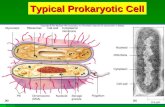
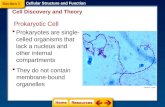
1.2.1 Draw a generalized prokaryotic cell
-
Upload
willis-waters -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
1
description
Transcript of 1.2.1 Draw a generalized prokaryotic cell

1.2.1 Draw a generalized prokaryotic cell as seen in electron micrographs.

1.3.1 Draw a diagram to show the ultrastructure of a generalized animal cell as seen in electron micrographs

1.4.1 Draw a diagram to show the fluid mosaic model of a biological membrane Note: include and label using these names -phospholipid bilayer (point out hydrophilic
head and hydrophobic tail) -cholesterol
-glycoproteins-integral proteins-peripheral proteins
Make sure to use term plasma membrane, not cell surface membrane

2.2.2 Draw the basic structure of a generalizedamino acid
no details about the R group are needed

Glucose
Ribose
2.2.3 Draw the ring structure of glucose and ribose

OCH3------(CH2)n--------C
OH
2.2.4 Draw the structure of glycerol and a generalized fatty acid
*don’t forget the “n” after the (CH2) in the generalized fatty acid (n means, could be any number of that part of the molecule)
Generalized fatty acid

A generalized dipeptide
2.2.4 Draw the structure of a generalized dipeptide, showing the peptide linkage

2.4.5 Draw a simple diagram of the molecular structure of DNA
-show complementary C:G and A:T pairs-identify hydrogen bonds (hold bases together)-number of H-bonds between complementary bases not required-details of base structure not required
Your diagram can be simple, just remember that A and G are double rings; C and T are single rings.Sugar phosphate backbone goes on outside of “ladder”Bases are the “rungs of the ladder”hydrogen bonds between bases are in very center
Key to thispicture:1. hydrogen bonds inPINK2. Bases ingreen andpurple3. Sugarphosphatebackbone inblackPhosphates inyellow

4.1.14 Draw the carbon cycle to show the processes involved.
Be sure to include:-photosynthesis-respiration-fossilization (you could substitute the word “fossilization” for “calcareous sediments” above-combustion (burning of fossil
fuels)
Point is to showinteraction ofliving organismsand the biospherethrough processesof photosynthesis,respiration,fossilization &combustion

4.2.2 Draw a graph showing the sigmoid (S-shaped) population growth curve
*you could use “organisms” or “population size” for the Y axis as well.
*S shape demonstrates that the population starts slow, rises exponentially, then plateaus at the carrying capacity of the environment
*

Topic 5.1.4 Draw a diagram of the digestive system Be sure to include
-mouth -liver-esophagus -pancreas-stomach -gall bladder-small intestine-large intestine-anus
(I have blanked out theitems you don’t need thatwere in this figure)

5.2.1 Draw a diagram of the heart showing all four chambers, associated blood vessels, and valves
Include-all blood vessels connected directly
to the heart-relative wall thickness of chambers
See also: Study guide handouts Page 48 (Page titleis “The Blood System” (given out during unit)

5.5.4 Draw a diagram of the ventilation system including trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and lungsSee also study guide handout (given during unit)page 51, titled “Gas Exchange”

Male
5.7.1 Draw diagrams of the adult male and female reproductive systems see handouts page 54 titled “Reproductive Systems” given during unit
Female

7.1.3 Draw the structure of a mitochondrion as seen in electron micrographs

7.2.1 Draw the structure of a chloroplast as seen in electron micrographs
be sure to include-thylakoid membranes-granum-inner membrane-outer membrane-starch grain-stroma containing 70s ribosomes (dots)-naked dna (dots or small circles)-lipid droplet (large dot in stroma)
chloroplastenvelope

7.2.7 Draw the action spectrum of photosynthesis

immature spermatids
mature spermatids
primaryspermatocyte
spermatogonium
interstitial cells
secondary spermatocyte
9.1.1 Draw the structure of testis tissue as seen using a light microscope
(draw one seminiferous tubule in transverse section with adjacent interstitial cells.
show outer basement membrane, spermatogonia, developing spermatozoa, and sertoli (nurse) cells

9.1.4 Draw the structure of the ovary as seen using a light microscope
-show primary oocytes (primordial follicles)-secondary oocyte in prophase II (preovulatory follicle)-corpus luteum-show also a follicle with egg being released

Acrosome
centrioles
first polar cell
haploid nucleus
cytoplasm (yolk)
corticalgranules
layerof folliclecells
zonapellucida
layerof folliclecells
9.1.6 Draw the structure of a mature sperm and egg. See also handout p 92 titled “Gametes”

motor end plate
11.1.2 Draw the structure of a motor neuron include: dendrites, cell body with nucleus, elongated axon, myelin sheath, nodes of Ranvier, motor end plates

11.2.3 Draw a diagram of the human elbow joint Be sure to include
-cartilage-synovial fluid ( around joint)-tendons-ligaments-bones (ulna)-biceps-triceps
Be able to identify the antagonistic muscle pair (biceps & triceps)See also study guide handout p 102 “Muscles,joints, and locomotion”.

11.2.5 Draw the structure of skeletal muscle fibers as seen in electron micrographs
include & label -sarcomere -dark bands -light bands -sarcoplasm -endoplasmic reticulum
-mitochondria

12.2.1 Draw the structure of the kidney Include
-cortex-medulla-renal pelvis-ureter-renal blood vessels
renal pelvis

12.2.2 Draw the structure of a glomerulus and associated nephron
Nephron

13.1.2 Draw a diagram to show the external parts of a named dicotyledonous plant
include-root, stem, leaf, axillary bud,
terminal bud

vascular bundle
vascularcambium
red=xylemblue=phloem
STEM
epidermis
pithcortex
ROOT
LEAF
stoma
13.1.3 Draw plan diagrams to show the distribution of tissues in stem, root, and leaf of a generalized dicotyledonous plant. (distribution of tissues, no cellular structure)

anther style
filament
ovarysepal
petal
13.3.1 Draw the structure of a dicotyledonous animal-pollinated flower, as seen with the naked eye and hand lens
limit diagram to sepal, petal, anther, filament, stigma, style,
and ovary

13.3.4 Draw the external and internal structure of a named dicotyledonous seed. (non-endospermic)
Include:-testa-micropyle-embryo root (radicle)-embryo shoot (plumule)-cotyledons
testaEXTERNAL
INTERNAL

G.4.5 Draw a diagram of a nitrogen cycleinclude the processes of -nitrogen fixation-denitrification-nitrification-feeding-excretion-root absorption-decay (ammonification)

H.1.4 Draw a diagram of the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland
include: portal vein, neurosecretory cells,hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, posteriorpituitary
posterior pituitary

ducts
secretory cells
acinus
acini
H.2.2 Draw the structural features of exocrine glands including secretory cells grouped into acini and ducts

H.3.1 Draw a portion of the ileum (in transverse section as seen under a light microscope)
Include mucosa, outer longitudinal muscle layer, inner circular muscle
layer, mucosa, and villi.
transverse section drawing
villi
longitudinalmusclelayer
circularmusclelayer
mucosa
lumen
FYI: light microscope section