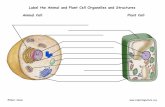
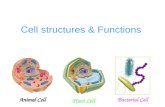
Animal Cell and - content.kopykitab.comChapter 1 of this book describes the general introduction and...
Transcript of Animal Cell and - content.kopykitab.comChapter 1 of this book describes the general introduction and...
Animal Cell and Tissue Culture
Shivangi Mathur
Department of Biotechnology
S.S. Jain Subodh Girls College, Jaipur
AGROBIOS (INDIA)
Published by:
AGROBIOS (INDIA)
Agro House, Behind Nasrani Cinema
Chopasani Road, Jodhpur 342 002
Phone: +91-291-2642319, Fax: 2643993
E. mail: [email protected]
Web Site: agrobiosindia.com
All Rights Reserved, 2012
First Published: 2006
Reprinted: 2008
Reprinted: 2012
All rights reserved. No part of the book or part thereof, including the title of the book, be
reprinted in any from or language without the written permission of the author and the
publishers. The copyists shall be prosecuted.
ISBN No. (10): 81-7754-297-4
ISBN No. (13): 978-81-7754-297-4
Price: Rs. 990.00 / US$ 50.00
Published by: Dr. Updesh Purohit for Agrobios (India), Jodhpur
Lasertypeset at: Yahsee Computers, Jodhpur
Cover Design by: Reena
Printed at: Hinglaj Offset Printers, Jodhpur
PREFACE
Man is considered to be the most powerful creature in universe, but he depends totally
on the biological entities for his all nutritional needs. Biotechnology use biological
entities for the betterment of human kind. Biotechnology derived from fusion of biology
and technology, is a very vast subject which includes Plant cell and Tissue culture,
Animal cell and tissue culture, Transgenic, Molecular biology, Recombinant DNA
technology, Genetic engineering, Medical biotechnology, Fermentation technology,
Microbiology, Enzyme technology, Biofuels, Environmental biotechnology,
Bioinformatics and Nanotechnology.
It may be pointed out that use of biological entities is not new. Ever since establishment
of civilization man is using biological organisms to satisfy his needs. But this can not be
regarded as biotechnology since production technology pertaining to agriculture and
animal husbandry etc. has now become distinct disciplines. However exploitation of
platn and animal cell in vitro as well as their constituents to generate some useful
product constitute biotechnology.
Animal cell and tissue culture is an integral part of Biotechnology and this book covers
all the aspects of animal cell culture. Animal cells are used for making new vaccines,
specific animal proteins such as intergerons, blood factors and hormones, monoclonal
antibodies for use as diagnostic and therapeutics, gene probes as diagnostic too,
enzymes and last but not the least many new and important compounds.
This book is beneficial to all students of undergraduation as well as post graduation of
all universities. This book comprises 13 chapters covering all aspects of Animal Cell
Biotechnology and very recent area of research i.e. Tissue engineering has also been
included with updated text materials and graphics.
Chapter 1 of this book describes the general introduction and basics about animal cell
and tissue culture. In chapter 2, chapter 3 and chapter 4 I have described how to get
start with animal cell culture and to establish cell lines for further studies use? Chapter 5
and chapter 6 tells about the selection and preservation of animal cells which becomes
necessary if we have to deal with genetically modified / clones cells. Chapter 7 gives an
idea about the feasibility of scale upprocess and chapter 8 covers all aspects of
fermentors used in scale up process of animal cells. Chapter 9 explains the most
extensive use of animal cell culture i.e. hybridoma technology and production of
monoclonal antibodies. Genetic manipulation of animal cells (transgenesis), a relatively
new field is dealt in chapter 10 and its applications are given in chapter 11 which are
very useful to all students of biotechnology as well as other students of relavant subjects.
Chapter 12 is the most important chapter which enhances the importance of this book.
Tissue engineering is an emerging area of research in medical biotechnology and has
shown good future for transplantation biology. Similarly chapter 13 is also comprising
new field of biotechnology; the Gene therapy. Gene therapy has already proven its
importance in the treatment of various diseases like SCID, cystic fibrosis etc.
In sincerely thank all those who have given their valuable time and help in completing
this book.
Author
CONTENTS
1. CELLS IN CULTURE: AN INTRODUCTION .......................................... 1
History ....................................................................................................................................... 1 Advantages and Disadvantages of Tissue Culture Methods ..................................................... 2
Advantages ............................................................................................................................. 2 Disadvantages ....................................................................................................................... 2
Biology of Cells in Culture ........................................................................................................ 2 Origin and Characterization ................................................................................................. 2 Differentiation ....................................................................................................................... 3 Kinetics of Cell Growth ......................................................................................................... 3 Genetics of Cultured Cells ..................................................................................................... 5 Laboratory Requirements for Animal Cell Culture ............................................................... 5
Choice of Materials ................................................................................................................... 7 Cell Type ................................................................................................................................ 7 Tissue Source ......................................................................................................................... 7 Subculturing ........................................................................................................................... 8 Selection of Medium .............................................................................................................. 8 Gas Phase .............................................................................................................................. 9 Selection of Substrate ............................................................................................................ 9 Size of Culture Vessel ............................................................................................................ 9 Feeder Layer on Substrate ................................................................................................... 10
Applications of Animal Cell Culture ....................................................................................... 10 Monoclonal Antibodies ........................................................................................................ 10 Recombinant Proteins .......................................................................................................... 10 Gene Targeting .................................................................................................................... 10 Cytotoxicity Testing ............................................................................................................. 11 Tissue Grafting .................................................................................................................... 11 Amniocentesis, Infertility and Embryo Transplantation ...................................................... 12
Problems Associated with Tissue Culture ............................................................................... 13 Contamination ..................................................................................................................... 13 Mycoplasma ......................................................................................................................... 13 Cross Contamination ........................................................................................................... 13 Instability ............................................................................................................................. 13 Ethical Considerations ........................................................................................................ 14
2. TISSUE CULTURE MEDIUM .......................................................... 15
Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 15 Natural Media ...................................................................................................................... 15 Biological Fluids ................................................................................................................. 16 Tissue Extracts ..................................................................................................................... 17 Chemically Defined Medium ............................................................................................... 20 Considerations for Designing of Media ............................................................................... 22 Surface Tension and Foaming ............................................................................................. 23 CO2 and Bicarbonates ......................................................................................................... 23 Temperature ......................................................................................................................... 23
Media Designing ..................................................................................................................... 24 Characteristics / Composition of Media .................................................................................. 25
Energy Source ...................................................................................................................... 25 Amino Acids ......................................................................................................................... 25 Vitamins ............................................................................................................................... 25 Minerals ............................................................................................................................... 25 Antibiotics ............................................................................................................................ 26 Serum ................................................................................................................................... 26
3. INITIATION OF CELL CULTURE- PRIMARY CULTURE ........................... 32
Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 32 Preparation and Sterilization of Glassware and Apparatus ...................................................... 32 Preparation and Sterilization of Reagents and Media .............................................................. 32 Preparation of Animal Material ............................................................................................... 34
Primary Culture ................................................................................................................... 34 Mechanical Disaggregation ................................................................................................ 37 Enzymatic Disaggregation ................................................................................................... 38 Disaggregation by Trypsin (for Embryonic Tissue) or Trypsinization ................................ 38 Warm Trypsinization ........................................................................................................... 39 Cold Trypsinization ............................................................................................................. 41 Disaggregation by Collagenase (for Embryonic, Normal and Malignant Tissues) ............. 43
Culture ..................................................................................................................................... 44 Primary Explantation Techniques ....................................................................................... 44 Slide or Coverslip Cultures .................................................................................................. 44 Flask Cultures ...................................................................................................................... 47 Test Tube Cultures ............................................................................................................... 48
Organ Culture .......................................................................................................................... 48 Characteristics of Organ Culture ........................................................................................ 48 Limitation of Organ Culture ................................................................................................ 49 Culture of Embryonic Organs .............................................................................................. 49 Organ Cultures on Plasma Clots ......................................................................................... 49 Organ Cultures on Agar ...................................................................................................... 50
Whole Embryo Culture ............................................................................................................ 50 Culture of Chick Embryo (Spratt, 1956) .............................................................................. 50
Histotypic Cultures .................................................................................................................. 51
Spheroides ........................................................................................................................... 51 Gel and Sponge Technique .................................................................................................. 51 Hollow Fibers ...................................................................................................................... 51
Applications of Cell Cultures .................................................................................................. 52 Animal Tissue Cultures in Biomdical Research: Genetics .................................................. 52 Tissue Cultures in Biomedical Research: Virology and Host-Parasite Relationships ........ 53 Tissue Cultures in Biomedical Research: Cancer ............................................................... 53
4. CELL LINES ............................................................................ 54
Need of Subculturing ............................................................................................................... 54 Subculturing ............................................................................................................................ 54
Immortalization of Cell Lines .............................................................................................. 55 Designation of Cell Line ...................................................................................................... 55
Selection of Cell Lines ............................................................................................................ 56 Finite Cell Line / Continuous Cell Line ............................................................................... 56 Species ................................................................................................................................. 56 Availability ........................................................................................................................... 56 Normal or Transformed Line ............................................................................................... 56 Growth Characteristics ....................................................................................................... 56 Stability ................................................................................................................................ 57 Validation ............................................................................................................................ 57 Control of Cell Line ............................................................................................................. 57
Routine Maintenance of Cell Lines ......................................................................................... 57 Cell Morphology .................................................................................................................. 57 Replacement of Medium....................................................................................................... 57
Protocol ................................................................................................................................... 58 Feeding the Culture ............................................................................................................. 58 Surface Area, Volume and Depth......................................................................................... 59 Subculture ............................................................................................................................ 59 Criteria for Subculture ........................................................................................................ 60 Procedure for Subculture ..................................................................................................... 60 Subculture of Suspension Culture ........................................................................................ 61
Protocol 2 ................................................................................................................................ 62 Subculture of Suspension ..................................................................................................... 62 Comparison of Monolayer and Suspension Culture ............................................................ 64
5. SELECTION AND CLONING OF CELLS ............................................. 65
Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 65 Objectives of Cloning .......................................................................................................... 65 Cloning of Monolayer and Suspension Culture ................................................................... 65 Dilution Cloning .................................................................................................................. 66 Factors Affecting Clonal Growth......................................................................................... 68 Cloning in Suspensions ........................................................................................................ 69 Cloning in Methocel ............................................................................................................ 74 Selection and Isolation of Clones ........................................................................................ 77
Other Isolation Techniques .................................................................................................. 79 Factors Affecting Cell Adhesion .......................................................................................... 80
6. CHARACTERIZATION AND PRESERVATION OF ANIMAL CELLS ............... 82
Need of Characterization ......................................................................................................... 82 Species Verification ............................................................................................................. 82 Intraspecies Contamination ................................................................................................. 82 Microbial Contamination .................................................................................................... 82 To Check Status of Cells ...................................................................................................... 83 To Check Genetic Stability of Cells ..................................................................................... 83
Techniques of Characterization ............................................................................................... 83 Techniques for Species Verification ..................................................................................... 83
Chromosome Banding ............................................................................................................. 83 Protocol: Chromosome Banding ......................................................................................... 83 DNA Content ........................................................................................................................ 86 DNA Hybridization .............................................................................................................. 87 Isoenzymology...................................................................................................................... 87 Protocol 2: Isoenzyme Analysis ........................................................................................... 88 Immunological Tests ............................................................................................................ 90 Techniques to Detect Intra Species Contamination ............................................................. 91 Techniques for Characterizing Cell Types........................................................................... 93 Techniques to Detect Microbial Contamination .................................................................. 94 Preservation of Animal Cell Lines ....................................................................................... 96 Steps of Cryopreservation .................................................................................................... 96 Evaluation of Cell Viability ............................................................................................... 102
Thawing ................................................................................................................................. 103 Cell Banks .......................................................................................................................... 104
7. SCALE UP OF ANIMAL CELL CULTURE ......................................... 106
Practical Considerations during Animal Cell Culture ...................................................... 106 Culture Parameters ........................................................................................................... 107 Medium .............................................................................................................................. 107 Non Nutritional Medium Supplements ............................................................................... 107 Oxygen ............................................................................................................................... 109 Redox Potential .................................................................................................................. 110 Growth Kinetics ................................................................................................................. 110 Culture Vessel and Growth Surfaces ................................................................................. 111 Cell Quantification ............................................................................................................ 111
Scale Up Process ................................................................................................................... 112 Scale Up of Monolayer .......................................................................................................... 112
Nunc Cell Factory .............................................................................................................. 113 Multitray Disks, Spirals and Tubes .................................................................................... 115 Roller Bottles / Tubes ......................................................................................................... 115 Microcarriers ..................................................................................................................... 116 Perfused Monolayer Culture ............................................................................................. 118
Microencapsulation ........................................................................................................... 121 Scale Up of Suspension ......................................................................................................... 121
Protocol: Suspension Cultures .......................................................................................... 121 Continuous Culture ............................................................................................................ 122
Mixing and Aeration in Suspension ...................................................................................... 123 Airlift Fermenters .............................................................................................................. 123 Perfused Suspension Culture ............................................................................................. 124 Rotating Chambers ............................................................................................................ 124 Fluidized Bed Reactors for Suspension Culture ................................................................ 125
On Line Monitoring of Cell Culture ...................................................................................... 125
8. FERMENTORS ....................................................................... 127
Continuous Culture ............................................................................................................ 127 The Components of a Fermentor ........................................................................................... 128 Parts of Fermentors................................................................................................................ 128
Vessel ................................................................................................................................. 128 Peripheral Parts and Accessories ........................................................................................... 130
Reagent Pumps .................................................................................................................. 130 Medium Feed Pumps and Reservoir Bottles ...................................................................... 130 Rotameter / Gas Supply ..................................................................................................... 130 Sampling Device ................................................................................................................ 130
Alternative Vessel Designs .................................................................................................... 131 Air Lift................................................................................................................................ 131 Fluidized Bed ..................................................................................................................... 131 Hollow Fibre ...................................................................................................................... 131 In Situ Sterilizable Fermentors .......................................................................................... 132 Containment ....................................................................................................................... 132
Additional Accessories and Peripherals ................................................................................ 132 Feed Pumps ....................................................................................................................... 132
Exit Gas Analysis .................................................................................................................. 134 Infra-Red Carbon Dioxide Analyzer .................................................................................. 134 Paramagnetic Oxygen Analyzer ........................................................................................ 134 Mass Spectrometer ............................................................................................................. 134
Types of Reactors .................................................................................................................. 134 Mechanically Agitated Stirred Tank Reactors ................................................................... 134 Air-Lift Bioreactor and Modified Air Lift Bioreactors ...................................................... 136 Novel Seesaw Bioreactor ................................................................................................... 138
Different Types of Fermentor Instrumentation ...................................................................... 139 Analogue Controllers – Rack System ................................................................................. 139 Analogue Controllers – Separate Modules in Housings .................................................... 139 Digital Controllers – Embedded Microprocessor ............................................................. 139 Digital Controllers – Process Controllers ......................................................................... 139 Digital Controllers – Direct Computer Control ................................................................ 139
Common Measurement and Control Systems ....................................................................... 140 Speed Control .................................................................................................................... 140
Temperature Control ......................................................................................................... 140 Control of Gas Supply ....................................................................................................... 140 Control of Dissolved Oxygen ............................................................................................. 142 Antifoam Control ............................................................................................................... 143
Transfer of Oxygen................................................................................................................ 147 Maintenance of Aseptic Conditions ...................................................................................... 149
9. HYBRIDOMA TECHNOLOGY AND MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES .............. 151
Hybridoma ............................................................................................................................. 151 Limitation of Traditional Method of Antibody Production ................................................ 151 Advantages and Disadvantages of Mabs Over Polyclonal Antibodies .............................. 152 Types of MAbs ................................................................................................................... 153 Chimeric MAbs .................................................................................................................. 155
Hybridoma Technology ......................................................................................................... 155 The Basis of Hybridoma Technology ................................................................................. 156
Production of Monoclonal Antibodies................................................................................... 157 Choice of Fusion Partners ................................................................................................. 157 Immunization of Mice ........................................................................................................ 157 Making Hybridomas .......................................................................................................... 158 Screening Procedures ........................................................................................................ 161 Long Term Storage ............................................................................................................ 163
Hybridomas from Different Species ...................................................................................... 163 Production of MAbs through Genetic Engineering ............................................................... 163 Alternative to Hybridoma ...................................................................................................... 164 Production of Human/Humanized Antibodies ....................................................................... 165 Application of MAbs ............................................................................................................. 166
Diagnosis Screening and Therapy ..................................................................................... 166 Monoclonal Antibodies as Enzymes (Abzymes) ................................................................... 167 Vaccine Production ............................................................................................................... 168 Purification and Quantitation of Compounds ........................................................................ 168
Raising MAbs ..................................................................................................................... 168 Purification and Quantitation ............................................................................................ 168 Radio Immunoassay (RIA) ................................................................................................. 169
Cytogenetic Analysis ............................................................................................................. 171
10. GENETIC MANIPULATION OF CELLS: TRANSGENESIS ........................ 172
Why Animal Cells are Chosen for Genetic Manipulation ..................................................... 172 Basics of Genetic Manipulation ............................................................................................ 173
Isolation of Gene ................................................................................................................ 173 Introduction of Gene into Suitable Vector ......................................................................... 174 Introduction of Recombinant Vector into Cells ................................................................. 175 Calcium Phosphate Transfection ....................................................................................... 175 Lipofection ......................................................................................................................... 179 Electroporation .................................................................................................................. 179 Microinjection.................................................................................................................... 179
Retroviral Infection ............................................................................................................ 180 Embryonic Stem Cell Transfer ........................................................................................... 182 Microprojectile / Biolistic .................................................................................................. 182
Screening for Recombinant Cells .......................................................................................... 182 Analysis of Transgene Integration ..................................................................................... 182 Detection of mRNA Expression .......................................................................................... 182 Assay for Protein Expression ............................................................................................. 183
Examples of Transgenic Animals .......................................................................................... 183 Integration of Microinjected Sequences into the Embryo: A Case Study of Mice ............. 183 Genotyping Transgenic Mice by PCR ................................................................................ 185
Specific Applications of Transgenic Mice ............................................................................ 186 Gene Expression ................................................................................................................ 186 Transgenic Mice as Models for Genetic Engineering ........................................................ 188
Transgenic Swine .................................................................................................................. 189 Production of Sheep Transgenic for Growth Hormone Genes .............................................. 190
Insertion of Genes .............................................................................................................. 191 Expression of Transgenes .................................................................................................. 192
Production of Transgenic Cattle by Pronuclear Injection ...................................................... 192 Collection of Embryos ....................................................................................................... 192 Pronuclear Injection .......................................................................................................... 193 Preparation of DNA ........................................................................................................... 193 Culture and Transfer of Embryos ...................................................................................... 193 Collection and Analysis of Tissue ...................................................................................... 194
Methods for the Introduction of Recombinant DNA into Chicken Embryos ........................ 195 Problems after Developing Transgenic Animals ................................................................... 195
The Nature of Patents ........................................................................................................ 195
11. APPLICATIONS OF TRANSGENIC ANIMALS ..................................... 196
Transgenic Animal Technology ............................................................................................ 196 Genuine Transgenic Animals and their Applications ............................................................ 198
Enhanced and Tissue-Specific Transgene Expression ....................................................... 198 Production of Sheep Transgenic for Growth Hormone Genes .......................................... 201 Production of Transgenic Cattle by Pronuclear Injection ................................................. 201 Methods for the Introduction of Recombinant DNA into Chicken Embryos ...................... 204
Present States of Art .............................................................................................................. 204 Gene Transfer by Microinjection .......................................................................................... 205 Other Methods ....................................................................................................................... 205 Use for Medical and Therapeutic Purposes ........................................................................... 206
Recombinant Protein Production ...................................................................................... 206 Xenotransplantation .......................................................................................................... 206
Genetic Engineering- Single Genes ....................................................................................... 207 Gene Mapping ....................................................................................................................... 208 Artificial Insemination and Germ Cell Storage ..................................................................... 209 Ectogensis .............................................................................................................................. 210 Amniocentesis ....................................................................................................................... 210
Significance of Amniocentesis ........................................................................................... 211 Transplantation ...................................................................................................................... 211 Cloning Technique ................................................................................................................ 211 Gene Therapy ........................................................................................................................ 212 Genetic Counselling .............................................................................................................. 212 In Vitro Fertilization and Embryo Transfer ........................................................................... 214
Surrogate Motherhood ....................................................................................................... 216 In Vitro Fertilization and Embryo Transfer for Improved Breeding Programmes ............ 216 Success of Embryo Transplantation ................................................................................... 216 Objectives and Applications of ET ..................................................................................... 217 Superovulation ................................................................................................................... 219 Physiological Basis of Superovulation .............................................................................. 219 Factors Which Influence the Superovulatory Response ..................................................... 219 Superovulation using Pmsg ............................................................................................... 221 Freezing of Embryos .......................................................................................................... 221 Frozen Embryos ................................................................................................................. 221 Embryo Sexing ................................................................................................................... 222 Success in Pre-Determining the Sex .................................................................................. 222 Micromanipulation of Embryos ......................................................................................... 223
Advantages of Cell Manipulation Technique ........................................................................ 223 Simple Method of Splitting Embryos .................................................................................. 224
Techniques of Nuclear Transplantation ................................................................................. 224 Sources of Eggs and Embryos ........................................................................................... 224
Gene Injection (Introduction of Foreign Cloned Genes) ....................................................... 225 Dense Cytoplasm and Gene Injection ................................................................................ 225
Selective Animal Breeding .................................................................................................... 225 Intensity of Selection and Reproductive Rate .................................................................... 226
Potential ................................................................................................................................. 226 Hazards of Artificial Breeding .............................................................................................. 227
Animals as Tennis Balls? ................................................................................................... 228 Down on the Farm ............................................................................................................. 228 Time to Decide ................................................................................................................... 229
12. TISSUE GRAFTING AND ENGINEERING .......................................... 230
Introduction ........................................................................................................................... 230 Historical Perspective ............................................................................................................ 230
Principle ............................................................................................................................ 230 Prerequisite for Tissue Engineering .................................................................................. 231 Semi-Natural and Natural Substrate ................................................................................. 232 Synthesis of Tissue Engineering Scaffolds ......................................................................... 234 Cell Sources ....................................................................................................................... 238 Assembly Methods ............................................................................................................. 239
Some Examples of Tissue Engineering ................................................................................. 240 Use of Biological Film as a Cultured Epidermal Autograft .............................................. 240 Tissue Engineering Peripheral Nerve Implants ................................................................. 242
Tissue Engineering for Vascular Graft .............................................................................. 243 Advantages and Disadvantages of Tissue Engineering ..................................................... 243 Ethical Issues ..................................................................................................................... 244 Future Prospects ................................................................................................................ 245
13. GENE THERAPY ..................................................................... 247
How does Gene Therapy Work? ........................................................................................ 247 Gene Therapy in the Treatment of Cancer ......................................................................... 248 Main Approaches of Gene Therapy ................................................................................... 248 Gene Therapy and Transfer of Genes Into Cells ............................................................... 252
Viruses used as Gene Therapy Vectors ................................................................................. 253 Retroviruses ....................................................................................................................... 253 Adenoviruses ...................................................................................................................... 253 Adeno-Associated Viruses .................................................................................................. 253 Herpes Simplex Viruses ..................................................................................................... 253
Current Status of Gene Therapy Research ............................................................................. 254 Gene Therapy Factors and Genetic Disease .......................................................................... 255
Short-Lived Nature of Gene Therapy ................................................................................. 255 Immune Response .............................................................................................................. 255 Problems with Viral Vectors .............................................................................................. 255 Multigene Disorders .......................................................................................................... 255
Recent Developments in Gene Therapy ................................................................................ 255 Subtle Gene Therapy Tackles Blood Disorder ................................................................... 256
DNA Nanoballs Boost Gene Therapy ................................................................................... 256 Risks Associated with Gene Therapy Trials .......................................................................... 257 Precautions for Gene Therapy ............................................................................................... 257
14. REFERENCES ........................................................................ 258
15. SUBJECT INDEX..................................................................... 262
Animal Cell And Tissue Culture
Publisher : Agrobios Publications ISBN : 9788177542974 Author : Mathur S
Type the URL : http://www.kopykitab.com/product/10901
Get this eBook