small amount of connective tissue made of areolar connective tissue called the lamina propria The lamina propia contains capillaries which nourish the epithelia and function in absorption. It also contains lymph nodes important in defense against bacteria and other pathogens.


Anatomy of the organs of the alimentary canal (GI tract)
Underlain the lamina propia there is a scant smooth muscle layer called the muscularis mucosae. The muscularis mucosae produces local movements and make small folds vastly increasing the surface area.

Anatomy of the organs of the alimentary canal (GI tract)
Submucosa
Made of dense connective contains a rich blood supply, lymphatic, elastic fibers and nerves. Contains the submucosal plexus which is part of the intrinsic nerve supply of the GI tract.


Anatomy of the organs of the alimentary canal (GI tract)
Muscularis externa
The muscularis externa is responsible for segmentation and peristalsis typically has an inner circular layer and outer longitudinal layers of smooth muscle. In many places the circular layer thickens to form sphincters that act as valves to control food passage. The myenteric plexuses the second intrinsic nerve supply of the GI tract lays between the circular and longitudinal smooth muscle layers.





Anatomy of the organs of the alimentary canal (GI tract)
Serosa-
The outermost protective is formed of aerolar connective tissue and mesothelium a single layer of squamouss epithelial tissue. The serosa contains the subserous plexus the third autonomic plexus . In the esophagus the serosa is replaced by an adventitia which is an ordinary fibrous connective tissue. Retroperitoneal organs have both a serosa and an adventitia


Basic functional concepts
1. All processes in GI tract are geared to control the lumen to maximize the digestive processess. The lumen is actually outside the body
How ??
By reflex arcs which involve neural and hormonal componenets. and stimuli sensed by sensors mechano and chemo

Basic functional concepts
2. Local control - short and long reflexes. Short reflexes are mediated entirely by the enteric plexuses inn response to GI tract stimuli. Long reflexes initiated by stimuli arising within or outside the GI tract and involve CNS centers and extrinsic autonomic nerves.







Digestive Processes1. ingestion
2. propulsion
3. mechanical digestion
4. chemical digestion
5. absorption
6. defecation

Digestion and absorptionCarbohydrates
Broken down to monosaccharides: glucose, fructose and galactose. Starting in mouth with salivary amylase, a little in the stomach before acid destroys it and finishing in the small intestine with pancreatic amylase. Absorbed in the first segment of small intestine by an active transport system which can not be saturated




Digestion and absorptionProtein
First to fragments in stomach by pepsin and small intestine by trypsin and chymotrypsin. Further by pancreatic carboxypeptidase and brush border aminopeptidase. Transported by secondary active transport linked to Na+. Small # of small intact proteins can cross the small intestine walls- passive immunity in infants



Digestion and absorption
Fat-
Quite complex digestion process. Fat are insoluble in water and therefore arrived at the small intestine as a TG fat droplet. They get emulsify by bile salts then lipase goes to work on their surface splitting TG into 2 free fa and a monoglyceride and make micelles.


Digestion and absorptionFat (continued)
Micelles get absorbed in the small intestine cell wall and during their passage the monoglycerides and free fa’s combine to form TG which are wrapped in a membrane in the rough ER called chylomicrons which get absorbed by the lacteal not the capillaries and end up in the general circulation

Digestion and absorption
Minerals and water
Water is highly diffusable and 95% of ingested is absorbed by passive diffusion in small intestine. Na+, K+, active transport Na, K ATPase pump. Other minerals such as calcium and potassium and trace minerals such as iron and zinc are also absorbed in the small intestine





Digestion and absorption
Vitamins
Fat soluble are solubilized in chylomicrons. Most soluble vitamins are absorbed by diffusion or carrier mediated transport with the exception of B12 which is a very large molecule and requires to bind to intrinsic factor released by parietal cells absorbed in the ileum.