39 - NPTELStress Isobar (or Pressure bulb) Stress contour or a line which connects all points below...
Transcript of 39 - NPTELStress Isobar (or Pressure bulb) Stress contour or a line which connects all points below...

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
39

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Module 3:
Lecture -1 on Compressibility and Consolidation

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Stresses in soil from surface loads; Terzaghi’s 1-D consolidation theory; Application in different boundary conditions; Ramp loading; Determination of Coefficient of consolidation; Normally and Over-consolidated soils; Compression curves; Secondary consolidation; Radial consolidation; Settlement of compressible soil layers and Methods for accelerating consolidation settlements.
Contents

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Stresses in soil from surface loads
An important function in the study of soil mechanics isto predict the stresses and strains imposed at a givenpoint in a soil mass due to certain loading conditions.
This helps to estimate settlement and to conductstability analysis of earth and earth-retainingstructures, as well as to determine stress conditions onunderground and earth-retaining structures

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Idealized stress-strain diagram
Stre
ssStrain
Elastic Plastic
Idealized stress-strain diagram
a
b c
At low stress levels the strainincreases linearly with stress(branch ab), which is the elasticrange of the material.
Beyond a certain stress level thematerial reaches a plastic state,and the strain increases with nofurther increase in stress(branch bc).

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
dxdy
x
y
z
dz
σxxτxyτxz
σzz
τzyτzx
σyyτyx
τyz
Normal and shear stresses in Cartesian coordinate system
An elemental soil mass with sides measuring dx, dy, and dz: Parameters σxx σyy, and σzz
are the normal stressesacting on the planes normalto the x, y, and z axes (Considered positive when they
are directed onto the surface)(If τij is a shear stress, it means thestress is acting on a plane normal to thei axis, and its direction is parallel to thej axis.)
For equilibrium:

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Equations of static equilibrium
dxdy
x
y
z
dz
τxy +

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Equations of static equilibriumAlong x-direction:
Along y-direction:

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Equations of static equilibrium
The last term of the preceding equation is the self-weight of the soil mass.
Thus,
Along z-direction:
These equations are written in terms of total stresses

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Equations of static equilibrium (in-terms of effective stresses)
Thus,
where is the γ′ submergedunit weight of soil.
Note that the shearstresses will not be affectedby the pore water pressure.

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Equations of static equilibrium (2-D)In soil mechanics, a number of problems can be solved by two dimensional stress analysis.
For a weight-less medium (i.e., γ = 0) the equationsof equilibrium are:

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Idealization of the stress–strain relationship
Typical stress–strain relationship
Linearly elastic behaviourbeing assumed between Oand Y′ (the assumed yieldpoint) followed byunrestricted plastic strain (orflow) Y′P at constant stress
⇒ In general, soils are non-homogeneous, exhibit anisotropyand have non-linear stress–strain relationships which aredependent on stress history and the particular stress pathfollowed.

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Elastic–perfectly plastic model
Non-hardening behaviour

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Rigid–perfectly plastic model
If only the collapse condition in a practical problemis of interest then the elastic phase can be omittedand the rigid–perfectly plastic model
Non-hardening behaviour

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Elastic–strain hardening and softening plastic models
In which plastic strain beyond the yield point necessitates further stress increase.
If unloading and reloadingwere to take placesubsequent to yielding inthe strain hardening model(i.e., at stress at new yieldpoint Y′′ > Y′)
An increase in yield stress is acharacteristic of strain hardening. A further idealization is theelastic–strain softening plasticmodel, represented by OY′P′
The plasticstrain beyond the yield point is accompanied by stress decrease.

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
In practice the most widely used solutions are those forthe vertical stress at a point below a loaded area onthe surface of a soil mass.
The vertical stress increment at a given point belowthe surface due to foundation loading is insensitive toa relatively wide range of soil characteristics such as:
heterogeneity,
anisotropy and
non-linearity of the stress–strain relationship.
Stresses in soil from surface loads

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Stresses in soil from surface loads Accordingly, solutions from linear elastic theory, in
which the soil is assumed to be homogeneous andisotropic, are sufficiently accurate for use in mostcases.
The main exceptions are loose sands and soft clays,particularly where they are overlain by a relativelydense or stiff stratum.
However, that increments of horizontal stress and ofshear stress are relatively sensitive to soilcharacteristics

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Stresses in soil from surface loads Displacement solutions from elastic theory can be usedat relatively low stress levels.
Requires a knowledge of the values of Young’s modulus(E) and Poisson’s ratio (ν) for the soil, either for un-drainedconditions or in terms of effective stress.It should be noted that the shear modulus (G), where
G is independent of the drainage conditions, assumingthat the soil is isotropic.

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Stresses in soil from surface loads The volumetric strain of an element of linearly elastic material under three principal stresses is given by:
If this expression is applied to soils over the initial part of the stress-strain curve, then for un-drained conditions ∆V/V = 0, hence ν =0.5
If consolidation takes place then ∆V/V > 0 and ν < 0:5 for drainedor partially drained conditions.
(E = 3G)

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Stresses in soil from surface loads The stresses within a semi-infinite, homogeneous, isotropicmass, with a linear stress-strain relationship, due to a pointload on the surface, were determined by Boussinesq in1885. The stresses due to surface loads distributed over a particular area
can be obtained by integration from the point load solutions.
The stresses at a point due to more than one surface load areobtained by superposition.
In practice, loads are not usually applied directly on the surface butthe results for surface loading can be applied conservatively inproblems concerning loads at a shallow depth.

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Stresses due to point load
Variation of vertical stressdue to point load ⇒
Variationof σz with z on the vertical through the point of application of the load Q
Variation of σz with r for three different values of z
Bell shapede.g., Vertical load transferred to the soil from an electrical power line

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Stresses due to point loadStresses at X due to a point load Q on the surface are as follows:
It should be noted that when v = 0.5, σθ = 0

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Stresses due to point load
can be written as:
⇒Expression for σz is independent of elastic modulus(E) and Poisson’s ratio (ν).

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Influence factors for vertical stress due to point load
As r/z ↑ Ip ↓ σz ∞

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Vertical stress distribution along a vertical line
As z increases, r/z ↓ for a constant value of rAs z2 is involved in the denominator of theexpression for σz, first it increases withdepth and attains a maximum value andthen decreases with further increase indepth.
Q
θ = 39°13′50′′
σz, max =
zr 0.0888Q

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
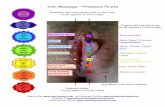
Stress Isobar (or Pressure bulb) Stress contour or a line which connects all points
below the ground surface at which the verticalpressure is the same.
Pressure at points inside the bulb are greater thanthat at a point on the surface of the bulb; andpressures at points outside the bulb are smaller thanthat value.
Any number of stress isobars can be drawn for anyapplied load.
A system of isobars indicates the decrease in stressintensity from the inner to outer ones.
Isobars are Leminscate curves

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Procedure for plotting Isobars
For example, σz = 0.1Q per unit area (10% Isobar)
= 0.1Z2
Z IP r/z r σz0.5 0.025 1.501 0.75 0.1Q
1 0.1 0.9332 0.832 0.1Q
1.5 0.255 0.593 0.890 0.1Q
2 0.40 0.271 0.542 0.1Q
2.185 0.4775 0 0 0.1Q

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
A single concentrated load of 1000 kN acts at theground surface. Construct an isobar for σz = 40 kN/m2
by making use of the Boussinesq equation.
Example Problem
Now for Q = 1000 kN, σz, = 40 kN/m2 , we obtain thevalues of r1 r2, r3 etc. for different depths z1,, z2, z3 etc.The values so obtained are:

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Example Problem

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Westergard stress distribution under a point load
Boussinesq assumed that the soil is elastic, isotropicand homogeneous; However, the soil is neitherisotropic nor homogeneous. The most common typeof soils that are met in nature are the water depositedsedimentary soils
The soils of this type can be assumed as laterallyreinforced by numerous, closely spaced, horizontalsheets of negligible thickness but of infinite rigidity,which prevent the mass as a whole from undergoinglateral movement of soil grains (For this case ν or µ = 0)

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Westergard stress distribution under a point load
(For this case ν or µ = 0)
For r/z = 0; Iw = 1/π = 0.3183

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Values of IB or Iw for use inthe Boussinesq orWestergaard equation
The value of Iw=0.3183 at r/z = 0 (Which is 33% less than Boussinesq IP)
Geotechnical engineersprefer to useBoussinesq's solution asthis gives conservativeresults.

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Vertical stress due to a line loade.g, long brick wall or railroad track
x
z
y ∞
-∞
Series of point loads (~qdy)(From Boussinesq’s solution)

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Vertical stress due to a line load
At x/z = 0 σz = 0.6366q/Z
can be used to estimate the lateralpressure on an earth-retaining structuredue to a line load on the surface of thebackfill.

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Vertical stress due to a line load
However, the structure will tend tointerfere with the lateral strain due to theload q and to obtain the lateral pressureon a relatively rigid structure a secondload q must be imagined at an equaldistance on the other side of thestructure.Then, the lateral pressure is given by
The total thrust on the structure is given by:

Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
Vertical stress due to a Strip load
A strip load is the loadtransmitted by a structureof finite width and infinitelylength of the soil surface.
qs (uniformly applied stress)
qs