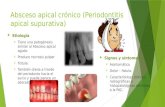
Acute apical abscess dr anirudh singh chauhan
-
Upload
anirudh-singh-chauhan -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
139 -
download
2
Transcript of Acute apical abscess dr anirudh singh chauhan

ACUTE APICAL ABSCESS [AAA]

“Evil Being the root of mystery, PAIN is the root of KNOWLEDGE.”
Simone Weil
(Philospher)

ACUTE: 1. Sharp, severe.
2. Denoting the swift onset and course of a disease.
Glossary of Periodontal Terms — The American Academy of Periodontology 2001

Apical : apex of a tooth.
Glossary of Periodontal Terms — The American Academy of Periodontology 2001

ABSCESS: Localized collection of purulent exudates (pus) in a cavity
formed by the disintegration of tissues
Glossary of Periodontal Terms — The American Academy of Periodontology 2001

ACUTE APICAL ABSCESS [AAA]
• A severe localized Inflammatory condition
characterized by formation of purulent exudates(
PUS) involving the dental pulp or pulpal remnants
and the tissues surrounding the apex of a tooth.

• An abscess is a natural defense mechanism in
which the body attempts to localize an infection
and wall off the microorganisms so that they
cannot spread throughout the body.
• So as a dentist we are part of QUICK
REACTION TEAM which makes sure that the
problem is timely diagnosed and prevented from
spreading.

Also Known As :
• # Periradicular abscess ( along the root)
• Periapical abscess( around the root tip)
• Apical Abscess ( at the root tip)
• DentoAlveolar abscess
• Tooth root abscess

ETIOLOGY
• Most common factor is Bacterial Invasion of the pulp from a carious lesion.
•
• Toxins from necrotic pulp
• Tooth trauma (infective, mechanical, thermal, chemical) resulting in pulpitis and necrosis.
• Acute exacerbation of a chronic situation, eg-may originate from a pre-existing apical granuloma or cyst.

• Iatrogenic / Procedural Mishaps during
endodontic treatment.
• Partially or previously endodontically treated (if
continued bacterial contamination and/or leakage
occurs)

Abscess can be seated inMultirooted tooth

• Inflammation of the periapical part of the
periodontal tissue being confined to a minute
space between the apex and its surrounding
bone may lead to resorption of :
–Adjacent Bone and
–Root Apex

CLINICAL SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
• Acutely painful to biting pressure, percussion &
Palpation
• No Response to Electric Pulp Testing (However
need not be Non Vital all the time.)
• Varying degrees of Mobility
• Tooth may be elevated in alveolar socket
(pressure from inflamed tissue around the tooth).

• Patient may exhibit raised temperature and
malaise.
• Fractured and/or discolored tooth
crowns/fillings.
• The cervical & submandibular lymph nodes
tender to palpation.

Sequalae Of Periapical Abscess
• Localized swelling( Intra & Extra Oral)
1. LOCALIZED- confined within oral cavity.
2. DIFFUSED- extensive, spreads through adjacent
soft tissues , dissecting tissue spaces along
fascial planes ( Cellulitis)
3. FLUCTUANT- Lying Superficially
4. FIRM-

Radiographically
• Thickening of apical PDL
• Ill defined apical radiolucent lesion. *

DIAGNOSIS
• Ask pointed subjective questions about the patients – pain, history, location, severity, duration, character, & eliciting stimuli if any .
• Meticulous oral examination to identify tooth (teeth) with pulpal pathology (caries, fractured teeth with pulpal exposure, discolored teeth, drainage tracts)
• X-ray to assess periapical status of affected tooth (teeth). Acute abscess may show varying appearances.

• The patient's pain is typically relieved to some
extent by application of cold substances to the
affected tooth.

The following criteria support this diagnosis:
• Acute pain, arising out of a long-standing
infection. Although the patient may not be aware
of a long-standing infection, the tooth now hurts
when biting, chewing, or tapping on it.
• Swelling may or may not be present
• Response to Pulp testing may or may not be there.
• Presence of fever and general malaise (feeling
poorly)

DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSISAbscesses generally result in the classic "toothache",
• But other things can make teeth ache as well:
1. Sinus infections may cause the upper back teeth to ache;
2. Heart pain (angina) can radiate into the jaws, producing the symptoms of a toothache.
3. Lymphoma has also been reported to cause repeated toothache pain.
4. Other types of cysts or tumors may also cause the jaws to ache and/or swell.
• It's important that any abnormal conditions in the mouth be identified and properly diagnosed, so that appropriate treatment can be prescribed, and ideal long term oral health maintained.

EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT
• The principle of treating all endodontic periapicallesions is same –
“TO ERADICATE IRRITANTS IN THE ROOT CANAL SYSTEM”
“START by doing what is NECESSARY, then what is POSSIBLE, and suddenly you are doing the IMPOSSIBLE”
(Francis of Assisi)

• FOREMOST Establish drainage to relieve pain
• Once acute phase subsides RCT should be
performed .

• DRAINAGE ACHIEVED BY :-
– Surgical Drainage
• Immediate relieve from Pain
– Access Opening and Drainage
first visit accomplishes two things
• Relief from pain and pressure
• Removal of potent irritants [pus]

ROOT CANAL TREATMENT

• Since abscess is localized ideal drainage can be
done through root canals.
• THUMB rule for managing all these infections is
to ACHIEVE DRAINAGE AND TO
REMOVE THE SOURCE OF INFECTION
• Although leaving these teeth open for a day has
been a COMMON PRACTICE however Current
Trend is NOT leaving open for Drainage.

Thorough Cleaning Of The
Canal
• CLEAN, CLEAN and CLEAN !!!
• Extremely important to remove the ROOT
CAUSE ( bacterial toxins) from within the ROOT
CANAL.
• PROGNOSIS depends on it.
• Avoid pushing of debris into periapex
• IRRIGANT, use Copious amount.

Over Instrumentation
• Establishes drainage & widens the apical constriction.
• Case selection very important
• Only done after thorough cleaning & shaping of canals.
• Reamers & K files instruments of choice.
• Viscous Pus is drained.
• Over instrumentation to be 1-1.5 mm beyond apex

CALCIUM HYDROXIDE
• Proven AntiMicrobial activity
• Due to High pH has the ability to alter acidic
environment of Inflamed Periapical Lesions.
• Can absorb exudate in root canal.
• Even if it goes beyond apex ,its good.

• SINGLE VISIT -VS- MULTIPLE
VISITS

Single Visit Endodontics
• Definitely NOT prefferred in Acute Apical Abscess.
• Patients body language to be OBSERVED CAREFULLY !! ( pt with pain/swelling)
• A green signal if :
1. Dry canals
2. Tooth Asymptomatic
3. Complete cleaning, shaping & filling of canals be achieved in single sitting.
– To be avoided incase of evidence of Pain, Swelling or Exudation

Multiple Visit Endodontics
• Provides shorter initial visit , thus considered
comfortable.
• Intervisit microbial dressing can be provided.
• In either cases the Elimination of BACTERIA is
of PRIME IMPORTANCE.

SURGICAL DRAINAGE
• Surgical management is needed in case :
- when drainage cannot be achieved through the canals
- Rapidly progressing infection
Apart from IMMEDIATE relief from swelling it ALSO reduces the total treatment time.
• Depending upon Location choose b/w Incision & Drainage and Aspiration.

INCISION & DRAINAGE (I&D) :
• Topical anesthesia usually sufficient.
• Else nerve block / infiltration (anterior and
posterior to the area) can be used.
• The area should be cleaned with a disinfecting
solution such as beta dine.
• Use no.11 blade to make the incision
• INCISION given at the site of GREATEST
FLUCTUANT swelling to encourage draining.

• Usually stab incision is made.
• Cut through the mucosa and sub-mucosa into the
abscess cavity eventually extending towards the
offending roots.
• Rinsing with LUKE warm SALT water keeps
wound CLEAN thus promotes drainage.

• This is a modification of technique described by Hoen
et al
• For this method patient should be scheduled for
appointments twice a week & done for 3-4 weeks.
• Topical anesthesia is applied on the mucosa over the
most fluctuant part
• Two 17 gauge needle are inserted side by side about 1
cm apart into the mucosa for a depth of 5-8 mm and
direction perpendicular to the mucosal surface.
• Into one of the needles an empty 10ml syringe is
attached
SIMPLE SYRINGE TECHNIQUE :

• The contents of the lesion is aspirated slowly
• If the patient experiences pain L.A can be injected in the periphery, without withdrawing the needle
• Then the syringe is replaced with another syringe containing normal saline

• Amount of saline must be equal to the amount of
fluid aspirated
• Then the saline is injected very slowly into the
lesion
• This procedure may be repeated three times
• This method is very effective and has
successfully given good results
• It also reduces the treatment time within 3-4
weeks .

TREPHINATION
• Done in absence of swelling.
• NOT in much TREND nowadays.
• Involves making a window through the mucosa and bone to the abscess at the root tip.
• Uses engine driven perforator to enter through the cortical bone.
• Often No Incision required.
• Provides immediate pain relief.
• High chances of causing irreversible injury to the tooth root or surrounding structures (BLIND APPROACH)

ANTIBIOTICS ??

• Antibiotics may be prescribed in conjunction
with Drainage of the tooth.
• In the event of patient with fever, or for an
immuno compromised patient, antibiotics may
be prescribed.
• Clinically when the tooth is tender , usually
antibiotics are prescribed.

• In the management of localized( EARLY) acute
apical abscess in the permanent dentition, the
abscess should be drained through a pulpectomy
or incision and drainage. This analysis indicated
that antibiotics are of no additional benefit.
– Debora C. Matthews, DDS, Dip Perio, MSc •
– • Susan Sutherland, DDS, MSc •
– • Bettina Basrani, DDS, Dip Endo, PhD •
– (© J Can Dent Assoc 2003; 69(10):660)

ANALGESICS
• Only to control/prevent the post operative pain.
• Ibuprofen 400mg is the drug of choice.
• Acetaminophen (max 4gm/24 hrs) is given to
ptnts contraindicated with NSAID’s & aspirin.

Tracing the sinus tract :
• Any sinus opening present has to be traced – this will direct the clinician to which tooth sometimes more specifically which root is the source of the infection
• A size#25 G.P cone is threaded into the opening of the sinus tract
• The cone should be inserted until a resistance is felt
• This may be slightly uncomfortable for the ptnt
• A periapical radiograph is taken

• The termination of the G.P cone shows the path taken
by the sinus tract from the opening to the source.

Advanced Pathway OF AAA or
SEQUELAE
Steven R. Singer, DDS


OSTEOMYELITIS
• Inflammation of the bone
• May spread to involve:
– Marrow
– Cortex Periosteum
– Cancellous portion
• Caused by pyogenic organisms from abscessed
teeth, trauma, or surgery
• Source of infection can not always be identified

• Paraesthesia of the lip may be present, suggesting
a malignancy
• Bacteria and by-products stimulate an
inflammatory reaction in bone
• Presence of sequestra is a hallmark of
osteomyelitis. These can be seen in both plain
films and CT
• SEQUESTRA : a portion of dead bone which
becomes seperated from the sound portion

Radiagraphic Features
• Location
– The most common location of osteomyelitis of
the jaws is the posterior body of the mandible
– Involvement of the maxilla is rare, perhaps due
to its excellent vascularity
• Borders
– The borders of these lesions are illdefined,
gradually blending into the normal trabecular
pattern

• Effects on adjacent structures
– Surrounding bone may be resorbed or laid down
– May cause resorption of the cortex

Treatment
• Acute Osteomyelitis :– Antibiotics Penicillin, clindamycin, cephalexin,
gentamycin
– Drainage
– Extraction Of the Tooth
– Sequestra should be removed.
• Chronic Ostemyelitis :– Intravenous antibiotics
– Removal of necrotic bone
– Immobilization of jaws
– Hyperbaric oxygen

CELLULITIS▪An edematous inflammation
▪Associated with diffuse spreading invasive micro-organism
throughout connective tissue and facial planes.
▪S/S: Diffuse swelling of facial or cervical tissues.
▪Sequelae of apical abscess that penetrates bone, allowing
the spread of pus along the path of least resistance
between the facial structures.
▪Implies usually the facial planes between muscles of face
and neck.
▪ It may or may not be associated with fever and malaise.
(ingle 6th edition)

• Fortunately these rarely occurs
• Rapidly progressive , painful . Severe discomfort
• Swelling not localized
• Regional lymphadenopathy with tenderness [ sub-
mandibular – cervical ]


Treatment
• Incision & Drainage
• Antibiotics
• Endodontic T/t after drainage
• If NO significant Improvement :
(Life Threatening)
– REVIEW diagnosis & t/t
– Referral for persistent infections
– Referral EVEN for Extra Oral Drainage

Ludwig's angina :
• Rapidly spreads to sublingual and submandibular spaces, bilaterally and almost simultaneously
• The characteristic features are diffuse swelling , pain, fever and malaise
• Swelling is tense and tender with characteristic board like firmness

• Overlying skin is tight and shiny
• Pain and edema limit the mouth opening and cause dysphagia
• Regional lymph nodes are swollen and tender
• Tongue becomes hard and pushed against the soft palate
• Systemic condition gets severe soon
• Airway obstruction can quickly result in asphyxia

Any abscessed tooth has the potential to become a life
threatening situation. Infection of a tooth in the lower jaw
can cause swelling of the cheek and under the jaw bone. If
the swelling under the jaw becomes too advanced,
swallowing and breathing can become critically impaired
(Ludwig's Angina).

Treatment
• REFER immediately…!!