Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
-
Upload
faith-vaughn -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
0
Transcript of Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 1/30
INFECTION CONTROL/PREVENTION IMMUNITY & DISEASES
FAITH VAUGHN RN, BSN, MSN

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 2/30

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 3/30
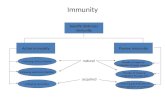
IMMUNITY (CONT’D) Active immunity:
• exposure to a disease organism triggers theimmune system to produce antibodies to thatdisease. There are 2 types:
• Natural active: antibodies develop duringinfection with the actual disease. (measles,chickenpox)
• Artificial active: introduction of a killed orweakened form of disease organism thru vaccines(MMR, Hep B, polio)

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 4/30
IMMUNITY (CONT’D) Passive immunity:person is given antibodies to a disease. There are 2
types:• Natural passive: mother to child thru placenta or
milk• Artificial passive: used during potentially fataldiseases. Provides an instant response of temporary antibodies (tetanus, gamma globulin)
Protection for active immunity is permanent andtakes several weeks to become active
Passive immunity is temporary and actsimmediately

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 5/30
BACTERIAL/VIRAL INFECTIONS
Immunosuppression:Occurs when the body’s immune system is
inadequate. A number of factors can lead to thiscondition, including:
• Advanced age and Frailty
• Chemotherapy
• Infection with Human immunodeficiency virus(HIV)
• Radiation therapy

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 6/30
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS (CONT’D)
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA):Is a virulent staph infection, normally found onskin and mucous membranes.
Resistant to antibiotic treatment, and can prove
fatal very quicklyVancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE):
Entero-cocci are found in the gastrointestinal tract.
Major cause of infections acquired in health care
facilities. Most strains are highly resistant tomany antibiotics.
Newer strains are resistant to vancomycin

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 7/30
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS CONT’D
Streptococcus A:
• Is a bacterium that produces very powerfulenzymes that destroy tissue and blood cells.
• Infection is pass on to others by coughing or
sneezing, touching environmental surfaceswithout washing your hands.
• Strep A infection occurs when bacteria enters thebody through minor trauma or a break in the skin
• Good hand washing helps reduce the risk of infection.
• Treatment with antibiotics and surgery, theresults are not always good

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 8/30
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS (CONT’D)
• Clostridium difficile (C.diff) is a bacterium whichcauses diarrhea> develops after a series of antibiotic therapy.> affects the lining of the intestine, causing
inflammation.> results in sudden, severe, foul-smelling, waterydiarrhea. More commonly acquired in hospitals
• Escherichia coli: commonly found in the intestinal
tract (feces). A small amt of this bacteria cancontaminate meat, especially ground beef
• Salmonella: a group of bacteria that cause mildto life threatening intestinal infection (food
poisoning)

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 9/30
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS (CONT’D)
Precautions:• Wash your hands regularly with soap and water
before and after patients care, and removal of gloves
• Wear gloves and gown when coming in contactwith infectious material• Encourage visitors to wash their hands before
and after patients visit to ensure that they don’tcarry germs
• Carry alcohol wipes and extra gloves to usebetween patients• Remove gown and gloves and dispose of them
appropriately as per policy, outside of patientsroom
• Have visitors report to the nurses’ station beforeentering room

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 10/30
TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION
Tuberculosis (TB): is an infectious disease causedby the organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis(tubercle bacilli)
• Tubercle bacilli: are spread by airborne dropletsexpelled when a person with active TB coughs,sneezes, or talks
• Individuals exposed to contaminated air may
breathe in the organism. This is more likely tooccur in poorly ventilated or closely confinedspaces (vehicles, trains, crowded areas)

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 11/30
TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION (CONT’D)
TB: an increase in the number of peoplewho are at risk, including those who are:
• HIV positive
• Infected but fail to take their meds
• Live in poverty and are malnourished
• Immigrants to the United States from
countries where TB is still common• Have had inactive TB but have grown
older and experience increased disability

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 12/30
TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION (CONT’D)
Latent TB:
• An estimate of 10 to 15 million people in the U.S.have latent TB infection
• A person infected and has a strong immune
system, is able to contain the infection and willnot become ill with the disease.
• Persons are not contagious (cannot transmit TBinfection to others
• Only 1 in 10 persons with latent TB infection willever develop active TB, as long as they are HIVnegative

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 13/30
TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION (CONT’D)
Active TB: occurs when an individual’s immunesystem fails to keep the TB organism contained
• Can involve almost any organ in the body, but is
most commonly spread from person to personwhen lungs or airways are involved
• Airborne precautions are required (mask,
negative pressure room) until three consecutiveAcid Fast Bacilus (AFB) sputum smears arenegative

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 14/30
TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION (CONT’D)
• Signs/symptoms of TB: as diseaseprogresses, the person will show one ormore symptoms:
• Fatigue
• Loss of appetite and weight• Weakness• Elevated temp in the afternoon and
evening
• Night sweats• Spitting up blood (hemoptysis)• Coughing

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 15/30
TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION (CONT’D)
TB diagnosis: the presence of TB bacterium in thebody can be shown by:
• A sputum culture: grows the organisms from aspecimen of secretions from the person’s lungs
• Chest X-rays: show the extent of the diseaseprocess in the lungs
• A positive skin test (Mantoux test) shows thepresence of antibodies to the TB organisms in thebody, and is not an indication of the activedisease
• Most health care workers must undergo a skintest for TB before employment

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 16/30
TUBERCULOSIS INFECTION (CONT’D)
TB treatment/prevention• A person with TB is treated with a selected
antibiotic or combination of antibiotics• Once drug therapy starts, the patient usually
becomes noncontagious (cannot spread thedisease organism) within two to three weeks• Cure for TB requires 6-12 months, or longer, of
continuous treatment• The course of treatment must be completed to
avoid recurrence• All new TB and suspected cases should bereported promptly to the Health Department bythe health care provider, as required by the state

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 17/30
AIDS AND HIV
• Acquired Immune Deficiency syndrome (AIDS),which is a serious condition that affects thebody’s ability to fight infections
• AIDS is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency
Virus (HIV)• HIV in the body, can destroy the immune cells
(T-cells and white blood cells) that defend thebody against infections
• Without these cells, the body cannot defend itself from illness
• Disease and infections can now move into thebody without a fight

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 18/30
AIDS AND HIV (CONT’D)
HIV can be transmitted by:
• Blood and plasma
• Semen
• Vaginal secretions
• Cerebrospinal fluid
• Bone marrow
• Sharing injection needles or syringes
• Placenta
• Breast milk
• Body fluids containing blood
• Body tattooing/piercing

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 19/30
AIDS AND HIV (CONT’D) HIV cannot be transmitted by:• Shaking hands• Coughing• A dry kiss
• Swimming pools• Sharing food• Donating blood• Hugging
• Sneezing• Toilet seats or rest rooms• Sharing eating or drinking utensils• Insects, including mosquitos• Door knobs
• Sweat, saliva, or tears

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 20/30
AIDS AND HIV (CONT’D) HIV tests and treatment:• Most widely used test is the enzyme-linked
immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test
• Positive results, the test is repeated. After twopositives, a Western Blot Test is done to confirmthe results
• No cure for AIDS and no vaccine available for
HIV.
• Antiretroviral therapy, which is known as cocktaildrugs, combination therapy, or highly activeantiretroviral therapy (HAART). Each type of drug
fights HIV differently to slow down the spread of the HIV virus (combivir, invirase, atripla, norvir)

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 21/30
AIDS AND HIV (CONT’D)
Stages of the Disease: Person who is exposed toHIV develops antibodies to the virus within 2 – 24 weeks (window period)
• Stage 1: Newly exposed persons may exhibit flu
like symptoms that may last one to two weeks• Stage 11: symptoms such as weight loss, night
sweats, fevers, swollen lymph nodes, drypersistent cough, oral candidasis (thrush), andfatigue
• Stage 111: T cell count is below 200/m3(normal T Cell count in a healthy adult is 800-1000)Stage 11 symptoms with one or more opportunistic
infections are present(Kaposi’s Sarcoma, pneumocystis carinni) develops

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 22/30
AIDS AND HIV (CONT’D) Standard precautions:• Assume that all blood and bodily fluids are
contagious
• Use appropriate Personal protective Equipment(PPE) (mask, gown, gloves, or goggles) whenappropriate
• Dispose of blood, body fluids, and contaminated
materials in the appropriate containers such as(red bags, needle/sharps boxes)
• Do not touch broken glass with your hand. Useforceps or tongs to dispose of glass

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 23/30
AIDS AND HIV (CONT’D)
Standard precautions:
• Keep all cuts and breaks on skin covered with aband-aid, and wear disposable gloves
• Disinfect surfaces contaminated with blood orbody fluids using 1:10 bleach solution
• Do not eat, drink, smoke, or apply cosmetics orlip balms in areas where there may be blood orbody fluids
• Do not store food or drink in refrigerators whereblood or body fluids may be present
• Practice hand hygiene frequently and thoroughly,even after using gloves

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 24/30
HEPATITIS AHepatitis A virus (HAV) is most common and
transmitted by:• Feces, saliva, and contaminated foodSymptoms: Yellowish color of skin (jaundice) and
sclera, fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue,abdominal pain, dark urine, and appetite loss.respiratory symptoms, rashes, and joint pain
Treatment:• Vaccine available
• Rarely fatal• Bedrest and avoidance of alcoholic beverages
Precautions: wash hands before and after handlingfood, wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 25/30
HEPATITIS B (CONT’D) • Hepatitis B virus (HBV)• Causes inflammation of the liver• Tissue response to virus may be mild, flu-like, or
so severe as to cause hospitalization
HBV may be present in blood and body fluids suchas:• Bloody saliva contacted during dental procedures• Blood• Semen
• Vaginal secretions• Cerebrospinal fluid• Synovial fluid (fluid lubricating the joints)

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 26/30
HEPATITIS B (CONT’D)
Full immunizations:
• Requires three doses of vaccines over a 4–6month period
• Personnel screened for the hepatitis B surface
antibody, after the immunization is completed(blood test to determine titer levels)
• Incidence of side effects to the vaccine is verylow
• Effective at providing protection against the HepB virus
• Vaccine is available at no cost through theEmployee Health Department

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 27/30
HEPATITIS B (CONT’D) Accident exposure to blood and body fluids:• You must be evaluated and treated by the
employee health department within four hours of exposure
• If the employee health department is closed, youshould go to the emergency room within thesame time frame of less than four hours of exposure
• Facility will provide upon consent, a confidentialmedical evaluation including blood tests, post-exposure prevention treatment and follow-upcounseling

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 28/30
HEPATITIS C (CONT’D) Hep C virus (HCV• Transmitted through blood and blood products• May be mistaken for the flu
Common signs and symptoms include:• Fatigue• Depression• Fever• Mood changes• Weakness• Pain and Loss of appetite• May cause liver cancer and liver failure

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 29/30
HEPATITIS C (CONT’D)
Protect yourself by:
• Using standard precautions
• Taking the vaccine, if available
• Practicing safe sex (using condoms)
• Not using illegal drugs
• Giving your full attention to the handling of sharps such as needles or razors

8/3/2019 Ceu-Infection Control 2 Immunity and Diseases
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/ceu-infection-control-2-immunity-and-diseases 30/30
PREVENTING INFECTION • Assist patients to maintain adequate fluid intake• Wipe from front to back when cleaning perineal
area
• Observe patient carefully and report to the nurse:> changes in frequency of urination> complaints of pain/burning on urination> coughing or respiratory problems> confusion or disorientation that is unusual
> drainage or discharge from any body openingor wound> changes in skin color> complaints of pain, discomfort or nausea
> elevated temp red swollen areas on body