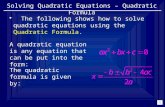
WorkSHEET 9.1 Quadratic graphs Name:© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 16 WorkSHEET 9.1...
Transcript of WorkSHEET 9.1 Quadratic graphs Name:© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 16 WorkSHEET 9.1...

© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 16
WorkSHEET 9.1 Quadratic graphs
Name: ___________________________

© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 17
1 Plot the graph of y = x2 for values of x from
−3 to 3 inclusive. State the equation of the axis
of symmetry and the coordinates of the turning
point.
2 Plot the graph of y = −x2 for values of x from
−3 to 3 inclusive. State the equation of the axis
of symmetry and the coordinates of the turning
point.

© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 18
3 Plot the graph of y = x2 – 1 for values of x from
−3 to 3 inclusive. State the equation of the axis
of symmetry and the coordinates of the turning
point.
4 Plot the graph of y = (x – 1)2 for values of
x from −3 to 3 inclusive. State the equation of
the axis of symmetry and the coordinates of the
turning point.

© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 19
5 Plot the graph of y = (x + 1)2 1 for values of
x from −3 to 3 inclusive. State the equation of
the axis of symmetry and the coordinates of the
turning point.
6 For the equation y = x2 + 2:
(a) state the vertical translation
(b) state the coordinates of the turning point
(c) sketch the curve.

© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 20
7 For the equation y = (x + 2)2:
(a) state the horizontal translation
(b) state the coordinates of the turning point
(c) sketch the curve.
8 Sketch the graph of the following quadratic
equations:
(a) y = 2x2
(b) y = 2
1x
2

© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 21
9 On the same set of axes, sketch the graphs of
the quadratic equations y = x2 and y = −x
2.
10 Sketch each of the following quadratic
equations:
(a) y = −(x – 2)2
(b) y = 2 – x2

© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 23
1 For each of the following graphs, state the
coordinates of the turning point and whether it
is a maximum or a minimum:
(a) y = (x + 3)2 7
(b) y = −(x – 4)2 + 2
2 For each of the following graphs, state the
coordinates of the turning point, whether it is a
maximum or a minimum, and whether it is
narrower or wider than y = x2.
(a) y = 0.2(x – 5)2 4
(b) y = −6(x + 4)2 + 9
3 Describe the translations required to change
y = x2 into:
(a) y = (x – 7)2 + 6
(b) y = (x + 8)2 – 9

© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 24
4 State the equation of each of the following:
(a)
(b)
5 For the equation y = (x – 2)2 + 5:
(a) state the coordinates of the turning point
(b) state whether it is a maximum or
minimum
(c) state the y-intercept
(d) state if it is wider or narrower than y = x2
(e) sketch the curve.

© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 25
6 For the equation y = −(x + 1)2 – 4:
(a) state the coordinates of the turning point
(b) state whether it is a maximum or
minimum
(c) state the y-intercept
(d) state if it is wider or narrower than y = x2
(e) sketch the curve.
7 For the equation y = 2(x 1)2 – 3:
(a) state the coordinates of the turning point
(b) state whether it is a maximum or
minimum
(c) state the y-intercept
(d) state if it is wider or narrower than y = x2
(e) sketch the curve.

© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 26
8 Complete the square on each of the following
to find the equation, and therefore the
coordinates of the turning point:
9102)a( 2 xxy
1113)b( 2 xxy

© John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd Page 27
9 Sketch the graph of y = x2 + 4x + 9 using the
completing the square method to find the
coordinates of the turning point.
10 Sketch the graph of 762 xxy using the
x-intercepts to find the coordinates of the
turning point.