Two-Source Constructive and Destructive Interference Conditions.
Constructive and Destructive Forces
Transcript of Constructive and Destructive Forces

Constructive and
Destructive Forces Processes That Act Upon Earth’s
Surface Features

What are Constructive and
Destructive Forces?
• Constructive Force
– A constructive force is
a process that raises
or builds up the
surface features of the
Earth.
• Destructive Force
– A destructive force is a
process that lowers or
tears down the surface
features of the Earth.

What Are Surface Features?
– Surface features are landforms and bodies of
water that cover the Earth’s surface such as:
• mountains
• valleys
• canyons
• gorges
• beaches
• sand dunes
• barrier Islands
• flood-plains
• moraines and drumlins
• volcanoes
• oceans
• lakes
• rivers

How Can a Surface Feature be
Changed by a Constructive Force?
– Natural forces such as wind, water, ice,
through the process of deposition.
• Deposition is the process of dumping sediment,
dirt, rocks, or particles in one place.
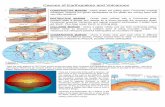
– The movement of the Earth’s crust through
Plate Tectonics

Constructive Force Examples of Deposition
Constructive
Process
Surface
Feature
Force/Agent
Deposition
Deltas water / river
Floodplains water / river
Beaches and
Barrier Islands
water / ocean
long-shore
current
Sand dunes wind
Moraines and
drumlins
Ice / glacier

Other Constructive Forces
Constructive
Process
Surface
Feature
Force
Folding Mountains Plate
tectonics
Faulting Mountains Plate
tectonics
Earthquake Trench
Fault
Plate
tectonics
Volcanic
Activity
Mountains
Islands
Plate
tectonics

How Can a Surface Feature be
Changed by a Destructive
Force?
– Physical or Chemical Weathering
• Weathering is the breaking down of rock into
sediment.
– Natural forces such as wind, water, ice,
through the process of erosion.
• Erosion is the movement of sediment from one
place to another.

Changing the Earth’s Surface by a
Destructive Force Examples of Weathering
• Mechanical / Physical
Weathering
– Temperature Change-Freezing and thawing of Rock
– Ice Wedging-Water freezing and expanding in cracks of rock
– Impact of organisms
• Root Pry
• Animals burrowing
• Chemical Weathering
– Oxidation / rusting
– Carbonic Acid / acid rain
• Caverns
– Impact of organisms
• Secretion of acid from Lichen

Destructive Force Examples of Erosion
Destructive
Process
Surface
Feature
Force/Agent
Erosion
Canyons,
Gorges, V-
Shaped Valleys
Water
Sea Arches,
Sea Stacks
Water
Buttes, Desert Wind
U-Shaped Valleys Ice
Mudslide,
Sinkholes
Gravity

Other Destructive Forces
• Volcanic Activity
– Movement of Earths Crust (Plate tectonics)
• Reshaping of Mountains
• Earthquakes
– Movement of Earths Crust (Plate tectonics)
• Trenches
– cracks in the Earth Curst

What Do You Think?

Deposition is a process
that…
A. Dissolves sediment
B. Breaks down rock to form sediment
C. Removes sediment from landforms
D. Drops sediment to form landforms

Where do deltas form?
A. In desert areas
B. At river mouths
C. On the banks of rivers
D. In valleys formed by glaciers

Long shore currents
help create…
A. Beaches
B. Dunes
C. Rivers
D. Drumlins

Volcanoes can create
new land when they
release…
A. Lava
B. Water
C. Faults
D. Mud

What forms moraines
and drumlins?
A. Wind
B. Rivers
C. Glaciers
D. Volcanoes

What landform forms
from deposition at the
mouths of rivers?
A. a delta
B. a floodplain
C. a sand dune
D. a moraine

What is weathering?
A. A type of climate
B. The transport of sediment
C. The breakdown of rock
D. The aging of rock

Which of these is
caused by chemical
weathering?
A. desert pavement
B. formation of U-shaped valleys
C. formation of rust
D. ice expanding in cracks in rock at is
weathering?

How do earthquakes
change the land?
A. They transport sediment.
B. They form cracks in the surface.
C. They release ash and lava.
D. They cause chemical weathering.

A river can form …
A. Sea arches.
B. U-shaped valleys.
C. V-shaped valleys.
D. Desert pavement.

Deposition forms these
features on coasts.
A. drumlins
B. floodplains
C. barrier islands
D. U-shaped valleys

What causes V-shaped
valleys to form?
A. deposition at river mouths
B. erosion by rivers
C. weathering by wind
D. erosion by glaciers

What does erosion do?
A. breaks down rock physically
B. moves broken pieces of rock
C. changes rock chemically
D. change sediment into rock