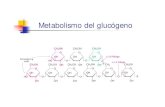
Chapter 36 Anatomy and Role of the Pancreas Alpha - glucogon - glucogen - glucose Beta - insulin...
-
Upload
brittany-rose -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
3
Transcript of Chapter 36 Anatomy and Role of the Pancreas Alpha - glucogon - glucogen - glucose Beta - insulin...

Chapter 36

Alpha - glucogon - glucogen - glucose
Beta - insulin
Delta - stomatostatin, balance

Diabetes MellitusDefinition: Lack of or resistance to Insulin
ClassificationsType 1 DiabetesType 2 DiabetesGestational

Impact of Diabetes6th leading cause of deathleading cause of renal failuremajor cause of blindnessmost frequent cause of non-trauma
amputationsaffects 17 millionincreasing prevalence of type 2


Historical FactsDiabetes is from the Greek word “to siphon” Mellitus is from Latin word “sweet”
Usually died within 2-3 years from starvation
1921 - Insulin discoveryincreased life span experiencing long term effects of diabetes
1979 - self monitoring with glucometers

Diabetes Mellitus - HistoricalChildren died of starvation

Diabetes and your nursing practiceImpact?Opportunity?
TeachingFollow-up
Future?

Diabetes Type 1Beta cells no longer produce insulin
hyperglycemiafats and protein are broken downdevelopment of ketosis
accounts for 10-15% of all casesoccurs in childhood or adolescence
juvenile onset or insulin dependent diabetes


Clinical ManifestationsHyperglycemia leads to
polyuriaglycosuriapolydipsiapolyphagiaweight lossmalaise and fatigueblurred vision

Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKAResults from a breakdown of fatoccurs when undiagnosed or known diabetic
has an increased energy needblood sugar >250mg/dLpH < 7.3ketones and glucose in the blood and urine

DKA - TreatmentRegular insulin - sub q or IV
Restore fluid balance - .9NS IV
Correct electrolyte imbalances - K+

Diabetes Type 2Definition - when fasting hyperglycemia
occurs despite endogenous insulinalso known as adult onset diabetesRisk Factors
family historyobesityrace - African American, Hispanic or Am.
IndianWomen - gestational diabetes, birth wt>9lbs

Cellular Resistance
Not enough insulin


Type 2 Diabetes - Clinical ManifestationsClient - usually unaware, doesn’t experience
wt. losshyperglycemiapolyuria, polydipsia, blurred visionfatigueparesthesiasskin infections

Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemia State - HHSLife threatening complication of type 2Characterized by increase in plasma
osmolarity, blood glucose and ALCPrecipitating factors
infection, therapeutic agent/procedure, acute or chronic illness
slow onset

HHSClinical Manifestations
altered level of consciousnessneurological
hyperthermia, motor/sensory impairment, seizuredehydration
TreatmentICU, correct fluid and electrolyte imbalances,
regular insulin

Complications of DiabetesHyperglycemia
DKA - associated with Diabetes Type 1HHN - associated with Diabetes Type 2Dawn phenomenon - rise in b.s. 4-8amSomogyi effect - hypoglycemia at night with re-
bound morning hypergylcemia

Complications of DiabetesHypoglycemia - b.s. 45-60mg/dLManifestations
early signs - cool clammy skin, rapid heart beat, hunger, nervousness, tremor, faintness, dizziness
late signs - unsteady gait, incoherent, vision changes, seizures, coma

HypoglycemiaTreatment
15gms of rapid acting sugar (1/2 cup of fruit juice, 8oz skim milk, 3 glucose tablets, 3 life savers)
15/15 rule, if still low, repeat 15 grams of sugar
IV - 25-50% of glucose

Why do you need to know about diabetes?
How would you feel if diagnosed with Diabetes today?

Tell us about Diabetes Type 1
pathoincidenceclinical
manifestationsDKA?

Tell us about Type 2 Diabetesrisk factors
clinical manifestations
hyperosmolar hyperglycemia state?

Tell us about complications, signs and symptoms and treatment
hyperglycemia
hypoglycemia


Complications of DiabetesCoronary Artery DiseaseHypertensionStrokePeripheral Vascular DiseaseDiabetic Retinopathy
retinal ischemialeading cause of blindness ages 25-74

Diabetic Retinopathy

Complications of Diabetes
Diabetic nephropathyglomerular changes in kidneys
leading to impaired renal function microalbuminuria
most common cause ESRD in America

Renal Involvement

Complications of DiabetesPeripheral and Autonomic Nervous System
changes in the blood vessels that supply nerves and result in impaired nerve conduction
peripheral neuropathies distal paresthesias - numbness/ tingling in
toes/feet pain, aching, burning feelings of cold impaired sensation
visceral neuropathies sweating G.I.

Other Complications from D.M.Increased susceptibility to infection
inflammatory response is diminishedslower than normal healing
Periodontal diseaseFoot ulcer and infections



Collaborative CareKeeping blood glucose levels close to normal
medicationsdietary managementexercise
Futurepancreatic transplant, beta cell transplant

Diagnostic Tests1. Symptoms of diabetes and random b.s.
>200mg/dL2. fasting glucose >126mg/dL3. Oral glucose tolerance test - OGTT
after 2 hrs glucose is >200mg/dL4. Glycosylated hemoglobin - Hemoglobin A1C
average glucose over 2-3 months
Routine accu checks for managementType 1 3x/day, Type 2 prn to reach glucose
goal

What can you tell us about this?
Type
Action
Administration
Nursing Care

MedicationsInsulin
all type 1, some type 2, gestational diabetics, those on TPN
Terms describing insulinonset, peak, duration
Typesrapid acting, short acting, intermediate, long
and combinations

Types of InsulinShort acting – Regular
onset 30 min to 1 hrpeak 2-3 hrsduration 4-6 hrs
Intermediate acting – NPHonset 1-2 hrspeak 6-14 hrsduration 16-24 hrs
Long acting – Lantusonset 2 hrs, peak not definedDuration 24 hours

Insulin AdministrationEquipment
syringecalibrated for U 100insulin pump
Routeparenterally only nasal spray recently approved for useresearch into oral forms

Insulin AdministrationStorage?Gently rollwithdraw without air bubblesclear to cloudyAdministration
subcutaneous tissue differs in absorption rates90 degree angle, no massage, avoid scars

Insulin Sites
Abdomen – most rapid absorption siteArmsThighsButtocks


Insulin AdministrationBest site for injection

Oral Hypoglycemic AgentsUsed to treat Type 2Combination with prescribed diet and
exerciseMany combinations of insulin and
hypoglycemic agentsglucotrol, glucophage
Aspirin therapy

Diet Management
Goalsnear-normal glucose levelsoptimal lipid levelsadequate calories to maintain reasonable wt.
Meal planningconsistent-carbohydrate planexchange list

Diet ManagementSpecifically for type 1
correlate eating with insulin onsetadjust according to self-monitoring
Specifically for type 2includes weight loss plan3 meals spaced 4-5 hours apart
“Sick Day Management Plan”

DM - Weight LossPlays important role

ExerciseIncrease uptake of glucose by muscle cellsDecrease cholesterol and triglyceride levelsADA Recommendations
proper footwear, inspect feetavoid temperature extremesavoid during times of poor glucose control

Diabetic Surgical ClientsMonitor for increased risk of
postoperative infectionsdelayed wound healingfluid and electrolyte imbalanceshypoglycemiaDKA

Diabetic Surgical ClientsPreop Care
insulin - may receive usual dose or 1/2 of the usual dose
early morning surgeryPost op Care
b.s. fluctuate depending on NPO, gastric suctioning
monitor at set intervals

Nursing DiagnosesRisk for Impaired skin integrity:Proper foot
care1. Daily inspection of the feet2. Checking temperature of any water before
washing feet3. Need for lubricating cream after drying but
not between toes4. Quit smoking

Nursing DiagnosesRisk for Infection
1. Frequent hand washing2. Early recognition of signs of infection and
seeking treatment3. Meticulous skin care4. Regular dental examinations and consistent
oral hygiene care

Nursing DiagnosesRisk for Injury: Prevention of accidents, falls
and burns
Sexual dysfunction1. Effects of high blood sugar on sexual
functioning2. Resources for treatment of impotence,
sexual dysfunction

Nursing DiagnosesIneffective coping
1. Assisting with problem solving strategies2. Providing information about diabetic
resources community education program support groups
3. Use all client contact as an opportunity to reinforce management, help coping and prevent complications