What are floaters? What are flashes? - M&S Opticians · 2020. 3. 24. · What are floaters?...
Transcript of What are floaters? What are flashes? - M&S Opticians · 2020. 3. 24. · What are floaters?...

What are floaters?Floaters are small, cloudy particles of various shapes and sizes swimming in the jelly fluid inside the eye called the vitreous. They are especially noticeable when out in the sun or looking at light backgrounds. They move as your eyes move and seem to disappear when you try to look at them directly.
Why do they occur?These spots are often caused by some protein or other matter trapped during the formation of the eyes before birth, or they can be a result of the deterioration of the vitreous due to ageing or certain eye diseases or injuries.
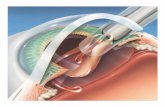
They can occur spontaneously, but tend to occur more frequently as you get older. The gel in the eye (vitreous humour) naturally becomes more liquid and shrinks with time. Sometimes the gel can shrink enough to completely separate from the light sensitive area at the back of the eye (the retina), which can produce a ring shaped floater.
Even though these spots are harmless and do not affect vision, they can be signs of more serious problems such as retinal detachment. Please see overleaf for more information.
What are flashes?You may see a brief flash of light in an arc shape in the extreme corners of your vision normally during the dark, which can come and go. These are different to the shimmering or zigzag lines that might be part of a migraine. These tend to last for about 30 minutes and can be associated with or without a headache.
Why do they occur?These occur when there is a pull on your retina, which is due to the vitreous humour separating from the retina. This can sometimes 'tug' on the retina, causing a brief flash.
Constant flashes, especially if associated with a shadow in the corner of the vision, may be a sign of a retinal tear or retinal detachment (where the retina becomes separated from its underlying layer), which is a rare but serious eye condition which requires immediate treatment to prevent permanent vision loss.
Who is most likely to develop a retinal detachment?Ÿ People with a family history of the conditionŸ Very short-sighted (myopic) peopleŸ People who receive a blow to the eye and/or head
How do I know if I have a problem?Please seek immediate attention at your local eye casualty department if you develop any of the following symptoms:Ÿ A sudden increase or shower of floatersŸ Flashes of light in the corners of your visionŸ A new, large floaterŸ Loss of vision - whether in part or full, like a shadow or curtain spreading
across the visionŸ Change in floaters or flashes after you receive a blow to the eye and/or head
MANDSOPTICIANS.COM MANDSOPTICIANS.COM