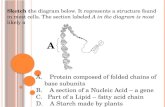
Sketch t he diagram below. It represents a structure found
description
Transcript of Sketch t he diagram below. It represents a structure found

Sketch the diagram below. It represents a structure found
in most cells. The section labeled A in the diagram is most
likely a
AA
A. Protein composed of folded chains of base subunits
B. A section of a Nucleic Acid – a gene
C. Part of a Lipid – fatty acid chainD. A Starch made by plants

HW QUIZ 2Take out a
sheet of paper and
number it 1-5

HOMEWORK QUIZ 1. Evolution can be defined as change in the
______ _____ over time.a) natural selectionb) gene poolc) genetic mutations
2. Mr. Andersen used the fingers on your hand to remember the different mechanisms of evolution. What did the “M” of the middle finger stand for?

HOMEWORK QUIZ3. What are two examples of gene flow?
a) exit and enterb) emigrate and immigratec) mutations and non-random mating
4. Which mechanism is the only one that leads to organisms better adapted for their environments?
a) non-random matingb) small populationc) ratural selection

HOMEWORK QUIZ5. What real-life example did Mr. Andersen
give to demonstrate how natural selection works?
BONUS: Speciation is equivalent to which of the following?
microevolution OR macroevolution

BELLWORK: JUST WRITE THE ANSWER. IS IT CO-EVOLUTION, CONVERGENT EVOLUTION, OR DIVERGENT EVOLUTION?
A. The tortoises on the Galapagos islands share a common ancestor, but over time they have become
adapted for obtaining food in different habitats on different islands by having different
neck lengthsB. Whales, sharks, and penguins all have the same bodies and fins/flipper for moving in water even though they belong in different animal groups (mammals, fish, and birds)
C. Hummingbirds have a beak just the right length to reach the nectar in a cardinal flower and as they feed their foreheads bump into the pollen structure. Cardinal flowers are red which hummingbirds can see, but bees can’t, and their pollen structure is at just the right height forthe hummingbird to pick up pollen as it feeds.

CO: I WILL ANALYZE AND EVALUATE THE EFFECTS OF OTHER EVOLUTIONARY MECHANISMS.
LO: I WILL WRITE A DIAGRAM FOR MY NOTES. I WILL TALK WITH MY CLASSMATES ABOUT OTHER EVOLUTIONARY MECHANISMS.

A GENE POOL IS THE TOTAL NUMBER OF GENES OF EVERY INDIVIDUAL IN AN INTERBREEDING POPULATION.

EVOLUTION CAN BE DEFINED AS A CHANGE IN THE GENE POOL OVER TIME.

THERE ARE 5 FACTORS THAT CAN AFFECT THE FREQUENCY OF A GENE IN THE GENE POOL.
1. Genetic Mutation2. Natural Selection3. Small Population4. Non-random mating5. Gene Flow

1. GENETIC MUTATION: Changes in DNA that happen due to errors in
replication, transcription, translation, or because of environmental factors. The source of all new genes/traits in a population

2. NATURAL SELECTION survival of the fittest advantageous genes are passed
on to the next generation while harmful genes are eliminated
the driving force of evolution

3. SMALL POPULATION• Genetic Drift is a
random change in the frequency of alleles in a population. This has an especially big effect in small populations.
• A) Bottleneck effect- when a large portion of a population dies causing a significant decrease in the size of the gene pool.

3. SMALL POPULATION• B) Founder effect- when a few individuals from a
population leave and start another population in a different location. This also decreases the size of the gene pool in the new population.

4. NON-RANDOM MATING• Not all mates are created
equal.• In many species, mates are
not selected at random. Instead they are chosen for specific characteristics. Many organisms compete for mating rites. Strong and good-looking organisms are typically favored.
• This limits the size of the gene pool because only the genes of the mating individuals are passed to the next generation.

5. GENE FLOW
GENE FLOW IS THE MOVEMENT OF GENES INTO OR OUT OF A POPULATION.
A) Emigration- when individuals leave a population decreasing the size of the gene pool.
B) Immigration- when individuals from a different population enter a new population and begin breeding. This increases the size of the gene pool.


EFFECTS OF GENE POOL SIZE A decrease in the size of a gene pool increases
the speed of evolution and visa versa.

SCENARIOS

MIX-FREEZE-GROUP
2 43• I am going to survive! Because I have the best genes
for my environment.• I am HUGELY affected by genetic drift.• I am VERY picky. I will only choose you, because your
traits are most attractive to me.• I am a mistake in the DNA sequence
5Natural Selection
SmallPopulation
GeneticMutation
Non-RandomMating

1. Amish people are required by their religion to only marry and have children with other Amish people.

2. The DNA sequence in a bird is changed from ATT CCG TTG to TTA CCG TTG which changes the beak shape from long and thin to short and fat.

3. Peppered moths are eaten by birds. The moth color varies from light to dark. Light colored moths can blend in with a nearby species of tree. In the 1800s factories released large amounts of soot, which changed the tree color, so the birds were able to more easily find the lighter moths instead of the darker moths.

4. Northern elephant seals were hunted almost to extinction by people in the 1890s. The remaining population has reduced genetic variation.

5. A lioness joins a new pride and has cubs with the male lion.

6. A small group of birds flies from the mainland to an island and starts a new colony. (The birds never return to the mainland.)