15-1: A New Kind of Politics. 1.) Define Missouri Compromise 2.) Describe how the Missouri...
-
Upload
chester-davis -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of 15-1: A New Kind of Politics. 1.) Define Missouri Compromise 2.) Describe how the Missouri...

15-1: A New Kind of Politics

1.) Define Missouri Compromise
2.) Describe how the Missouri Compromise led to the addition of new states.
3.) Analyze how the Missouri Compromise impacted the balance of power in Congress.

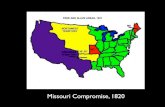
Sectionalism stood out when Missouri applied for statehood…People in the state wanted slavery.
At this time, US had 11 free and 11 slave states, and a new slave state would tilt the balance of power in Congress (pg.380).
Divisions began in the US that reflected the very different economies of the country=
Sectionalism, began to replace nationalism!

Also, Maine applies for statehoodHenry Clay suggests that Maine enter as a free state and Missouri enter as a slave state to keep the balance!
Also, slavery would be banned in the Louisiana Territory north of the 36th parallel.

Won election of 1828 (1829-1837)
Jacksonian Democracy: Everyday people began gaining more
political power.(read aloud page 383 “New Political Era” – today?)

Since the War of 1812 the US gov’t pushed Indians west of the Mississippi River.
No matter how the Indians behaved whites wanted their land.
(Cherokee attempts pg. 384)
1830 Jackson’s Indian Removal Act: Indians must move to public lands west of the Miss. River to reservations.
(today OK state)

2 violent examples 1832 Black Hawk War: Indians try to return to
homeland from Iowa reservation; stopped by Illinois militia!
1835 Seminole Wars: Indians fought for 7 years to stay in Florida homeland; most died, others fled.
1 peaceful example
1832 Cherokee appealed to Supreme Court Justice John Marshall who ruled in favor of the Cherokee that GA had no right to overrule a federal gov’t treaty with the Indians that protected their land.

1838: Jackson sent troops to physically move
15,000 Cherokee to reservations.
The Trail of Tears Cherokees refused to obey the
Indian Removal Act, the US govt sent 7,000 troops, who
forced them out of their homes. The Cherokees didn't even get
a chance to gather their belongings, which were soon
looted by the white settlers that came to claim their land. This
started the Trail of Tears, called such because over 4,000
Cherokee died from the cold and harsh conditions of the trail.
Hunger and disease also claimed quite a few before they
had reached their allotted western lands.


I CAN…I CAN…1.) Define states’ rights1.) Define states’ rights
2.) Explain how states’ rights 2.) Explain how states’ rights continued to divide the countrycontinued to divide the country
3.) Explain the purpose and 3.) Explain the purpose and effects of tariffs enacted before effects of tariffs enacted before
the Civil War the Civil War
I CAN…I CAN…1.) Define states’ rights1.) Define states’ rights
2.) Explain how states’ rights 2.) Explain how states’ rights continued to divide the countrycontinued to divide the country
3.) Explain the purpose and 3.) Explain the purpose and effects of tariffs enacted before effects of tariffs enacted before
the Civil War the Civil War

VP John Calhoun proposed the doctrine of nullificationCongress had no authority to pass
laws that favored one section of the nation over the others When it did, a state had the right to declare that law null and void w/in the state
Another version of states’ rights

Hayne’s views: 1.) Rights of the states came before the
unity of the nation 2.) State could nullify any federal law it
judged to be unfair Webster’s views:
1.) Laws made by Congress were not subject to the approval of each state
2.) Laws represented the will of the people as a whole
Southern states lost the backing of the western states and looked to Pres. Jackson for help Did not get it

Jackson asked Congress to lower the tariff and they did
SC still thought it was too high and voted to nullify itSC said they would secede from the
Union if Congress tried to enforce it Jackson mad but VP Calhoun said each
state chose to join and they could choose to leave
Jackson announces that he will enforce tariffs and send troops to SC if needed
Clay steps in w/ a compromise to gradually lower tariffs over next 10 yrs Jackson signs it into law and SC stays
in Union

15-4 PROSPERITY & PANIC15-4 PROSPERITY & PANIC
Ch15: Ch15: Age of JacksonAge of Jackson 1829-18371829-1837

POLITICAL PARTIESPOLITICAL PARTIES
Dem.Rep. for Jackson Dem.Rep. for Jackson a.k.a. DEMOCRATS a.k.a. DEMOCRATS (Jackson is considered the ‘father’)(Jackson is considered the ‘father’)
• Low tariffsLow tariffs• States rightsStates rights• South/Western South/Western
supportsupport
Dem.Rep. who opposed Dem.Rep. who opposed Jackson a.k.a. Jackson a.k.a. National National REPUBLICANSREPUBLICANS or WHIGS or WHIGS
• High tariffsHigh tariffs• Strong nat’l gov’tStrong nat’l gov’t• NortheastNortheast

Panic of 1837 – next Panic of 1837 – next PresidentsPresidents
Jackson left office under US prosperity.Jackson left office under US prosperity. By year end, under Van Buren, economic By year end, under Van Buren, economic
crisis or Panic of 1837:crisis or Panic of 1837: Paper money value Paper money value Supply of gold and silver Supply of gold and silver Factories and Jobs Factories and Jobs
Dem. Van Buren 1837-1841Whig W.H.Harrison 1841
Whig Tyler 1841-1845… ??
Dem. Polk 1845-1849
Whig Taylor 1849- interesting, huh!

Section 1: The Impact of Section 1: The Impact of ImmigrationImmigration
Section 1: The Impact of Section 1: The Impact of ImmigrationImmigration

1.) Define IMMIGRATION 2.) Define NATIVISTS 3.) Explain how the diverse
peoples of the US developed a common nat’l identify
4.) Explain how immigration changed geographic patterns in the US

One of the largest immigrant groups Did not speak English, but were
educated and came w/ money and skills
Settled along Erie Canal and Great Lakes
Brought a large community of German Jews who settled in the West
Opposed slavery

Moved to the West and the North
Brought deep religious faith and strong sense of community

1845- Irish potato famine caused 1,000’s to leave the country
Most stayed in NY, Boston, and Philly Took jobs that they could get
Lived in crowded shacks and tenements Banded together and joined Democrat
Party Became local political leaders
Heavily involved in Roman Catholic Church

Some native-born Americans saw the newcomers as a threat
Worried that immigrants would take jobs from Americans (sound familiar??)
Some refused to hire immigrants, some got violent, and some formed secret societies
Supreme Order of the Star-Spangled Banner-> “Know-Nothings”-> American Party
Gained support on East Coast w/ anti-immigration platform
Nativism continues today… so does immigration!

16-2 SPIRIT OF REFORM 1820-1860
I Can… explain how diverse peoples of the US developed a common nat’l ID.
I Can… describe historical limitations on participation of women in US society and their efforts to gain equal rights.

Second Great Awakening• A revival of religious faith in the early
1800s – inspired by worries about the future, Americans felt a need to solve new issues/changes and religious preaching’s led to a spirit of reform… it would help solve society’s problems.
[1740, First Great Awakening] • This movement was led by women
within the church.
I Can… explain how diverse peoples of the US developed a common nat’l ID.
I Can… describe historical limitations on participation of women in US society and their efforts to gain equal rights.

American Reform 1820-1860
Work Conditions: Early labor mvmt got a few
health and safety laws – Pres. Van Buren backed a 10 hour work day.
School: Children- a demand for free
and good public education for all children.
Women- at first banned from HS and college, some started going to schools for females.
AA- North; elementary schools for blacks, few going to college. South; illegal to school blacks.
I Can… explain how diverse peoples of the US developed a common nat’l ID.I Can… describe historical limitations on participation of women in US society and their
efforts to gain equal rights.

American Reform 1820-1860
Rehabilitation: Prisoners- organize prisons
to separate types of criminals & men, women and children.
Mentally ill- improve their hospital conditions and care to include specialized institutes.
Temperance: giving up alcohol to improve quality of life.
From sermons to pledges to state laws being passed and then repealed, this mvmt. had power.
I Can… explain how diverse peoples of the US developed a common nat’l ID.I Can… describe historical limitations on participation of women in US society and their
efforts to gain equal rights.
A large group of women and some men gathered outside of Family Groceriesin Waynesville, Ohio during the Women's Temperance Crusade of 1873-1874.
The women were protesting the sale of alcoholic beverages.

Section 3: Call for Equality
I CAN…1.) Define the abolitionist movement
2.) Explain how the abolitionist movement continued to divide the country
3.) Identify Fredrick Douglass and his role in the abolitionist movement
4.) Identify Elizabeth Cady Stanton and her role in the fight for women’s rights

Expanding Democracy
• At this point, most white men can vote– Specifically in direct elections for
gov’t officials– Also in nat’l conventions to choose
party delegates for Pres. and VP•This gave ordinary people a stronger voice in the party nominations

Equality vs. Slavery• Abolitionists: wanted to abolish, or put an end to, slavery• Fredrick Douglass:
– Born a slave– Escaped to Massachusetts– He spoke about his life and against slavery in his
newspaper, “The North Star”• Sojourner Truth:
– Freed slave– One of the first AA women to speak against slavery
• Underground RR:– Informal system moving runaway slaves north with
help from “conductors” through hiding places called “stations”
• Harriet Tubman:– Escaped slave – Most famous conductor who risked over 19 trips
to the South to help free over 300 slaves

Women’s Rights• Elizabeth Cady Stanton and other women
attended int’l conference against slavery yet were silenced by men– Most state laws kept married women as property of the
husband
• Seneca Falls Convention:– 1848 NY meeting of men and women about women’s
rights– Stanton’s speech “Declaration of Sentiments” declared
all men and women were created equal– The Convention called for women’s equality at work,
school, church, plus before the law
• Susan B. Anthony:– Active in Temperance, an Abolitionist, and women’s
rights movement– Most influential leader for women’s suffrage

I Can explain how the diverse peoples of the US developed a common nat’l identity!

A spirit of democracy and equality swept through the country changing attitudes & American life.
By mid 1840’s, American writers were taking pride in their country’s culture. They were creating a unique American philosophy and style. This helped create a common national identity – a New American Culture.

Ralph Waldo Emerson: lectures and writings based on Jacksonian ideals and realities of American life.Emerson taught it was important for people to truly understand themselves to be self-reliant and be able to survive.
His teachings led to a new American philosophy known as
Transcendentalism(a belief or way of life emphasizing human thought and
spirituality
over science and material things) He urged Americans to develop their own way of thinking – no longer based on European influence!
AMERICAN LIT AND ART


Henry David Thoreau: a student of Emerson, he believed in simplicity and living in harmony with nature. He influenced many future world leaders through a practice of passive resistance in refusing to obey unfair laws, peacefully.
AMERICAN LIT AND ART

I Can explain how the diverse peoples of the US developed a
common national identity! 1800’s American Literature and Art
R.W.Emerson’s teachings & writings
Transcendentalism
H.D.Thoreau
Transcendentalism & Slavery
(1820-1855)