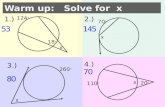
Warm Up Find each product. 1. ( x – 2)(2 x + 7) 2. (3 y + 4)(2 y + 9)
description
Transcript of Warm Up Find each product. 1. ( x – 2)(2 x + 7) 2. (3 y + 4)(2 y + 9)

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
Warm Up
Find each product.
1. (x – 2)(2x + 7)
2. (3y + 4)(2y + 9)
3. (3n – 5)(n – 7)
Find each trinomial.4. x2 +4x – 325. z2 + 15z + 366. h2 – 17h + 72
6y2 + 35y + 36
2x2 + 3x – 14
3n2 – 26n + 35
(z + 3)(z + 12) (x – 4)(x + 8)
(h – 8)(h – 9)

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
Simplify and write the
answer in scientific notation
10
35 10

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
Factor quadratic trinomials of the form ax2 + bx + c.
Objective

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
In the previous lesson you factored trinomials of the form x2 + bx + c. Now you will factor trinomials of the form ax + bx + c, where a ≠ 0.

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
2Factor 2 7 3x x
22x
3
26x
7x6x x
6x
x
2x
x
3
1
2 1 3x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
Factor 6x2 + 11x + 4
26x
4
224x
11x8x 3x
8x
3x
2x
3x
4
1
2 1 3 4x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
6x2 + 11x + 3
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
26x
3
218x
11x9x 2x
9x
2x
3x
2x
3
1
3 1 2 3x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
3x2 – 2x – 8
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
23x
8
224x
2x4x6x
4x
6x
3x
x
2
4
3 4 2x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
2x2 + 17x + 21
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
22x
21
242x
17x3x14x
3x
14x
2x
x
7
3
2 3 7x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
3x2 – 16x + 16
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
23x
16
248x
16x4x12x
4x
12x
3x
x
4
4
3 4 4x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
6x2 + 17x + 5
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
26x
5
230x
17x2x15x
2x
15x
3x
2x
5
1
3 1 2 5x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
9x2 – 15x + 4
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
29x
4
236x
15x3x12x
3x
12x
3x
3x
4
1
3 1 3 4x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
3n2 + 11n – 4
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
23n
4
212n
11n
n12n
n
12n
3n
n
4
1
3 1 4n n

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
2x2 + 9x – 18
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
22x
18
236x
9x3x12x
3x
12x
2x
x
6
3
2 3 6x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
4x2 – 15x – 4
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
24x
4
216x
15xx16x
x
16x
4x
x
4
1
4 1 4x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
6x2 + 7x – 3
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
26x
3
218x
7x2x9x
2x
9x
3x2x
3
1
3 1 2 3x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
–2x2 – 5x – 3
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
22x
3
26x
5x2x3x
2x
3x
x2x
3
1
1 2 3x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
–6x2 – 17x – 12
Place the quadratic and constant terms in
opposite corners of a 2 x 2 square.
Place the product of these terms in the
upper quadrant of a 2 x 2 diamond. Place the
linear
Step 1:
Step 2
term of
:
the trinomial in the lower quadrant
of your 2 x 2 diamond.
Fill in the left and right quadrants of
your diamond with linear terms whose product is
the upper quadrant of the diamond and whose
sum
Step
is t
3:
he lower quadrant of the diamond.
Use the left and right quadrants of your
diamond to fill in the remaining cells of your square.
Determine the factors of each cell of
your 2
Step 4:
Step 5:
x 2 square.
Ste The sum of these factors make up the
binomial factors of your trino
p 6:
mial.
26x
12
272x
17x8x9x
8x
9x
3x2x
3
4
3 4 2 3x x

Holt Algebra 1
8-4 Factoring ax2 + bx + c
HW pp.552-554/25-69 odd,75-81,83,90-96