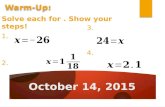Warm Up/Homework
description
Transcript of Warm Up/Homework

Warm Up/HomeworkWarm Up/Homework What is the difference between structure and What is the difference between structure and
function?function?
Homework: QUIZ on Vocabulary from pages Homework: QUIZ on Vocabulary from pages 60-7560-75
IB Word of the Week: “THINKER” Can you IB Word of the Week: “THINKER” Can you connect what you thing you knowconnect what you thing you know

What is the difference between What is the difference between structure and function?structure and function?
Structure makes reference to how something is Structure makes reference to how something is made (materials its made of/how it looksmade (materials its made of/how it looks
Function makes reference to what a particular Function makes reference to what a particular thing DOES! Function is the item job or rolething DOES! Function is the item job or role

CellsCellsS7L2 Students will describe the structure and function of S7L2 Students will describe the structure and function of
cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems.cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems.
..b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm,
chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic cell functions.chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic cell functions.c. Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into c. Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems, and systems into organisms.organs, organs into systems, and systems into organisms.
d. Explain that tissues, organs, and organ systems serve the d. Explain that tissues, organs, and organ systems serve the needs cells have for oxygen, food, and waste removal.needs cells have for oxygen, food, and waste removal.

CellsCells All Living things have certain characteristics:All Living things have certain characteristics:
Use EnergyUse Energy Cellular OrganizationCellular Organization
Unicellular or MulticellularUnicellular or Multicellular Contain Similar ChemicalsContain Similar Chemicals
Lipids, Proteins, Carbohydrates and Nucleic AcidsLipids, Proteins, Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids

Cells: Its Alive!Cells: Its Alive! Grow and DevelopGrow and Develop
Development is the process of change that occurs Development is the process of change that occurs during an organisms life, makes a more complex during an organisms life, makes a more complex organismorganism
Respond to Their SurroundingsRespond to Their Surroundings StimulusStimulus ResponseResponse
Can ReproduceCan Reproduce

CellsCells There are some There are some basic needsbasic needs that all living things have: that all living things have: EnergyEnergy
AutotrophAutotroph: an organism that makes its own food: an organism that makes its own food HeterotrophHeterotroph: an organism that can not make its own food: an organism that can not make its own food
WaterWater
Living SpaceLiving Space
Stable Internal ConditionsStable Internal Conditions Homeostasis:Homeostasis: the maintenance of stable internal conditions despite the the maintenance of stable internal conditions despite the
changes in the surroundings.changes in the surroundings.

CellsCells Cell Theory:Cell Theory:
All living things are All living things are made up of cellsmade up of cells
Cells are the basic unit Cells are the basic unit and structure and and structure and function of all living function of all living thingsthings
All cells are produced by All cells are produced by other cells.other cells.
Spontaneous GenerationSpontaneous Generation::
The mistaken idea that The mistaken idea that living things arise from living things arise from nonliving sources.nonliving sources.

Cells: Its Alive!Cells: Its Alive! What is the difference What is the difference
between the Cell Wall between the Cell Wall and the Cell Membrane?and the Cell Membrane?
Cell WallCell Wall Cell MembraneCell Membrane

Cells: Its Alive!Cells: Its Alive! What is the function of the cell What is the function of the cell
wall?wall? The cell wall has a rigid layer The cell wall has a rigid layer
of nonliving material that of nonliving material that surrounds the cell of plants and surrounds the cell of plants and some other organisms.some other organisms.
The cell wall helps protect the The cell wall helps protect the cell and give it structure and cell and give it structure and support.support.

Cells: Its Alive!Cells: Its Alive! What is the Cell Membrane?What is the Cell Membrane? In some organisms, once you pass through the In some organisms, once you pass through the
cell wall there next structure is the cell cell wall there next structure is the cell membrane.membrane. The cell membrane is the “gatekeeper” of the cell; The cell membrane is the “gatekeeper” of the cell;
it regulates what materials enter and exit the cell.it regulates what materials enter and exit the cell.

Describe the Cell MembraneDescribe the Cell Membrane Cell membranes contain lipids, proteins and Cell membranes contain lipids, proteins and
phospholipids.phospholipids. Some of the proteins and lipids control the Some of the proteins and lipids control the
movement of items in or out of the cellmovement of items in or out of the cell Cell membrane has 2 layers of lipidsCell membrane has 2 layers of lipids
Hydrophobic- inner part, contain lipid tails that are Hydrophobic- inner part, contain lipid tails that are “water fearing”“water fearing”
Hydrophilic- Phospholipid head “water loving”Hydrophilic- Phospholipid head “water loving”

Cells: Its Alive!Cells: Its Alive! What significant role does the nucleus play?What significant role does the nucleus play?
The nucleus is the “control center” of the cell; or The nucleus is the “control center” of the cell; or perhaps the “brain” of the cell. perhaps the “brain” of the cell.
The nucleus directs all the activities of the cell.The nucleus directs all the activities of the cell.
The nucleus is also where genetic material can be The nucleus is also where genetic material can be found. (DNA an RNA)found. (DNA an RNA)

Explain the structure of the NucleusExplain the structure of the Nucleus The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that
contains the cell’s DNA. DNA contains the information on how to make a cell’s proteins.
Messages for how to make proteins are copied from the DNA. These messages are then sent out of the nucleus through the membranes.
The nucleus is covered by two membranes. Materials cross this double membrane through pores.

RibosomesRibosomes Organelles that make proteins are called
ribosomes. Unlike most organelles, ribosomes are not covered by a membrane.
Proteins are made of organic molecules called amino acids. All cells need proteins to live. All cells have ribosomes.

Endoplasmic RectiuculumEndoplasmic Rectiuculum The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a system
of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other materials are made.
The ER is part of the internal delivery system of the cell. Substances move through the ER to different places in the cell.

Endoplasmic RectiuculumEndoplasmic Rectiuculum• Endoplasmic reticulum is either rough ER or
smooth ER. • The part of the ER covered in ribosomes is
rough ER. • ER that lacks ribosomes is smooth ER.

What is the function and structure of What is the function and structure of the Mitochondriathe Mitochondria
• A mitochondrion is the organelle in which sugar is broken down to produce energy. Mitochondria are the main power source of a cell.
• Mitochondria are covered by two membranes, as shown at right.

What is the function of ChloroplastWhat is the function of Chloroplast
• Chloroplasts are organelles in plant and algae cells in which photosynthesis takes place.
• Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and algae use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make sugar and oxygen.

ChloroplastsChloroplasts• Chloroplasts are
covered by two membranes, as shown at right.

Describe the function of the Golgi Describe the function of the Golgi ComplexComplex
• The organelle that packages and distributes proteins is called the Golgi complex. The Golgi complex modifies lipids and proteins to do different jobs.

Golgi ComplexGolgi Complex• Final products are
enclosed in a piece of the Golgi complex membrane, which pinches off to form a small bubble.