Chapter 15 Central Europe. Section 1 : Germany ● Identify some key events in the history of...
-
Upload
mavis-bruce -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
0
Transcript of Chapter 15 Central Europe. Section 1 : Germany ● Identify some key events in the history of...

Chapter 15 Chapter 15 Central EuropeCentral Europe

Section 1 : Germany ●Identify some key events in the history of
Germany.
●Describe some features of German culture.
●Examine the German economy.
●Evaluate the issues and challenges faced by Germany.

Give a brief explanation of Germany’s early history.
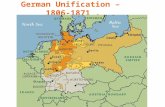
700 AD : many tribes untied by Charlemagne later separated into a loose confederation called “Holy Roman Empire”
1300’s : 100 Northern towns formed trade group called “Hanseatic League” dominated trade
1700’s : states controlled by Prussia, this led to the uniting of North and South in 1871
1890-1914 : Prospered and became industrial. Grew as a military power.

Describe what happened to Germany during the World
Wars. Balance of Power upset in Europe by growth of Germany. This brings tension in Europe and with the assassination of Arch Duke Franz Ferdinand WWI starts. Britain, France, Russia, & USA vs.. Germany, Bulgaria,
Austro-Hungarian & Ottoman Empires.
After WWI German economy collapses amid harsh war sanctions, giving rise to the Nazi party and Adolf Hitler. A push for strong military and an alliance with Italy & Japan forms.
1939 Germany invades Poland and WWII is started. Britain, France, Russia, & USA (Allied) vs. Germany,
Italy, & Japan (Axis)
1945 WWII is ended while Germany and most of Europe lay in ruins.

Briefly explain what happened in Germany after
WWII. Country split into Eastern & Western Germany West controlled by
democracy, East controlled by communism
West become economic power
1990 Fall of communism & the 2 halves are united. Democracy new gov’t

Give information about German Culture.
Capital is Berlin
16 states or Landers, Bavaria is the largest
German is the dominant language
German foods: bratwurst (sausage) various pastries
Strict environmental laws Limit deforestation
Pollution
Oktoberfest: annual celebration of royal wedding, ends in the beginning of Oct.

Give 3 facts about the German economy
4th largest GDP in the world, behind US, Japan, and China
Is prominent member of European Union
Diverse economy Business, Industry, Agriculture (1/2 of land used)

Challenges facing German
Immigration Turks come in and isolate themselves due to culture
Raising standards in the East to those in the West, and stopping the civil unrest between Ossis(E) and Wessis(W)

Section 2 Alpine Countries
●Describe some important features of Austria’s history, culture, and economy.
●Analyze the political, cultural, and economic features of Switzerland.

Who are the Alpine Countries?
Austria Switzerland
Why are they called the Alpine Countries?

What does Austria have in common with Germany?
Culture (language & religion)
Members of the Holy Roman Empire
Ruled by the Habsburgs
At one time were under the control of the Austrian Empire
Austria controlled by Germany prior to WWII

Give info about Austria today?
Vienna Capital Largest City Political &
Cultural center of Central Europe
Currently Members of the European Union
Diverse Economy Industrial, Hydroelectric power, & high quality goods

What 2 composers called Austria home?
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart Ludwig Von Beethoven

What makes Switzerland different from Austria?
Has 4 languages German
French
Italian
Romanish
English is becoming 5th most popular
Most people are multilingual
It is a confederation of 26 Cantons or states
Extremely stable country, tends not to take sides during conflicts

What is important about:
Zurich largest city and world’s leading Banking community
Basel transportation center located on the Rhine River
Bern capital city located between the German and the French speaking populations

Would Switzerland be considered a developed country?
-Yes
A.High Standards of living
B.Banking and insurance are big segments of economy
C.Famous for clocks/watches, Swiss cheese, & chocolate
D.Major tourist attraction

What do Poland and the Baltic Countries have in
common?Both
controlled by the Soviet Union after World War II and during the Cold War.

What are the Baltic What are the Baltic Countries?Countries?
Estonia, Latvia, LithuaniaEstonia, Latvia, Lithuania

What is an exclave?
An area separated from
the rest of a country by the
territory of other countries.

What are the major cities in Poland?Warsaw
Krakow
Gdansk

How has Poland’s economy changed?
Has changed from communist (agriculture centered) to a capitalist or free market (industry centered).
Hurt farmers
Gov’t owned businesses went private
New member to the EU.
Change from Communism has allowed the Roman Catholic religion to become dominant.

Who brought Christianity to
Estonia & Latvia?
The Teutonic Order of Knights
They also were responsible for
bringing a strong element of German
Culture to this region.
Hermann von Salza served as the fourth Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights (1209 to 1239).

Why are the cultures in the Baltic countries
related to so many other countries?
Due to the Baltic Sea being a major trade route for goods and information, many
cultures were present and blended together
over time to form what we now see in this
region.

What is a complementary region?
The combining of 2 areas with different activities or strengths, each of which benefit the other. Farming community(Slovakia) joining together
with an industrial community(Czech Republic).

How was Czechoslovakia a complementary region?
Czech Republic controlled land with mineral resources for raw materials, as well as had industrial factories.
Slovakia had an economy based from agriculture
The 2 regions joined together to meet the needs of each that were not being met. Slovakia gave food to the Czech Republic, and in turn received goods needed that they could not produce themselves.

Since the fall of the Soviet Union, how have things changed for these
countries?Czech Republic
Life here has become more Americanized due to a stable economy of industry and the selling of raw materials. Especially in its capital of Prague.
Slovakia
The move away from communism has been tough due to high unemployment and a lack of industry. The economy is unstable due to being based on agricultural production. Its capital of Bratislava is the only major city.

What makes Budapest different from other cities?
Reason
It is actually 2 cities separated by the Danube River. The cities of Buda and Pest joined together in 1873, and still function as one city today.
Picture

Briefly explain Hungary’s economy.
Strong Agricultural production
Industry has bounced back from the Communist era and has changed to a market economy
Businesses are now privately owned, increasing competition
Have attracted new industries, foreign investments, & tourism
Have joined NATO and are a new member to the EU

The main ethnic The main ethnic background for Czech background for Czech
Republic, Slovakia, and Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary is?Hungary is?
MagyarMagyar

Define Exclave
Confederation
Alliances
Cantons
Multilingual
an area separated from the rest of a country by the territory of other countries.
a group of states joined together
an agreement between two countries to support one another against enemies
states in Switzerland
speaking several languages