CELLS!
description
Transcript of CELLS!

CELLS!Unit 3 – Lesson 2

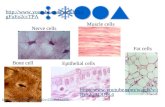
Cells• There are many different kinds of
cells, and they do many different things.
• Many organisms live life as a single cell! We say they are unicellular!
• Other organisms are clusters of cells. We say they are multicellular!

ATOMS COMBINE TO MAKE SMALL BASIC UNTIS OF
LIFE!We call these CELLS

Multicellular or Unicellular?

Multicellular Organisms• Multicellular organiams are
ORGANIZED. The cells don’t just float around at random, They work together to make different structures.

CELL TISSUE
ORGAN
ORGAN SYSTEMORGANISM

So, since we are talking about cells…what does the INSIDE of a cell look like? Is it organized
too?


Comparing Cells• Since there are so many
different cells, we categorize them into two types.
• Prokaryotes• Eukaryotes

Prokaryotes• Prokaryotes – lack membrane bound
organelles.
• Examples:– Single-cell organisms– Bacteria
Uhh, what’s a
membrane?

BACTERIA

Eukaryotes• Eukaryotes – cells that contain
membrane bound organelles.
• Examples: • Protists• Fungi• Plants• Animals

Eukaryotes• There are two main types of
eukaryotic cells. – Plant cells– Animal cells
Animal Cell
Plant Cell

ANIMAL CELL

PLANT CELL

Cell Organization

Cell Organization• All life is organized, remember? So cells have tiny
structures that help with their function.
• We call these ORGANELLES!
Looks like
mini-organs!

Cell Wall
• Tough rigid outer coverings that protects the cell and give it shape.
• Found in plants, algae, fungi, and some bacteria.
Animal Cell
Plant Cell

Cell Membrane• Protective layer
around all cells.
• For cells with a cell wall, the cell membrane is inside the cell wall.
• It allows food and oxygen into the cell and waste products out of the cell.
Animal Cell
Plant Cell

Cell (Plasma) MEMBRANE
The pink structure indicates a protein in the cell membrane


Cytoplasm• The “soup” in which
all other organelles reside. A gelatin like mixture.
• Chemical reactions occur within the cytoplasm.
• Holds organelles in place.
Animal Cell
Plant Cell

Nucleus
• Contains the DNA responsible for providing the cell with its unique characteristics.
• Acts as the control center.
• Contains a nucleolus.
Animal Cell
Plant Cell

Chloroplasts• Green organelle that
makes food for a plant.
• Contains chlorophyll.
• Where photosynthesis occurs (photosynthesis allows the plant to make food).
Animal Cell
Plant Cell
CO2H2O
Sugar

Mitochondria
• Provides the energy a cell needs to move, divide, produce secretory products, and contract.
• Where cellular respiration occurs.
Animal Cell
Plant Cell
ENERGY
Sugar O2

Ribosomes
• The site of protein synthesis.– making proteins
for the cell
• Can be found on Rough ER.
Animal Cell
Plant Cell

Endoplasmic Reticulum
• Where cellular materials are processed.
• Smooth ER – when no ribosomes are present.
• Rough ER – when ribosomes are attached.
Animal Cell
Plant Cell

Golgi Bodies• Sort proteins and
other cellular substances and package them into vesicles.
• Vesicles deliver substances to other areas of the cell.
Animal Cell
Plant Cell

Vacuole• Stores water, waste
products, food, and other cellular material.
• In a plant cell, vacuoles are very large! This is because plants need to store more materials.
Animal Cell
Plant Cell

Lysosome• Breaks down food molecules, cell
wastes, and worn out organelles.
Lyse = CutSome = Body
Animal Cell
Plant Cell

LYSOSOME
BACTERIA

BACTERIA

BACTERIA

BACTERIA

BACTERIA





RECYCLED PARTS
RECYCLED PARTS
RECYCLED PARTS
LYSOSOME

Other Organelles• Cells can move using a flagella or cilia.
Animal Cell
Plant Cell