Visual pathway kHem
-
Upload
khemchand-sahu -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
169 -
download
4
Transcript of Visual pathway kHem

VISUAL PATHWAY& PUPILLARY REFELEXES
Presented By:Khemchand SahuMBBS Final Part I
Guided By:Dr. Divya Verma
Asst. ProfessorDept. of Ophthalmology
Lt. Shri Lakhiram Agrawal Memorial Medical College, Raigarh

Visual Pathway 2
Contents• Anatomy & Physiology of Visual Pathway• Lesions of the Visual Pathway• Pupillary Reflexes• Abnormalities of Pupillary Reflexes
28/11/2016

Visual Pathway 3
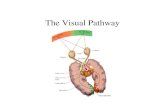
Visual Pathway• Visual pathway or Optic Pathway is the nervous
pathway that transmits impulses from retina to visual center in cerebral cortex
• Components• Optic Nerve• Optic Chiasma• Optic Tract• Lateral Geniculate Bodies• Optic Radiations • Visual Cortex
28/11/2016

Visual Pathway 428/11/2016

Visual Pathway 528/11/2016

Visual Pathway 6
OPTIC NERVE• 2nd cranial nerve• Extent : optic disc to optic chiasma• 47-50 mm• Formation
• Axons of ganglionic cells of retina
28/11/2016

Visual Pathway 7
• Parts of Optic Nerve• Intraocular part• Intraorbital part• Intracanalicular part• Intracranial part
28/11/2016

• Intraocular part• 1 mm• Starts from optic disc, pierces the choroid & sclera,
converting it into sieve like structure Lamina Cribrosa
• Intraorbital part• 30 mm• From back of the eyeball to optic foramina• Relation
• Ant : Seperated from the ocular muscle by the orbital fat• Post : Closely surrounded by Annulus of Zinn
• Retro bulbar Neuritis : Painful ocular movements

Visual Pathway 9
• Intracanalicular part• 6-9 mm in length• Lies within the optic canal• Relation
• Inferolateral : Ophthalmic artery• Medial : Ethmoid & Post. Ethmoid Sinus
• Intracranial part• 10 mm• Lies above the cavernous sinus
28/11/2016

Visual Pathway 10
OPTIC CHIASMA• Flattened structure• 12 mm horizontally, 8
mm anteroposteriorly• Lies over tuberculum
& diaphargma sellae• Fibers originating
from nasal halves of the retina decussate at the chiasma
28/11/2016
OpticChiasma

Visual Pathway 11
OPTIC TRACT• Cylindrical bundle of
nerve fibers• Runs outward &
backward from posterolateral aspect of optic chiasma
28/11/2016
OpticTract

Visual Pathway 12
LATERAL GENICULATE BODY• Oval structure• Situated at posterior termination of optic tract• Each geniculate body consists of 6 layers of
neurons (Grey Matter) alternating with white matter
28/11/2016
Lateral Geniculate
Body

Visual Pathway 13
OPTIC RADIATION• 3rd order neuron• Extend from lateral geniculate body to visual
cortex
28/11/2016
Optic Radiation

Visual Pathway 14
VISUAL CORTEX• Location : medial aspect of occipital lobe, above
and below calcarine fissure• Areas• Primary Visual Area (Area 17)
• Perception of visual impulses
• Secondary Visual Area (Area 18)• Interpretation of visual impulses
• Occipital Eye field (Area 19)• Concerned with movement of eye ball
28/11/2016

Visual Pathway 15
Blood Supply of Optic Nerve Head• Surface Layer : capillaries
from retinal arterioles• Prelaminar region : Vessels of
peripapillary choroid & lamina cribrosa
• Lamina Cribrosa : posterior ciliary arteries, areterial circle of zinn
• Retrolaminar part– Centrifugal branches of central
retinal artery– Centrifugal branches from Pial
plexus
28/11/2016

LESIONS OF VISUAL PATHWAY

Lesions of Visual Pathway 1728/11/2016

Lesions of Visual Pathway 18
OPTIC NERVE LESION• Causes
• Optic atrophy• Traumatic avulsion of optic nerve• Indirect optic neuropathy• Ischemic optic neuropathy• Acute optic neuritis
• Clinical features
28/11/2016
Proximal Optic Nerve Lesion Distal Optic Nerve Lesion
•Ipsilateral Blindness•Contralateral hemianopia•Abolition of direct light reflex on affected side & consensual on contralateral side•Near reflex is intact
•Ipsilateral blindness•Abolition of direct light reflex on affected side & consensual on contralateral side•Near reflex is intact

Lesions of Visual Pathway 19
CHIASMAL LESION• Causes– Intrinsic
• Gliomas• Multiple sclerosis
– Extrinsic : compressive lesion• Pituitary adenoma• Craniopharyngiomas• Meningiomas
– Other• Metabolic• Toxic• Inflammatory
28/11/2016

Lesions of Visual Pathway 20
Clinical feature of chiasmal lesion
• CHIASMAL SYNDROME
28/11/2016
Anterior Chiasmal Syndrome
Affected part : Ipsilateral Optic Nerve fiber & Contralateral inferonasal fiber
Junctional Scotoma
Middle Chiasmal Syndrome
Affected part : Decussating fibers in the body of chiasma
Bitemporal hemianopia
Posterior Chiasmal Syndrome
Affected part : Caudal fiber
Paracenbitemporal field defectHomonymous hemianopia on
contralateral side

Lesions of Visual Pathway 21
• LATERAL CHIASMAL LESION• Causes• Distension of 3rd ventricle• Atheroma of the carotid or posterior
communicating arteries
• Features• Binasal Hemianopia
28/11/2016

Lesions of Visual Pathway 22
OPTIC TRACT LESION• Causes• Intrinsic• Demyelinating diseases• Infarction
• Extrinsic• Pituitary adenoma• Craniopharyngioma
• Others• Syphilitic meningitis• Tubercular meningitis
28/11/2016

Lesions of Visual Pathway 23
• Clinical Feature• Incongruous Homonymous Hemianopia• Wernicke’s reaction• Optic disc changes• Descending partial optic atropy : temporal pallor on
side of lesion & bow-tie atrophy on contralateral side
28/11/2016

Lesions of Visual Pathway 24
LESION OF LATERAL GENICULATE BODY• Features• Homonymous Hemianopia• Normal pupillary reflexes• Optic disc pallor due to partial descending
atrophy
28/11/2016

Lesions of Visual Pathway 25
LESION OF OPTIC RADIATION
• Causes• Vascular occlusion• Tumor• Trauma• Temporal lobectomy
28/11/2016

Lesions of Visual Pathway 26
• Features
Visual Field Defect
Superior Quadrantic Hemianopia
Inferior fibers
involved
Inferior Quadrantic Hemianopia
Superior fibers
involved
Complete Homonymous Hemianopia
Total fiber of optic radiation
involved
28/11/2016

Lesions of Visual Pathway 27
LESION OF VISUAL CORTEX• Causes• Occlusion of posterior cerebral artery• Head injury
28/11/2016

Lesions of Visual Pathway 28
• Visual Field Defect• Congruous Homonymous
hemianopia (sparing the macula)
• Congruous Homonymous Macular defect
• Bilateral Homonymous macular defect
• Bilateral Homonymous Hemianopia with macula sparing
• Other Manifestation• Cortical Blindness• Dyschromatopsia• Visual Hallucination• Palinopsia• Polyopsia
Features
28/11/2016

PUPILLARY REFLEXES

Pupillary reflexes 30
LIGHT REFLEX• When light is shone in one eye both the pupils
constricts.• Two Types:• Direct Light Reflex• Indirect (Consensual) Light Reflex
• Constriction of pupil to which light is shone : Direct Light Reflex and that of other : Indirect Light Reflex
28/11/2016

Pupillary reflexes 31
Afferent Fiber
From retina to pretectal nucleus
28/11/2016
Pathway of light Reflex

Pupillary reflexes 3228/11/2016

Pupillary reflexes 33
NEAR REFLEX• Occurs on looking at near object• Two components• Convergence Reflex : Contraction of pupil on
convergence• Accommodation Reflex : Contraction of pupil associated
with accommodation
28/11/2016

Pupillary reflexes 34
Pathway of Near Reflex
28/11/2016

Pupillary reflexes 35
PSYCHOSENSORY REFLEX• Dilatation of pupil in response to sensory &
psychic stimuli
28/11/2016

Pupillary reflexes 36
EXAMINATION OF PUPILLARY REFLEXES
• Direct Light Reflex• Normal pupil reacts briskly &
its constriction to light is well maintained
• Consensual Light Reflex• Normally contralateral pupil
should also constrict when light is thrown on to one pupil
28/11/2016

Pupillary reflexes 37
• Swinging Flash Light Test• Performed when relative
afferent pathway defect is suspected in one eye
• Normally, both pupil constrict equally & pupil to which light is transferred is tightly constricted
• MARCUS-GUNN Pupil
28/11/2016
• Near Reflex• Pupil constrict while looking at near object

Pupillary reflexes 38
ABNORMALITIES OF PUPILLARY REACTIONS
• AMAUROTIC LIGHT REFLEX• Absence of
• Direct light reflex on affected side• Consensual light reflex on normal
• Lesion : Optic Nerve, Retina of affected side
28/11/2016
• EFFERENT PATHWAY DEFECT• Absence of
• Both direct & consensual light reflex on affected side
• Presence of• Both direct & consensual light reflex on normal side
• Cause : Sphincter paralysisParasympatholytic Drug (Atropine)IIIrd nerve paralysisInternal Ophthalomoplegia
AMAUROTIC PUPIL

Pupillary reflexes 39
• WERNICKE’S HEMIANOPIC PUPIL• Light reflex is ABSENT
• When light is thrown on temporal half retina of affected side & nasal half of opposite side
• Light reflex is PRESENT• When light is thrown on nasal half of affected side & temporal half of
opposite side
• Lesion of optic tract
• MARCUS-GUNN PUPIL• Seen in Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD)• Affected pupil will dilate when light is moved from normal to
abnormal eye• Earliest indication of optic nerve disease• Cause : Incomplete optic nerve lesion, Severe retinal disease• Test : Swinging Flash Light Test
28/11/2016

Pupillary reflexes 40
• ARGYLL ROBERTSON PUPIL (ARP)• For both pupil• Reaction to near reflex : Present• But light reflex : Absent
• Both pupil slightly small in size• Cause – Neurosyphilis in region of tectum
28/11/2016

Pupillary reflexes 41
• ADIE’S TONIC PUPIL• Reaction to
• Light reflex : Absent• Near reflex : Very slow & tonic
• Affected pupil is larger (Anisocoria) initially• Cause : Postganglionic parasympathetic pupillomotor damage• Constricts with weak Pilocarpine (0.125%), while normal does not
28/11/2016

Pupillary reflexes 42
ANISOCORIA
• Normal size pupil : 3-4 mm• Difference between size of two pupil is called
Anisocoria • Causes• Physiological • Pathological
• Difference of 2 mm or more
28/11/2016

Pathological Anisocoria
Abnormal Miosis
Iridocyclitis
Horner Syndrome
Parasympathomimetic Drug
Mydriasis
Parasymapatholytic Drug
Retinal Glaucoma
3rd nerve Paralysis

Pupillary reflexes 44
• Evaluation of Anisocoria• Pupil Size• Anisocoria in dark & bright illumination :
Physiological• Anisocoria greater in dim illumination : Horner
Syndrome
• Pupillary Light Reflex• Normal light reaction followed by dilatation lag :
Horner Syndrome• Poor light reaction : Parasympathetic System Defect
(3rd nerve palsy, tonic pupil, anti-cholinergic drug)
28/11/2016

Pupillary reflexes 45
– Pharmacological Test :
28/11/2016
For suspected parasympathetic palsy : PILOCARPINE TEST
Pupil Constrict to low conc. of pilocarpine (0.125%)• Adie’s Tonic Pupil
Pupil Constrict to usual conc. of pilocarpine (1-2%)• 3rd nerve palsy
Pupil does not constrict to pilocarpine• Pharmacological mydriasis

46
…tHANK yOU28/11/2016