Cellular organization and cell reproduction
-
Upload
maryjane0116 -
Category
Education
-
view
114 -
download
0
Transcript of Cellular organization and cell reproduction

Cellular Organization and Cell Reproduction
4th Quarter

Background Information Living things are made up of
cells. (Cell Theory) Cells vary in structure in
relation to the function they perform.

Background Information Cells differ greatly in shape and
size. However they have the same main parts:
- cytoplasm, the part of the cell where most life activities take place;
- cell membrane, which envelopes the cytoplasm; and
- nucleus, the part of the cell where the genetic material is formed.

Background Information

Background Information The cell membrane, a living
double layer of fats and proteins, regulates the entry and exit of materials in the cell.

Background Information Found in the cytoplasm
are the following: mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and vacuoles.

Background Information

Background Information The nuclear membrane, a
double layer of fats and proteins, covers the nucleus. Inside it are the nuclear sap (nucleoplasm), nucleolus and chromosomes.

Background Information

Importance of Cell Division to Living Things
Growth Development Repair of damaged body
parts and tissues (gametes).
Reproduction


At Interphase cell grows, accumulates
nutrients and replicates its genetic material – all important events that prepare the cell division.
three stages: G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase
90% of the entire cycle is devoted to the interphase.


Stage 1 – G1 (Growth or Gap 1) Phase
cell is still young and undergoes rapid growth, cell attains its normal size
organelles are formed DNA and proteins the longest phase in most
cells

Stage 2 – S (Synthesis) Phase
DNA inside the chromosome doubles by a process called replication
sister chromatid – strand of the double-stranded chromosome produced joined by the centromere


Stage 3 – G2 (Growth) Phase
preparations for cell division cell synthesizes proteins and
continues to increase in size assembly of proteins RNA and proteins are made

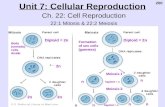
Stage 4 – M (Mitosis/Meiosis) Phase
cell undergoes division division of nucleus –
karyokinesis (nuclear division)
2 types of karyokinesis: mitosis and meiosis
division of cytoplasm – cytokinesis