Block Diagram Manipulation
-
Upload
mohd-fazli -
Category
Documents
-
view
158 -
download
4
description
Transcript of Block Diagram Manipulation

Control Engineering
EMM 4423

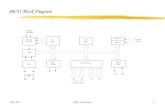
Block diagram is used to represent the control system
Relationship among the variables in the system.
Block diagram - > Complex system
Block diagram -> simplified -> single transfer function
Output/input -> transfer function
2 methods to simplify block diagram -> block diagram reduction, signal flow graph (mason’s
rule)
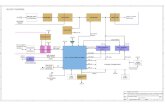
(a) Block diagram reduction
Block Diagram Manipulation


Example: Reduce to block diagram as shown below to a single transfer function

Solution

(b) Signal Flow Graph

Terminology
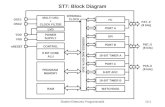
Node: It represents a system variables. For example: Figure 1(X1, X2,X3,X4 and X5)
Figure 1
Branch: A signal travels along a branch from one node to another in the direction indicated by the branch arrow and in the process gets multiplied by the gain of the branch. Example:-Figure 1(Signal reaching node X3 from node X2 is given by G23X2 where G23 is the gain
Input node: Node with only outgoing branches.Example-Figure 1(X1)
Output node: Node with only incoming branches.
Figure 2

Forward path: It is a path from input node to the output node.Example : There are 2 forward paths in Figure 2 as shown in Figure 3
Figure 2 Figure 3
Loop: It is a path which originates and terminates at the same node. For example, there are 5 loops in figure 2 as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4

Non touching loops: Loops that do not possess any common node.For example there are 2 possible combinations of nontouching loops in Figure 2 as shown in Figure 5
Figure 2
Figure 5

Forward path gain: It is the product of the branch gain encountered in traversing a forward path
Example (a) G12 G23 G34 G45
(b) G12 G23 G35
Figure 6
Loop gain: It is the product of the branch gains encountered in traversing a loop.
Example: G23 G34 G42
figure 7

Example:
Find the transfer function of the following system using Mason’s rule.

Solution:

Solution: