Cell Structures & Organelles Plasma Membrane. Cell Organelles Phospholipid Molecule.
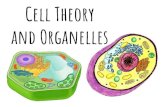
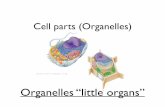
Cell Organelles
description
Transcript of Cell Organelles
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondria
Nucleus
Cell membrane
Lysosome
Ribosome
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
• Jelly-like liquid that fills up most of the space in a cell and contains hundreds of different chemicals.
• New substances are made and energy is released and stored there.
Nucleus
• Controls many of the functions of the cell – including growth, metabolism and reproduction
• Contains DNA
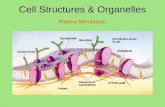
Cell membrane
• Forms a barrier between the inside and the outside of the cell
• Controls movement of substances into and out of the cell
• Semi permeable – some substances can move in and out, while others cannot
Mitochondria
• Powerhouse of the cell• Produces energy by converting the stored
energy in glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
• This energy is for cellular activities
Endoplasmic reticulum
• Smooth – transports materials through the cell
• Rough (covered in ribosomes) – transports materials through the cell
Vacuole
• ‘Bubbles’ of cell sap (dissolved sugars and salts)
• Digest cell nutrients and waste• Help with plant rigidity