Cell Organelles. Cell Membrane Controls chemical traffic in and out of the cell Selectively...
-
Upload
abner-fitzgerald -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
1
Transcript of Cell Organelles. Cell Membrane Controls chemical traffic in and out of the cell Selectively...

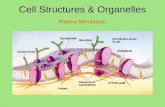
Cell Organelles

Cell Membrane
• Controls chemical traffic in and out of the cell
• Selectively Permeable
• 8 nm thick

What is Selective Permeability?
• Allows some substances to cross more easily than others
• Why must it be selective?

Why Must Cells Allow Some Substances to Pass Across the
Membrane?• To maintain HOMEOSTASIS =
– the tendency to maintain stability in an organism amid environmental change
– (ability to adjust to changes)– ---------------------------------------------------------– *cells must be able to receive info, move water
molecules, food particles, & ions across the membrane

Membrane Structure• Synthesized in ER
• sugars added in ER & Golgi

Cell Membrane Synthesis
• AP Bio Book Reference

Membrane Structure (Con’d)
• Lipid Bilayer (2 layers of phospholipids)
layer #1
layer #2

The Phospholipid• hydrophilic (water loving) polar heads
•hydrophobic (water fearing) nonpolar tail

Phospholipid Bilayer
• Polar head - attracted to H2O (hydrophilic)
• Nonpolar tails - push away or repel H2O (hydrophobic)
• -----------------------------------------------------
• In order to best interact w/ H2O inside & outside of cell, membrane forms 2 layers of phospholipids
• hydrophobic interactions hold membrane together


What is allowed to easily pass through?
• 1) Nonpolar (hydrophobic) molecules dissolve easily in membrane
-hydrocarbons (molecules with C & H)
-oxygen
-(smaller molecules move faster)

What can easily pass through?
• 2) Polar (hydrophilic) uncharged molecules
- water, carbon dioxide

What can easily pass through?
• 3) Small, polar molecules- pass easilly between membrane lipids

What cannot pass through easily?
• Ions & large polar molecules
-do not easily pass thru membrane hydrophobic area

Fluid Mosaic Model
• 1) Lipid Bilayer -tough but flexible• 2) Transport (channel or carrier) Proteins• 3) Receptor Proteins• 4) Marker Proteins• http://www.virtualcell.com/

Lipid Bilayer (con’d)
• 1) Stops large polar molecules
-cannot pass thru NONPOLAR tails
-thus, membrane serves as protective BARRIER

Lipid Bilayer (con’d)
• 2) is FLUID-not rigid
-phospholipid & proteins
can move laterally
(rarely flip)

Membrane Fluidity
• Dependent on composition
-unsaturated vs. saturated fatty acid tails
-cholesterol


Transport Proteins
• Look like doughnuts in membrane surface
• allow many impt. molecules & ions to cross
• specific for substances they transport or translocate
• like locked doors - will only let some thru

Transport (Carrier) Proteins
Can be carrier proteins which do not extend all the way thru the membrane

How Carrier Proteins Work
Carrier Proteins bond and drag molecule thru bilayer and release on other side

Transport (Channel) Proteins
Can be channel proteins that span the length of the membrane

How Channel Proteins Work
Molecules randomly move through by a process called diffusion

Physical Structure of Transport Proteins
-unilateral: embedded partway thru membrane
-transmembrane: completely span membrane

Types of Transport Proteins
• 1) uniport: carries single solute
• 2) symport:
-translocates 2 different solutes
-move simultaneously in same direction
• 3) antiport:– exchanges 2 solutes– transports molecules in opposite directions– ex: (Na/K pump)

Receptor Proteins
• Shaped like boulders in membrane
• convey info to inside of cell (communication)
-hormones
• special shape holds only certain type of molecule

How Receptor Proteins Work
* when molecule of right shape fits receptor protein, it causes a change at other end of receptor, triggering response in cell

Receptor Proteins

Marker Proteins
• Look like trees sticking out of membrane
• Have carbohydrates on surface
• “Name Tags” of cells
• Different for every individual

Marker Proteins

Cell-Cell Recognition• Based on recognition of cell surface macromolecules• oligosaccharides are probably important cell
recognition markers - vary!• glycolipids
-sugars covalently linked to lipids• glycoproteins
-sugars covalently linked to proteins
N-linked = asparagine
O-linked = serine, threonine

How can proteins which can be polar fit into nonpolar region of
membrane?• Proteins made of amino acids
• Of 20 aa, some polar & some nonpolar
• Some aa can attract neighboring aa
folding, twisting
unique function

Protein Variation
• Allows for channel proteins - embed themselves in membrane
• receptor proteins
• marker proteins