ميحرلا نمحرلا للها مسب ByCell Injury The morphology of cell and tissue injury...
Transcript of ميحرلا نمحرلا للها مسب ByCell Injury The morphology of cell and tissue injury...

م رحي ل ا لرحمن ا هلل ا سم ب
By:
PhD (Histopathology & Cytopathology), M.BA
(Total Quality Management)
Consultant Medical Laboratory Scientist
Assistant Professor of Histopathology & Cytopathology

Introduction
Pathology is the study of disease
mechanisms.
It is a discipline that bridge clinical
practice and basic sciences, and it
involves the investigation of the
causes (aetiology) of diseases as well
as the under lying mechanisms
(pathogenesis) that result in the
presenting signs and symptoms of the
patients.

Introduction
Pathology concern with the
understanding the structural
(morphology) and functional changes
that occur in the cell, tissues, and
organs so as to render diagnosis and
guide therapy.

Introduction
Traditionally pathology is divided
into: general pathology and systemic
pathology.
General pathology: focuses on the
fundamental cellular and tissue
responses to pathologic stimuli , while
Systemic pathology: examine the
particular responses of specialized
organs.

Cell Injury
Causes of cell injury
The causes of cell injury range from
the gross physical trauma of a motor
vehicle accident to the single gene
defect that result in a defective
enzyme underlying a specific
metabolic disease.
Most injurious stimuli can be grouped
into the following categories:

Cell Injury
Chemical Agents.
Physical Agents.
Infectious Agents.
Genetic Defects.
Aging.
Nutritional Imbalances.
Oxygen Deprivation.

Cell Injury
Chemical Agents
An enormous number of chemical
substance can injure cell such as ;
insecticides, CO, asbestos, ethanol.
These substances can cause severe
damage at the cellular level by
altering membrane permeability.

Cell Injury
Physical Agents
Trauma, extreme of temperatures,
radiations , electric shock, and
sudden change in atmospheric
pressure all have wide range affect on
the cell.

Cell Injury
Infectious Agents
These range from sub-microscopic
viruses to metre long tapeworm.
These organisms can invade the
human body and cause severe cell
injury.

Cell Injury
Genetic Defects
Genetic defects can be conspicuous as
the congenital malformations
associated with Down syndrome or
It may be subtle as the single amino
acid substitution in haemoglobin S
giving rise to sickle cell anaemia.

Cell Injury
Aging
Aging leads to alterations in
replication and repair abilities of
individual cell and tissues.

Cell Injury
Nutritional imbalances
Protein and calorie insufficiency,
vitamins deficiency, and over excesses
of nutrition’s are also important
causes of morbidity and mortality.

Cell Injury
Oxygen Deprivation
Hypoxia; oxygen deficiency, interferes
with the aerobic oxidative respiration
and is an extremely important and
common cause of cell injury and
death.
Ischemia; is loss of blood supply in a
tissue due to impeded arterial follow
or reduced venous supply.

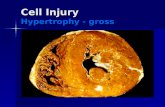
Cell Injury The morphology of cell and tissue injury
(I). Reversible cell injury
The two main morphologic correlates
of reversible cell injury are cellular
swelling and fatty changes.
Cellular swelling: is the result of
failure of energy-dependent ion pump
in the plasma membrane, leading to
an in ability to maintain ionic and
fluid haemostasis.

Cell Injury The morphology of cell and tissue injury
Fatty changes: occurs in hypoxic
injury and various toxic or metabolic
injuries, it is manifested by the
appearance of small and large lipid
vacuoles in the cytoplasm.

Cell Injury The morphology of cell and tissue injury
(II). Irreversible cell injury
Persistent or excessive injury causes
cell to pass (THE POINT OF NO
RETURN) into irreversible cell injury
and death. Although there are no
definitive morphologic or biochemical
correlates of irreversibility, two
phenomenas consistently characterise
irreversibility;

Cell Injury The morphology of cell and tissue injury
The inability to reverse mitochondrial
dysfunction (lack of oxidative
phosphorylation and ATP generation).
Profound disturbances in membrane
function.

The End