Chapter 5. A. The integument is either considered an organ or organ system. (The terms integument &...
-
Upload
basil-strickland -
Category
Documents
-
view
246 -
download
1
Transcript of Chapter 5. A. The integument is either considered an organ or organ system. (The terms integument &...

THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
Chapter 5

I. INTRODUCTION
A. The integument is either considered an organ or organ system.(The terms integument & integumentary system are interchangeable)

B. Components of the I.S.:
1. Cutaneous membrane:a) Epidermis- superficial epitheliumb) Dermis- underlying connective tissues
2. Accessory structures:a) Hairb) Nailsc) Exocrine glands

3. Subcutaneous layer (aka. hypodermis or superficial fascia):
a) Loose connective tissue located below the dermis
b) Not necessarily considered part of the integument

C. GENERAL FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN:
1. Protection of underlying structures
2. Excretion of salts, water & wastes
3. Maintenance of body temperature
4. Synthesis of vitamin D3 (used in Ca absorption)
5. Storage of nutrients
6. Detection of stimuli

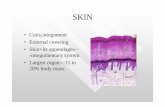
II. THE EPIDERMIS
A. Physiology: provides physical protection, prevents fluid loss, and helps keep microorganisms out of the body
B. Anatomy: stratified squamous epithelium

C. Keratinocytes- the most abundant cells in the epidermis
1. Thick skin (on hands & feet) has 5 layers
2. Thin skin (everywhere else) has 4 layers

D. LAYERS OF THE EPIDERMIS (DEEP TO SUPERFICIAL)

1. Stratum Germinativum (aka. Stratum Basale)a) Firmly attached to the basement membrane
b) Epidermal ridges & dermal papilla form ridges & valleys i. Increases surface areaii. Creates contours on the skin surface (ex.
fingerprints)

c) Cell types:i. Basal cells: germinative cells that replace
keratinocytes
ii. Merkel cells: sensitive to touch
iii. Melanocytes: pigment cells

2. Stratum Spinosum “spiny layer”a) 8-10 layers of cells bound together by cell
junctions
b) Contain Langerhans cells- part of the immune response

3. Stratum Granulosum “grainy layer”a) 3-5 layers of keratinocytes
b) most cells stop dividing and start producing keratin and keratohyalin (fibrous proteins)
c) Cells eventually die & become less permeable
4. Stratum Luciduma) Found only in thick skin of the palms & soles
b) Cells are flattened, densely packed and filled w/ keratin

5. Stratum Corneuma) Located at the surface of both thick and thin
skin
b) 15-30 layers of keratinized cells
c) Usually shed in sheets, not individually
d) Cells take 15-30 days to travel from the stratum germinativum to the stratum corneum and about 2 weeks until they are shed or washed away
e) Normally relatively dry, inhibiting the growth of microorganisms

THICK SKIN

f) This layer is water resistant, not waterproof:i. Insensible perspiration: interstitial fluid
slowly moves to the surface to evaporate (~500 ml/day)
ii. Damage to the epidermis can increase fluid movement
iii. Blister- when damage separates layers of the epidermis & fluid accumulates in pockets
iv. Greater damage can cause greater water loss, like in burn victims
v. Sitting in water causes water to move in (freshwater) or out (salt water) due to osmosis

Please answer the 4 questions on the bottom of page 151 for tomorrow.
Try this quiz

E. SKIN COLOR1. Skin pigment composition &
concentrationa) Carotene
i. Orange-yellow pigment
ii. Accumulates inside epidermal cells & also in fatty tissues of the dermis
iii. Most apparent in cells of the stratum corneum of light-skinned people
iv. Also found in vegetables like carrots & squash
v. Can be converted to vitamin A (needed for maintenance of epithelia & the eyes)

b) Melanini. Brown, yellow-brown or black pigment
produced by melanocytes
ii. The effect on skin color depends on where it is released in the epidermis:
In white people, it is released in the stratum germinativum & stratum spinosum
In black people, it is also released in the stratum granulosum
Protects the epidermis and dermis from ultraviolet radiation from sunlight, which can cause burns, premature wrinkles and DNA mutations leading to cancer

2. The dermal blood supplya) Blood contains the pigment
hemoglobin, which turns bright red when it binds with O2
b) Most obvious in light-skinned people
c) Variations:i. Blushing or inflammation- blood vessels
dilate
ii. Pale skin- reduced blood supply
iii. Cyanosis- sustained reduction in blood supply in response to cold or problems such as heart failure or severe asthma

F. The Epidermis and Vitamin D3
1. When exposed to sunlight, cells in the stratum spinosum and stratum germinativum make vitamin D3
2. The liver converts vitamin D3 into a product used by the kidneys to make the hormone calcitriol.
3. Calcitriol is needed for the absorption of calcium and phosphorous by the small intestine

Please answer the 3 questions on the top of page 154.

III. THE DERMIS
A. Dermal Organization1. Two major components:
a) Papillary Layer (superficial)i. Consists of loose connective tissueii. Contains capillaries & sensory neurons
b) Reticular Layer (deep)i. Meshwork of dense irregular connective tissue
(collagen & elastin)ii. Bundles of collagen fibers extend into the layers
above and below, so boundary is indistinctiii. Also contains blood vessels and nerves

2. WRINKLES & STRETCH MARKSa) Collagen fibers are strong & resistant to stretching
b) Elastic fibers permit stretching and will then return to the original length
c) The skin will stretch only as far as the collagen fibers will allow, thus preventing tissue damage
d) Water in the skin also allows flexibility
e) Aging, hormones & damage from UV rays reduces the amount of elastin in the dermis, producing wrinkles & sagging skin
f) Stretch marks occur from extensive distortion of the dermis (pregnancy, weight gain, growth spurts)


3. LINES OF CLEAVAGEa) Most collagen and elastic fibers at
any one location are arranged in parallel bundles
b) The orientation of bundles depends on stresses that occur during normal movements
c) The resulting pattern establishes lines of of cleavage of the skin
d) A surgeon will cut parallel to the lines instead of perpendicular to them to keep the cut from pulling open

B. DERMAL CIRCULATION & INNERVATION
1. The Dermal Blood Supplya) Read more about this on page 155 in your
text
b) Ulcers or bedsores may affect bedridden or immobile peoplei. Circulation is cut off when blood vessels are
pressed against deeper structures for extended periods of time
ii. Eventually this will lead to necrosis (tissue death)
c) Birthmarks & “port wine stains” occur from tumors in the dermal blood supply


2. THE INNERVATION OF THE SKIN
a) Nerve fibers control:i. Blood flowii. Adjust gland secretion ratesiii. Monitor sensory receptors in the dermis & deep
epidermis
b) The dermis & deep epidermis contains sensory receptors for:i. Light touchii. Painiii. Temperatureiv. Deep pressurev. vibrations

Please answer the 2 questions near the bottom of page 156.

IV. THE SUBCUTANEOUS LAYER (HYPODERMIS)
A. Stabilizes the position of the skin relative to underlying tissue (muscle, organs), while permitting independent movement
B. Consists of loose connective tissue w/ lots of fat cells and elastic fibers
C. Only the superficial region contains large arteries & veins
D. Some drugs are administered by a hypodermic needle to the deep hypodermis

E. “Baby fat” in infants & children: 1. Reduces heat loss2. Energy reserve3. Padding
F. In adults fat is distributed:1. Men: neck, arms, lower back, buttocks,
abdomen2. Women: Breasts, buttocks, hips, thighs,
abdomen

V. ACCESSORY STRUCTURES
A. Hair1. Location: Project into the dermis & usually
into the hypodermis2. Functions:
a) Protect skin from UV raysb) Provide paddingc) Guard entrances to the bodyd) Provide sensitivity to touche) Provide insulation
i. Arrector pili muscles cause goosebumps- hairs stand up
ii. Doesn’t really insulate humans

3. Types of hairs:a) Vellus Hairs: fine “peach fuzz” b) Terminal Hairs: heavy, darker
4. Hair color:a) Melanocytesb) White hair: lack of pigment + air bubbles
5. Growth & Replacement of Hair: * read about this on page 159 (fyi only)

6. Hair Structure:a) Hair Follicles:b) Hair Papilla:c) Hair Bulb:d) Hair Matrix:e) Medulla:f) Cortex:g) Cuticle:h) Root:i) Hair Shaft:j) Root Hair Plexus:

B. NAILS
1. Function: protect the exposed tips of fingers and toes
2. Nail Structure: (know these parts)a) Nail Body:b) Nail Bed:c) Nail Root:d) Cuticle (Eponychium):e) Lunula:f) Nail Grooves & Nail Folds:g) Free Edge:h) Hyponychium:

3. Cells that produce nails can be affected by conditions that alter body metabolism
4. Changes in the nails can help with diagnoses:* Examples on page 162

C. GLANDS
1) Sebaceous Glands (Oil Glands)a) Holocrine glandsb) Sebum- a waxy, oily substance secreted into hair
follicles and onto the skinc) Arrector pilli muscles contract to release secretiond) Sebum lubricates hair and skin and prevents
bacterial growth(Shampoo removes sebum, which can dry the hair)
e) Sebaceous Follicles- large sebaceous glands w/o hairs
Found in skin of the face, back, chest, nipples & male sex organs
f) Glands can become infected with bacteria or blocked with sebum and then infected (ex. acne, folliculitis)

2. SUDERIFEROUS GLANDS (SWEAT GLANDS)
a) Apocrine Sweat Glandsi. Found in armpits, nipples & groinii. Begin secreting a sticky, cloudy secretion at puberty
(yay!)
b) Merocrine Sweat Glands (aka Eccrine Sweat Glands)i. More numerous and widely distributed (2-5 million per
adult)Palms and soles have the most
ii. Secrete sensible perspiration99% water along w/ salt, nutrients & wastes
iii. Functions:Cools the skinExcrete water & other substances (up to 1 gallon/hour!)Discourages growth of microorganisms

3. Other Integumentary Glandsa) Mammary Glands
b) Ceruminous Glands- secrete cerumen (ear wax)

VI. INJURY AND REPAIR
A. The skin can regenerate effectively because stem (germ) cells are found in both epithelial and connective tissues.

B. FOUR STAGES OF REGENERATION
1. Bleeding occurs, mast cells trigger inflammation
2. A blood clot (scab) forms to restore integrity and keep bacteria out.
Cells from the stratum germinativum migrate along the sides of the wound.
Macrophages patrol for pathogens & debris.

3. The clot will begin disintegrating while it is being pushed up by new tissue growth.
Fibroblasts produce large amounts of inflexible collagen fibers to replace lost connective tissue. (Scar tissue)
4. Scab is shed.
Scar tissue gradually evens out with epidermis.

VII. AGING & THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
Check out page 164 for a list of affects aging has on the components of the integumentary system.