Cell Structure Notes & Study Guide Plant & Animal Cells.
-
Upload
donald-dorsey -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Structure Notes & Study Guide Plant & Animal Cells.
Cell Theory
I. Cells are the building blocks of all living things• can be single-celled (called protozoa)• can be multi-celled, where they have a specific function
II. All life processes take place in cells• Energy production• Growth & reproduction
III. New cells are produced from existing ones• Cells divide into 2, then into 2 more… =exponential growth
Parts of a Cell
• Organelles = structures that perform specific functions in cells• Cytoplasm = clear fluid surrounding organelles
• Differences between Plant & Animal Cells:• Cell wall (plants)• Large single vacuole (plants)• Chloroplasts (plants)
Functions of the Organelles
• Cell Wall- The cell wall is an outer layer that surrounds and protects the cell and it also gives the cell its shape
• Cell Membrane- material that holds the contents of the cell inside• Vacuole - organelle that stores nutrients and waste• Chloraplast- organelles found only in plant cells that produce plant’s food (sugar)• Cytoplasm - clear, jelly-like substance that holds organelles in place• Nucleus- cell’s control center Contains chromosomes with DNA which contain the chemical instructions of life• Mitochondria - organelles that release energy (H2O, CO2) from combo of food and oxygen• DNA: - chemical that tells functions of life to cell
Others Not Included in Science Book
• Ribosome - make protein for cell• Golgi Apparatus - pack and carry proteins for cell• Endoplasmic Reticulum - an organelle for cell reactions
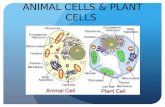
The Cells We’re Studying:Animal Cell Plant Cell
Cell Membrane
Nucleus
Ribosome
E.R.
Golgi Vacuole
Mitochondria
CytoplasmCell Wall
Cell Membrane
Golgi
Ribosome
Chloroplast
MitochondriaE.R.
Vacuole
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Animal Cell
ChromosomesContain DNA
CytoplasmClear fluid
MicrotubulesStructural basis of the cells, used in mitosis
Nucleus Pore
VacuolesStores nutrients and waste
Cell MembraneControls what substances
enter & leave cell
MitochondriaCreates energy
Smooth ER*RibosomesMake Proteins
Rough ER*
Golgi apparatusFedEx: Transport System
Nucleolusregulates all cell activity by controlling the enzymes present.
NucleusControl Center
Nuclear membranecontrols what enters and leaves the nucleus
CentriolePull apart chromosoes during mitosis
*ER : produces proteins and lipids for the cell's organellesRough contains Ribosomes
VacuoleStores nutrients and waste
MitochondriaCreates energy
Golgi apparatusFedEx: Transport System
Smooth ER*
Rough ER*ChloroplastMake sugars for food
Cell wallNucleus
Control Center
Cell MembraneControls what substances enter & leave cell
Nuclear membranecontrols what enters and leaves the nucleus
RibosomesMake Proteins
Nucleolusregulates all cell activity by controlling the
enzymes present.
DNAProvides cell instructions for
reproduction
CytoplasmClear fluid
MicrotubulesStructural basis of the cells, used in mitosis
*ER : produces proteins and lipids for the cell's organelles
Rough contains Ribosomes
Nuclear pore
Plant Cell
Some Plant Cells have a centriole
Animal vs. Plant: What’s the Difference?
Animal Cell Characteristics• SMALL VACUOLE• NO CELL WALL• Nucleus• Mitochondria• Cytoplasm• Cell membrane• DNA• Chromosomes• Golgi Bodies• Ribosome• E.R.• DNA
Plant Cell Characteristics• CHLOROPLASTS• CELL WALL• BIG VACUOLE • Nucleus• Mitochondria• Cytoplasm• Cell membrane• DNA• Chromosomes• Golgi Bodies• Ribosome• E.R• DNA
Name all of the organelles in the
plant cell with BLUE shape by
their label.
WORD BOX
1. Cell Wall 4. Nucleus
2. Cytoplasm 5. Chloroplast
3. Mitochondria 6. Vacuole
7. Cell Membrane
ORGANELLES OF THE CELL
• NucleusThe main control center of the cell
• CytoplasmThe jelly-like substance inside of the cell keeping the cell inflated, and allows
flow of nutrients
• NucleolusA small circular structure within the Nucleus which produces Ribosomes and
proteins
• Cell Membrane Allows transfer of nutrients and oxygen, and acts as a filter
ORGANELLES OF THE CELL
• Cell Wall (plant cell only)Provides structural supportand protects the cell
• RibosomesThe small particles containing RNA and other proteins, these are found
in the cytoplasm of the cell
• MitochondriaThe part of the cell that makes food into energy
ORGANELLES OF THE CELL
• LysosomeThe part of the cell that contains digestive enzymes
• Chloroplast (plant cell only)The part of the cell that produces thegreen coloring and performs photosynthesis
• GolgiThe part of the cell that modifies proteins for specific functions and
prepares them for transport to other parts of the cell
Cell Family Tree
Cells
Prokaryote (no Nucleus)
Bacteria
Eukaryote(have a Nucleus)
Protozoa
Plant
Animal
Multicellular Organisms:5 Structural Levels of Organization
Cell
building block of life
Perform a specific function
Tissue
Organ SystemOrgan
Perform a specific job – made of at least 2 types of tissue
Organism
Complete living thing that relies on cells for life functions
Cell Reproduction
• Cells Reproduce Through Two Processes:
1. Mitosis= asexual reproduction• A 6 step process where body cells reproduce by cell division.• Create exact replicas of themselves for building tissues• Examples: muscle cells, skin cells, nerve cells, blood cells• Also Protozoa create exact replicas of themselves by cell division
Cell Reproduction
2. Meiosis = Sexual Reproduction• A 9 step process involving multiplication then division of cells. • The reproductive process where new cells and organisms are formed
• Chromosomes from both parents are mixed when the sperm and egg cells combine to produce a fertilized egg