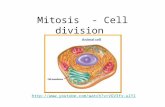
Chapter 10: Cell Division & Mitosis. Mitosis Division of cell nucleus Common to ALL living things--...
-
Upload
buddy-mitchell -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
2
Transcript of Chapter 10: Cell Division & Mitosis. Mitosis Division of cell nucleus Common to ALL living things--...

Chapter 10: Cell Division & Mitosis

Mitosis
• Division of cell nucleus• Common to ALL living things-- but details
of mitosis vary from organism to organism• The sequence of phases is fixed in all
organisms, but time spent in each phase varies

Biologists Compare Cell Division
1) In different organisms by comparing their cell cycles
2) Between different kinds of tissues within the animal/plant
3) Between normal tissue and tissue repair after injury
4) Between the young child and elderly person

Biologists Compare Cell Division cont.
5) Between embryological (unspecialized cells) and in fetal cells that develop into tissues (specialized cells)
6) Between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
- Prokaryotic & some protists binary fission
7) Between cancer and normal cells

Cell Division in Eukaryotes
1) Unicellular organisms– cell division new individuals (reproduction)
2) Multicellular organisms-- cell growth/ repair/ maintenance/ reproduction
a. Plants- formation of roots, stems, leaves
b. Animals- formation of specialized cells (nerve, bone, muscle)– blood and skin cells are replaced as needed throughout life (106 mitotic cell division/sec)

Cell Division in Eukaryotes cont.
3) In all cell divisions there is chromosome replication/ duplication
- Body/ somatic cells= 46
chromosomes (23 pairs/
1 set from each parent)
- Gametes/ sex cells= 23
chromosomes (1 set from
parent)

Controls of Cell Division ( Cell Cycle)
1) Rate varies between species and between tissues within same organism-anywhere from min/hr/day/never
a. Go Phase
• Cells never leave G1 phase
• In this way, specialized cells remain very active-- never having to stop working to divide; all energy is used to carry out important specialized functions
Ex: Nerve and muscle cells (can enlarge through use of anabolic steroids), Heart cells (can enlarge in athletes), Leaf cells (palisade, xylem, phloem), Red blood cells (in circulation) complete cycle only in growth tissues

Controls of Cell Division ( Cell Cycle) cont.
b. Some cells divide very rapidly
Ex: Bacteria E. coli (prokaryote- every 30 min)
Skin and blood (106 div/sec)
Digestive tract (6 hrs)
Respiratory tract (8 hrs)

Controls of Cell Division ( Cell Cycle) cont.
2) Could be caused by some “trigger protein”-- some molecular on/off switch like a hormone of an enzyme
- Turned on rapidly in times of cell stress or gradually increases during G1 phase to a level when S phase can begin

Controls of Cell Division ( Cell Cycle) cont.
3) Or by special regions called TELOMERES-- found at the ends of chromosomes
- These telomeres shorten with every subsequent division until division stops
a. Changes seen in normal/ cancer cells
b. Changes seen in early aging (Progeria)/ normal

Overview of Cell Cycle

Phases of Cell Cycle
• Sequence is fixed from start to finish (for entire life cycle)a. Interphase (non-dividing cells) has 3 distinct
phases: G1, S, G2
b. Mitosis (dividing cells) has 4 phases in nucleus: P, M, A, T
c. Cytokinesis: C

Phases of Cell Cycle cont.

INTERPHASE (3 phases)
1. G1 phase (Growth 1- just after cell is formed)
• Very active metabolically-- biochemical pathways: photosynthesis, cell respiration, biosynthesis
• ↑ in molecules-- enzymes, hormones, proteins, mRNA
• ↑ in number of cellular organelles• ↑ in size-- usually doubles in size• Length varies from hours to several days

INTERPHASE (3 phases)
2) S phase (Synthesis- must occur prior to mitosis)
• DNA double exactly (replication) all genes copies
• DNA polymerase (enzyme) is very active-- nucleotide assembly
• Histone proteins (for DNA support) increase
• Nucleosomes formed (DNA packing occurs)
• Usually 3-6 hours• 2 chromatids attached at
centromere-- end result


INTERPHASE (3 phases)
3) G2 phase (Growth 2- getting ready for division)• Twice as much DNA as G1
• Protein synthesis (microtubules/ microfilaments) form spindles
• Centrioles replicate (in animal cells only)• 2-5 hours, relatively constant among cells

MITOSIS (P, M, A, T)
• Phases covered later

CYTOKINESIS
• Division of the cytoplasm• Occurs during telophase of mitosis

2 Major Phases of Mitotic Cell Division
1) MITOSIS• Process of cell division in eukaryotic cells in
which the nucleus is divided into 2 nuclei, each with the same number and kinds of chromosomes
• This phase is divided into the:a. Growth period-- Interphase
b. And 4 stages-- Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase (P,M,A,T)
• The stages conserve chromosome number by equally distributing replicated chromosomes to each of the daughter cells

2 Major Phases of Mitotic Cell Division cont.
2) CYTOKINESIS• The division of the cytoplasm to form 2
separate daughter cells immediately after mitosis

MITOSIS (replication and division of the nucleus)
1) INTERPHASEa. G1 phase
o Growth phase of a cello Cell grows rapidly and carries out its routine
functionso For most organisms, this phase occupies the major
portion of the cell’s life between cell divisions
b. S phaseo Time during which DNA is being replicatedo At the end of this phase, an individual chromosome
consists of 2 chromatids attached by a centromere

MITOSIS – INTERPHASE cont.
c. G2 phase o Time during which preparations are made for
nuclear divisiono Mitochondria and other organelles replicateo Microtubules reassembled-- will be used to form
the spindle apparatus that moves the chromosomes
d. M phaseo Phase where mitosis occurso Mitosis is the replication and division of the
nucleus to form 2 identical nuclei, each with the same number and kinds of chromosomes

Cell Cycle

Interphase

MITOSIS
2) PROPHASE: 2 Major Phasesa. Early Prophase
o Replicated chromatids are present
o Replicated centrioles (only in animal cells) migrate to opposite poles of the cell
o Spindle fibers become visible
b. Late Prophaseo Nucleolus and nuclear
envelope disintegrate o Chromatids condense to
form dense coils

Prophase

MITOSIS cont.
3) METAPHASEoChromatids are at the
same midline (called the equatorial plate in plants)
o Spindle fibers are very dense
o In animal cells, the aster is visible around the centrioles

Metaphase

MITOSIS cont.
4) ANAPHASEoCentromeres separate and the chromatids
now become individual chromosomesoChromosomes migrate to opposite poles of
the cell

Anaphase

MITOSIS cont.
5) TELOPHASEo Phase of mitotic cell division in which the
cytoplasm divides and 2 identical cells formoCytokinesis occurs during this phase

2 Major Differences Between Animal and Plant Cell Division

Animal vs Plant


MITOTIC CELL DIVISION IN PLANT CELLS

MITOTIC CELL DIVISION IN PLANT CELLS cont.

MITOSIS

PRACTICE! Name that Stage!

PRACTICE! Name that Stage!

PRACTICE! Name that Stage!

PRACTICE! Name that Stage!