Web viewPp. 1-3. What are three ... What do the two parts of the word Homeostasis mean? Homeostasis...
Transcript of Web viewPp. 1-3. What are three ... What do the two parts of the word Homeostasis mean? Homeostasis...

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________The Human Body: An Orientation
Chapter 1 Study GuideAnswer all of the questions in the order they are given. The questions are in order as you read—if you read the chapter, you will find the answers to the questions in the correct order. When I grade study guides, I will grade a certain number of questions each time. If you skip around, you will not do as well because you will miss some of the ones I am going to grade. Usually diagrams count more than other questions—you need to completely draw, color and label diagrams. This is an important part of learning anatomy! Answer in complete sentences unless you are asked to list something.
Pp 1-31. What are three pieces of evidence that humans are naturally curious about our bodies?
a. ______________________________________________________________________
b. ______________________________________________________________________
c. ______________________________________________________________________
2. Define Anatomy
3. What is the difference between grow anatomy and microscopic anatomy?
4. Define Physiology
5. What would a neurophysiologist study?
6. What do the following word parts mean?a. Ana—____________________________
b. –tomy ___________________________
c. Physio—_________________________
d. –ology ___________________________
7. Structure determines what ____________________ can take place in the body. Describe the example given in the book.
Page 1 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________8. Why would you have a hard time learning and understanding physiology if you did not also understand
anatomy?
9. Diagram figure 1.1 on page 3 (its ok if you don’t draw well….show the drawings as best you can and label/define everything that is shown. You can draw a stick figure for the organism if you want
10. What is the simplest level of the human body? _________________
11. What are three examples of molecules in the human body?
a. _________________________ b. ______________________c. _______________________
12. What are the smallest units of all living things?____________________________
13. How many different tissue types exist?____________________
14. At the organ level of organization, extremely ___________________________ functions become possible.
15. Explain how the small intestine is complex as an organ.
Page 2 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________
16. Why is the digestive system an organ system and not an organ?
pp. 3-71. Complete the Table below. Structure means what is the system made of (list some of the major parts),
Function means what it does (list some of the major functions), and location is where does it exist in the body.
System Structure Function Location
Page 72. Like all complex animals, human beings:
a. Maintain __________________________________________
b. __________________
Page 3 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________c. Respond to ________________________________________
d. Take in and _________________________________________
e. Carry out ___________________________________________
f. Dispose of __________________________________________
g. ---------------------------------------------- themselves
h. ________________________________
3. Why do living organisms need to maintain its boundaries?
4. What system encloses the body as a whole?
5. Why is this system necessary?
6. What systems are involved in allowing us to move?
7. Label figure 1.3 below from page 8.
Page 4 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________
8. What does responsiveness mean?
9. What happens in your body if the level of CO2 becomes too high?
Page 910. What is digestion?
11. What is metabolism?
12. How is the process of metabolism and the molecule ATP related to one another?
13. If the body is to continue to operate as we expect it to, it must get rid of the non-useful substances produced during ____________________________ and ________________________________
14. What organ systems participate in excretion and what are their jobs?
15. Explain how reproduction can occur at two different levels.
16. For growth to occur, _______________________________ activities must occur at a faster rate than ____________________________________ ones.
17. What kind of molecule helps to regulate growth?
18. What things do we need to survive?a. ___________________________________
b. ___________________________________
c. ___________________________________
d. ___________________________________
e. ___________________________________
Page 5 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________19. Name the four major groups of nutrients needed in our bodies and the purpose of each.
Nutrient Purpose
20. Why do we need oxygen---how does it work to keep us alive?
21. What is the single most abundant chemical substance in the body?
22. Why do we need so much of this substance?
23. What happens if our normal body temperature drops too much?
Page 121. Where does most of our body heat come from?
2. What is atmospheric pressure?
3. Why do humans need an appropriate atmospheric pressure in order to survive?
4. What do the two parts of the word Homeostasis mean?
5. Homeostasis does not really mean an unchanging state, instead it indicates a ______________________ equilibrium.
Page 6 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________6. What does equilibrium mean?
7. Virtually every _______________________________________ plays a role in maintaining the constancy of the _________________________________________ environment.
8. What is essential within the body in order for homeostasis to occur?
9. What two systems usually regulate homeostasis?
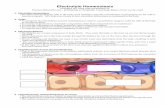
10. Draw, color and label figure 1.4 on page 13.
11. What are the three major parts of all homeostatic control mechanisms?
Page 7 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________12. What is the difference between afferent pathways and efferent pathways?
Page 1313. What are negative feedback systems?
14. Describe a biological example of a negative feedback system.
15. What are positive feedback systems?
16. Describe a biological example of a positive feedback system.
17. What is homeostatic imbalance?
18. When we begin to become dehydrated, we usually get thirsty, which causes us to drink liquids. Is the thirst sensation part of a negative or a positive feedback system? Defend your choice.
Page 141. Why do anatomists use directional terms to help study anatomy?
2. Describe anatomical position.
Page 8 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________3. Complete the table below—YOU MUST PROVIDE YOUR OWN EXAMPLE---NOT THE ONE IN THE
TEXTBOOKTerm Definition Illustration Example
Superior/Cranial/ Cephalad
Inferior/Caudal
Ventral/Anterior
Dorsal/Posterior
Medial
Lateral
Intermediate
Proximal
Distal
Superficial/external
Deep/Internal
Page 9 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________Page 16-18
4. Label figure 1.5 below from page 16.
Page 10 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________
5. Where do each of the anterior body landmarks occur?
6. Where do each of the posterior body landmarks occur?
7. When preparing to look at an internal structure of the boy, medical students make a __________________________.
8. When the section is made through the body wall or through an ____________________ it is made along an imaginary line called a _____________________.
9. Because the body is three dimensional, we can refer to three types of __________________ or ________________________ that lie at ______________________ angles to one another.
10. Draw a diagram below that shows a median or midsagittal section.
11. Draw a diagram below that shows a frontal or coronal plane.
12. Draw a diagram below that shows a transverse plane.
Page 11 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________13. Describe each of the following:
a. Sagittal section
b. Midsagittal or median section
c. Frontal or coronal section
d. Transverse or cross section
14. What kind of technology would be used to view body organ positioning?
Page 19-2015. What are the two parts of the dorsal body cavity?
16. Where is the ventral body cavity?
17. What are the subdivisions of the ventral body cavity?
18. What region separates the lungs into right and left cavities?
19. What cavity is inferior to the diaphragm?
20. Which body cavity is most vulnerable to physical trauma in a car wreck? ______________________ Explain why.
Page 12 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________
21. The abominopelvic cavity is divided into four _________________________________.
22. Sometimes the abdominopelvic cavity is divided into nine separate ____________________________ by ____________________ planes.
23. Where are each of the following located?a. Umbilical region
b. Epigastric region
c. Hypogastric region
d. Inguinal regions
e. Lumbar regions
f. Hypochondriac regions
24. Label Figure 1.8 below from page 20.
Page 13 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________25. Label Figure 1.9 below from page 20.
26. Describe each of the following:
a. Oral cavity
b. Digestive cavity
c. Nasal cavity
d. Orbital cavity
e. Middle ear cavity
27. If you wanted to separate the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity of a cadaver, which type of section would you make?
28. Of the spinal cord, small intestine, uterus and heart, which are in the dorsal body cavity?
Page 14 of 15

Name: _____________________________Date: ___________ Class: ________ Seat: ________Page 10-11
1. Explain how an x ray works.
2. What is nuclear medicine?
3. What is a CT scan?
4. Explain how a CT scan works.
5. What is DSR and what is it used for?
6. What is DSA and what is it used for?
7. What is PET and what is it used for?
8. What is ultrasound imaging and what is it used for?
9. What is MRI and what is it used for?
10. What is MRS and what is it used for?
11. What is fMRI and what is it used for?
Page 15 of 15