glovereducation.weebly.com · Web viewPancreas secretes insulin and glucagon, hormones that...
Transcript of glovereducation.weebly.com · Web viewPancreas secretes insulin and glucagon, hormones that...

Biology 12
9.2 Accessory Organs of Digestion
The accessory digestive organs are the pancreas, liver, and gall bladder.
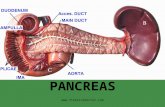
The PancreasThe pancreas is an organ that has both endocrine and exocrine functions.
• Exocrine function of the pancreaso Pancreatic cells produce
pancreatic juice (to neutralize stomach acid) and digestive enzymes
• Endocrine function of the pancreaso Pancreas secretes insulin and
glucagon, hormones that regulate blood glucose (sugar) levels
Structure and Function of the PancreasThe pancreas contains pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans), which are clusters of at least three types of endocrine cells:
• Alpha cells: produce glucagon• Beta cells: produce insulin• Delta cells: produce somatostatin
Insulin• Hormone secreted when blood glucose
level is high• Stimulates the uptake of glucose by cells
(liver, muscle, adipose tissue) to lower blood glucose
Glucagon• Hormone secreted when blood glucose
level is low • Stimulates the liver to break glycogen
down into glucose to increase blood glucose
• Stimulates adipose tissue to break fat down to glycerol and fatty acids (to make glucose)

Biology 12
Somatostatin• A growth-hormone-inhibiting hormone• Also produced by cells in the stomach and small intestine• Inhibits the release of growth hormone• Suppresses the release of insulin and glucagon• Decreases the absorption of nutrients
The LiverThe liver is the largest gland in the body. The liver has many functions, including:
• Detoxifying blood • Making plasma proteins• Maintaining blood glucose levels• Producing bile, which contains bile salts that
emulsify fat in the small intestine• Producing urea, a nitrogenous waste product from the breakdown of amino acids
Structure and Function of the LiverThe liver contains about 100 000 lobules that serve as its structural and functional units.Three structures are located between the lobules:
• Bile duct: takes bile away from the liver• Hepatic artery branch: brings oxygen-rich blood to the liver• Hepatic portal vein: transports nutrients from the intestines• The liver contains about 100 000 lobules that serve as its structural and functional units.• Three structures are located between the lobules:• Bile duct: takes bile away from the liver• Hepatic artery branch: brings oxygen-rich blood to the liver• Hepatic portal vein: transports nutrients from the intestines
Figure 9.8: A hepatic lobule

Biology 12
The Gall BladderThe gall bladder is a muscular sac attached to the surface of the liver.
• Excess bile from the liver is stored in the gall bladder• Bile leaves the gall bladder and proceeds to the duodenum
via the common bile ducto Bile emulsifies fat to prepare it for further
breakdown by digestive enzymes
Figure 9.10 Hepatic portal system. The hepatic portal vein takes the products of digestion from the digestive system to the liver, where they are processed before entering a hepatic vein.