An overview of toxoplasmosis
-
Upload
shifa-ul-haq -
Category
Education
-
view
288 -
download
1
description
Transcript of An overview of toxoplasmosis

+
An overview of ToxoplasmosisDr Shifa Ul HaqUVAS, Lahore-Pakistan

+Introduction
Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic disease caused by T gondii
It belongs to phylum Apicomplexa, family Sarcocystidae
It’s derived from a Greek word “Toxon” mean bow as unique crescent shaped trophozoites, half the size of RBC
The parasite was 1st observed in rodents in 1908
In 1970 parasite life cycle was studied

+Introduction
Infection is seen in wide range of animals, birds but doesn’t produce disease in them
It can virtually infect all warm blooded animals
Members of Felidae family are final hosts that
excrete oocysts
An infected cat excrete 300,000 to 100 million oocysts in 10-20 days

+Introduction…
In USA 22% of population of 12 years old is seropositive
Seroprevalence increased with age
High seroprevalence in countries where undercooked meat is eaten like France and central America (Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras etc.)
In some communities up to 95% population is seropositive
Infection is high in hot, humid condition and low altitude
Cysts are highly resistant, survive even up to 18 months

+Life Cycle of Toxoplasma
Unsporulated oocysts shed in cat feces, take 1-5 days to sporulate and become infective
Intermediate host ingest oocysts>sporozoites released>penetrate epithelial cells and invade macrophages
Divide by endogony (merogony) and make two daughter cells> cell rupture> tachyzoites released and attack new calls
If immunity prevails development slows down and tachyzoites become bradyzoites and encysted in the tissues
If cat eat infected tissue, merogony occurs in intestinal cells and secrete oocysts in the fces

+Life Cycle of Toxoplasma

+Routes of Transmission
1. Foodborne
Undercooked, contaminated meat esp. pork, lamb
Accidental ingestion; not hand washing, contamination with knives, utensils, cutting boards

+Routes of Transmission
2. Animal to human Cats eat infected tissues and rodents, birds so get
infection. Cat passes millions of oocysts in environment after 3 week of ingestion. Human get infection if swallow accidentally
Cleaning contaminated litter box
Drinking contaminated water
Eating raw fruit and vegetable
No hand washing

+Routes of Transmission
3. Mother-to-child
During pregnancy infection can pass disease to fetus
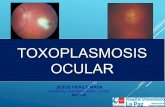
Congenital Toxoplasma infections can cause serious eye, ear, and brain damage in new born.
If infection in early pregnancy, immunity will control
If new infection in last trimester: Miscarriage Still birth Disease in infant

+Diagnosis
Serologically by IgG and IgM can be used
Amniotic fluid of fetus for the detection of parasite DNA
MAT- Modified Agglutination Test for detection of antibodies in blood and serum
MRI and Computed Tomography for brain
Dye-Test (DT) Sabin-Feldman Test

+Treatment
The majority of affected people have no symptoms, usually a self-limiting disease in healthy persons
But serious problem is seen especially in immunodepressed and in pregnant women
If symptoms develop: muscle stiffness, swollen lymph nodes, confusion, headache, poor coordination

+Treatment
Combination of pyramethamine, 50mg on day 1st followed by 25mg/day and sulphadiazine 1-1.5 gram 4 times a day for 3-6 weeks
To prevent bone marrow toxicity folic acid 10-15mg/day
Dexamethasone 10-15mg/day also recommended during infection
During pregnancy Spiramycin 1gram/day
During 4th month of pregnancy pyrimethamine 50mg twice a day. Then pyrimethamine 50mg/day with sulphadiazine 1 gram four times a day for 4-6 weeks

+Control of Toxoplasmosis
Meat should be cooked properly at 70 °C until there is no reddish color.
Freezing the meat for more than 3 days at -15 °C or at -20 °C for 2 days will kill bradyzoites cysts
Wash, peel vegetables and fruits
Wash knives, cutting boards, dishes, utensils

+Control Cont.…
Avoid untreated water
Wear gloves when handling soil like gardening
Teach children about importance of washing hands
Keep sand boxes covered
People who keep cats in their houses should dispose off their fecal
material daily, wash cat boxes/cages thus eliminating the oocysts
before they have chance to sporulate and become infective
A serological negative cat in the home of pregnant women should be
removed from the house because it could acquire a primary infection
and can contaminate the environment with oocysts

+Control Cont.…
Flies and cockroaches should be controlled because they
act as transport host for fecal oocysts of cats.
Keep cats indoor and feed canned, cooked or frozen feed
Don’t adopt stray cats, and if pregnant
Use carbolic acid to kill oocysts in the soil, floors etc.
Educate people to avoid eating raw vegetables &
undercooked meat

+Have a Nice Day!
Dr Shifa Ul HaqUVAS, Lahore-PakistanTo contact me please Google “Shifa Ul Haq”