Concept: Density. A. The diagram below shows 4 samples of Copper. Which sample will have the highest...
-
Upload
bernard-holt -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Concept: Density. A. The diagram below shows 4 samples of Copper. Which sample will have the highest...

Concept: Density

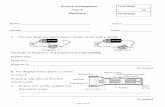
A. The diagram below shows 4 samples of Copper. Which sample will have the highest density?
B. The diagram below show a sample on an unknown substance. What is the density of the substance?

C. What is the purpose of the “tare” button?
D. What is the mass of the liquid in the graduated cylinder?
E. What is the volume of the liquid in the graduated cylinder?
F. What is the density of the liquid in the graduated cylinder?

Answers:
A.They all have the same density because they are all the same substance. The size of the sample does not change the density.
B.D=M/V D=12g/6cm3 D=2g/cm3
C. The tare button is used to zero the balance so that you do not have to record and subtract the mass of the graduated cylinder.
D. 120g ( The mass does not include the mass of the graduated cylinder. See answer to C.)
E. 22ml ( measure at the bottom of the meniscus. )
F.D=M/V D=120g/22ml D=5.5g/ml ( Obviously this is not water because the density of water is only 1g/ml.)