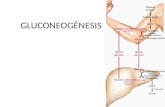
Where on the diagram would the following take place? 1. glycogenesis 2. gluconeogenesis 3....
-
Upload
loreen-white -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Where on the diagram would the following take place? 1. glycogenesis 2. gluconeogenesis 3....

Where on the diagram would the following take place?
1. glycogenesis
2. gluconeogenesis
3. glycogenolysis
Now explain each term.
glycogenesisgluconeogenesis
glycogenolysis

Continue with questions from last lesson. Extra info:
The hepatic portal vein is a blood vessel that conducts blood from the gastrointestinal tract and spleen to the liver. This blood is rich in nutrients that have been extracted from food, and the liver processes these nutrients; it also filters toxins that may have been ingested with the food.
The liver receives about 75% of its blood through the hepatic portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins.

DiabetesWhat is the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes?

What is diabetes?What does this video show?
Some people are unable to regulate their blood glucose levels because their pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or their cells do not respond to it properly. This is called diabetes. Diabetes is a serious condition, but if it is carefully managed diabetics can live normal lives. There are two main types of diabetes – type 1 and type 2.
What do you know about diabetes?

Glucose as an energy sourceGlucose is a type of sugar used by the body to provide energy.
Sometimes there is too much glucose in the blood, and sometimes there is not enough.
eating causes blood glucose levels to rise
vigorous exercise causes blood glucose levels to fall.
The amount of blood glucose therefore needs to be regulated.How does the body do this?
What affects the level of blood glucose?

Blood glucose levelsBlood glucose rises just after eating, but quickly returns to normal.
blo
od
glu
cose
(mg
/100cm
3)
normal
after meal
after vigorous exercise
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
Where does the sugar go, and why is it not left in the blood?

The hormones of the pancreas
Blood glucose levels are controlled by the pancreas.
pancreas
If blood glucose levels are too high, the pancreas releases the hormone insulin. This makes the liver convert glucose into glycogen, which is stored in the liver and muscles.
If blood glucose levels are too low, the pancreas releases the hormone glucagon. This makes the liver convert glycogen into glucose, and release it into the blood.

Maintaining a safe blood glucose level

Key terms

The symptoms of diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes develop quickly and can be severe. Initial symptoms include:
increased thirst, hunger and production of urine
loss of weight, tiredness and nausea.
Later symptoms include vomiting and abdominal pain. If untreated, diabetes can lead to coma and even death.
The lack of insulin control in a diabetic means that blood glucose levels can rise dangerously high after eating, which can cause cell damage.

How does diabetes affect the body?

1.Use the information provided to fill in the table.
2.Use your knowledge and understanding from the passage, plus your textbooks and notes to answer the two questions.

2. too much sugar in the blood and not enough in the cells for energy. Affects water potential and cell stability in terms of structure by osmosis.

Treating type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes develops when the insulin-producing cells in a person’s pancreas are destroyed, and their body cannot produce enough insulin. This means that glucose builds up in their blood. Type 1 diabetes often develops in childhood.
People with type 1 diabetes must inject themselves with insulin before they eat. This helps to keep their blood glucose at a safe level. The amount of insulin needed depends on how much the person eats and how active they are.
The injection is usually into the subcutaneous fat – the fat that is stored directly beneath the skin.

Treating type 2 diabetesType 2 diabetes develops when a person’s body becomes resistant to insulin. This type typically affects people over 40 years old, and accounts for 85–95% of people with diabetes.
Most people with type 2 diabetes can manage their illness through diet and exercise.
Physical activity will reduce the amount of glucose in the blood.
Eating small, regular meals can stabilize blood glucose levels, and avoiding sugary foods can prevent blood glucose levels from rising.

If I am the answer, what is the question?
1. Islets of Langerhan
2. Glycogen
3. Liver
4. Insulin
5. Glucagon
6. Thirsty, hungry, tired
7. Early onset
8. Obesity