Bonding What do you know about bonding?. Learning Objectives Define Key terms. Describe Ionic...
-
Upload
oswald-mclaughlin -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Bonding What do you know about bonding?. Learning Objectives Define Key terms. Describe Ionic...

Bonding
What do you know about bonding?

Learning Objectives
• Define Key terms.
• Describe Ionic Bonding
• Construct Dot/Cross diagrams for ionic compounds.

Match upIonic Bonding Formed when atoms of
different elements chemically bond together
Covalent Bonding Generally a metal bonded to a non metal. Electrons are transferred, and ions are formed.
Metallic bonding. Electrons are shared between all the atoms (delocalised outer electrons)
Compound Electrons are shared between 2 non metals
Now look in your book for a copy of the ‘definition’ what do you think the key parts are??

Ionic Bonds
• Electrons are transferred from the metal atom to the non metal atom.
• Oppositely charged ions are formed which are held together by electrostatic attraction.
• A giant ionic lattice is formed.

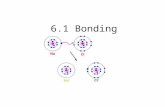
THE IONIC BONDTHE IONIC BOND
Ionic bonds tend to be formed between elements whose atoms need to “lose” electrons to gain the nearest noble gas electronic configuration (n.g.e.c.) and those which need to gain electrons. The electrons are transferred from one atom to the other.
Sodium Chloride
Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 Na+ 1s2 2s2 2p6
Cl 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5 Cl¯1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
An electron is transferred from the 3s orbital of sodium to the 3p orbital of chlorine; both species end up with the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas the resulting ions are held together in a crystal lattice by electrostatic attraction.
_

Half equations and electron configurationsHalf equations and electron configurations
Na ——> Na+ + e¯ 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 1s2 2s2 2p6
Cl + e¯ ——> Cl¯ 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6

ELECTRON
TRANSFER
Mg ——> Mg2+ + 2e¯ and 2Cl + 2e¯ ——> 2 Cl¯
Mg
Cl
Cl
e¯
e¯
THE IONIC BONDTHE IONIC BOND
FORMATION OF MAGNESIUM CHLORIDE
What would the electron configurations be? For all species? (4 of them)
Draw your own diagrams with electron configurations and half equations for:
Calcium oxide (CaO), Sodium Oxide (Na2O) and Aluminium Fluoride (AlF3)

This question is about different models of bonding and molecular shapes.
Magnesium sulfide shows ionic bonding.(i) What is meant by the term ionic bonding?..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................[1] (ii) Draw a ‘dot-and-cross’ diagram to show the bonding in magnesium sulfide. Show outer electron shells only.

Ionic bonding and the periodic table
• 1. Drawn a dot/cross diagram (outer shell) for a) MgO, b) CaBr2, c) Na3P, d) Al2O3
• 2. Write out the electron configuration for K and K+, S and S2-

Learning Objectives
• State common molecular ions
• Be able to predict ionic charge
• Apply to exam questions

Notes
• In general:• Group 1-3 lose elctrons to form the configuartion of PREVIOUS
noble gas.• Group 5-7 gain electrons to form the configuration of the NEXT
noble gas.
• Be, C, B and Si don’t tend to form ions due to too much energy being required to remove electrons.
• Transistion Metals: • Iron (II) Fe 2+ Iron (III) Fe 3+
• Copper (I) Cu+ Copper (II) Cu 2+ (Just look at the roman numerals)

Ions formed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Atom Li Be B C N O F
Ion
Atom Na Mg Al Si P S Cl
Ion
Atom K Ca Br
Ion

Molecular Ions
• Some such as NH4+ and OH- can be worked out.
• Others such as sulphate, think about what the acid would be.•
1+ 1- 2- 3-Ammonium NH4
+
Hydroxide OH- Carbonate CO32- Phosphate PO4
3-
Nitrate NO3- SulphateSO42-
Nitrite NO2- Sulphite SO32-
Hydrogen Carbonate HCO3
-
Dichromate Cr2O7
2-

Working out ionic formulae
Calcium Chloride
Atom Ion Charge Ratio
Ca Ca2+ 2+ 1
Cl Cl- - 2
= CaCl2

Questions
Lithium Nitride
Calcium Iodide
Aluminium Sulphide
Magnesium Phosphide
Nickel (II) Chloride
Copper(I) Oxide
Iron (III) Chloride
Titanium (IV) Chloride
Aluminium Sulpahte
Calcium Hydroxide
Iron (III) Sulphite
Chronium (III) Nitrite
Manganese (VI) Oxide
Chromium (III) Oxide
Ammonium Phosphate
Sodium Dichromate

Apply to exam question