Central dogma of molecular biology with video slide.
-
Upload
asheesh-pandey -
Category
Science
-
view
198 -
download
2
Transcript of Central dogma of molecular biology with video slide.
PowerPoint Presentation
Molecular Biology: Central Dogma, DNA Replication, Transcription, Translation, mRNA processing Dogma: (Greek word): A principle or set of principles laid down by an authority as incontrovertibly true.
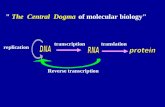
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
Thecentral dogma of molecular biologyis an explanation of the flow of genetic information within a biological system. It was first stated byFrancis Crickin 1956and re-stated in aNaturepaper published in 1970.
The central dogma ofmolecular biologydeals with the detailed residue-by-residue transfer ofsequential information. It states that such information cannot be transferred back from protein to either protein or nucleic acid. Francis Crick
DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid
DNA strands are termedpolynucleotidessince they are composed of simplermonomerunits called nucleotides
Each nucleotide is composed of one of fournitrogen-containingnucleobaseseithercytosine(C),guanine(G),adenine(A), orthymine(T)AsugarcalleddeoxyriboseAphosphate group.
Nitrogenous baseSugar molecule
E. coliIIIIIIPolymerization: 53+++Exonuclease activity:35+++53+Synthesis from:IntactDNAPrimed single strands+Primed single strands plus single-strand indingprotein++In vitro chain elongation rate (nucleotides per minute)600?30,000Molecules present per cell400?1020Mutation lethal?++Mammalian Cells*Polymerization: 53+++++Exonuclease proofreading activity:3 5+++Synthesis from:RNAprimer++?DNAprimer+++++AssociatedDNAprimase+Sensitive to aphidicolin (inhibitor of ellDNAsynthesis)+++Cell location:Nuclei++++Mitochondria+