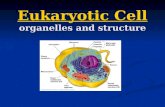
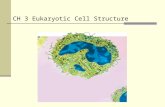
AIM: How are eukaryotic organisms different? DO NOW: What are the two Major types or categories of...
-
Upload
mildred-shepherd -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of AIM: How are eukaryotic organisms different? DO NOW: What are the two Major types or categories of...
• AIM: How are eukaryotic organisms different?• DO NOW: What are the two Major types or
categories of cells? • HW: Handout from yesterday
How are prokaryotes and eukaryotes different?
Organization of the nucleusCell size
Membrane bound organelles
Cell types• Prokaryote
– Kingdom Monera• Bacteria• Archaebacteria
• Eukaryote– Kingdom Protista– Kingdom Fungi– Kingdom Plant– Kingdom Animal
Eukaryote
• Multi or Single celled organisms– Protista
• Parmecium• Ameba
– Fungi• Yeast• Mushrooms
– Animal– Plant
Kingdom Protista characteristics• Eukaryotes• Heterotrophic and Autotrophic• Unicellular • Mostly aquatic • Mostly asexual• Things like: slime molds and algae, paramecium,
ameba, euglena
Kingdom Protista: Paramecium• Oral groove: ingest nutrients• Gullet: back of the throat• Cilia: movement• Contractile vacuole: able to
contract and expel excess water
• Food vacuole: responsible for digestion
• AIM: How are eukaryotic organisms different?• DO NOW:• HW: Textbook Read pages 244-247.
Questions 1-4 pg 247. Write out the question followed by the answer
Characteristics of the Kingdom Fungi
• Eukaryote• Heterotrophic• Unicellular and Multicellular• Mostly terrestrial• Asexual and sexual• Mushrooms,molds, yeasts,puffballs
Kingdom Fungi Unicellular yeast
• Single celled • Mostly asexual
reproduction through budding
• Some by binary fission• Used in baking and
alcohol fermentation
Kingdom Fungi Multicellular Mushroom
• Heterotrophic saprobes• Decomposer or recyclerDecomposer or recycler
Breaks down dead and Breaks down dead and decaying matter to decaying matter to release back into the release back into the environmentenvironment
Characteristics of Plantae Kingdom
• Eukaryote Multicellular • Autotrophic • Mostly Terrestrial • Asexual and Sexual • Nonmotile Things like: mosses, ferns, conifers, and
flowering plants
Kingdom Animalia• largest of the kingdoms
in terms of its species diversity.
Eukaryote Multicellular• heterotrophs = other
feeder• multicellular • In most animals, these
cells are organized into tissues that make up different organs and organ systems.