Unit 3: Microscopes, cells and Viruses · scanning tunneling electron microscope (STM)-involves...
Transcript of Unit 3: Microscopes, cells and Viruses · scanning tunneling electron microscope (STM)-involves...

Unit 3: Microscopes, cells
and Viruses
pp. 191-200

Modern Microscopes
Compound light microscope
– Contain more than one
______ and uses _________
bent through _________ to
magnify objects. Type of
microscope used in the
classroom, ours magnifies up
to 430 times, others can
magnify up to a 1000 times
lens light rays
glass

Electron microscope –
Uses magnets to aim a
beam of ________ at thin
slices of cells. . Offers the
advantage of much greater
____________. There are
4 types of electron
microscopes:
scanning electron
microscope or SEM -
traces the ___________ of
the specimen and forms a
3D image
electrons
magnification
surface

transmission electron
microscope or TEM - aims
electron beam through
specimen. Used to examine
____________cell
structures. Can magnify up
to 500,000X
Disadvantages of these two:
specimen must be kept in a
____________; therefore
must be
____________________
internal
vacuum
dead

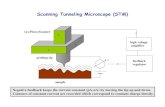
scanning tunneling electron microscope
(STM)- involves bringing the charged tip of a
probe extremely close to the specimen so that
the electrons “tunnel” through gaps between
the specimen & the tip. Can create 3D
computer images of objects as small as atoms
& can be used on living specimens.
• atomic force microscope (AFM)- measures
various forces between the tip of a probe and
the cell surface. Creates a visual image of a cell
using a microscopic sensor that scans the cell

What about Viruses? Are They Alive?
Based on what we learned in Unit 1, viruses would
be considered non-living because they do not
exhibit all the characteristics of life:
• Do not contain____________ for ____________
• Not made of ________; lack a ______________
• Do contain______________________________
• Cannot _____________ without a ________ cell
• Typically referred to as a ______________ or
__________
enzymes metabolism
cells Cell membrane
Genetic material
reproduce host
particle
virion

Structures of Viruses
The following structures are found in all
viruses:
• Genetic material- The genome of a virus
may be either ____ or ____, but never both.
It can be ____________ or
________________, _________________
or ____________.
DNA RNA
Single-stranded
Double-stranded circular
linear

• Protein coat- The DNA or RNA is
surrounded by a protein coat called a
capsid. The proteins making up the
capsid are known as ___________ and
play an important role in the
_____________ of the virus. In addition,
the capsid has ___________ ID tags
known as _______________ which can
__________ to enable the virus to escape
detection by a host cell’s immune system.
capsomeres
pathogenicity
carbohydrate
glycoprotein
mutate

The following additional structures may be
present:
•Viral envelope- Many viruses have an outer
membrane known as an envelope. A viral particle
“steals” the components for its envelope from the
host cell membrane, so a viral envelope is
primarily composed of _________________. It
aids in the attachment of the virus to the host
cell, but a virus enclosed by an envelope is also
more sensitive to ______________.
phospholipids
drying

• Tail Fibers- Viruses that infect _________
are known as ____________. They have
“tail fibers” to aid in attachment.
• Examples of viruses with envelopes are:
_________________________________
bacteria
bacteriophages
HIV, flu virus, cold virus

The ____________ of surface _______________ on a virus fits
perfectly with the proteins embedded in the host _______
________________. As a result, a virus can only infect certain cell
types of certain species.
proteinsshape
cell
membrane
Phospholipid
envelope
Viral
DNA or
RNA
Protein
capsid
Surface protein or
glycoprotein
Naked
Capsid Virus
Enveloped
Virus

Viral Reproduction
Two ways viruses reproduce using a host cell
• Lytic infection- _____________ cycle in
which viruses ____________ host cell DNA.
Examples are _________________________
___________
• Lysogenic infection - _____________ cycle
in which viral DNA is incorporated into
________________. Examples are
__________________
symptomatic
destroys
Cold, flu, rabies, measles, etc… most
viruses
asymptomatic
Host cell DNA
HIV, chicken pox virus

Viral Reproduction
There are two initial steps that are common
to all types of viral infections:
1.Virus attaches to _____________ of
_____________.
2.Virus releases____________ into cell,
either by _______________ typically
through ____________ or ___________
genetic material into it.
Cell membrane
host
Genetic material
Entering cell
endocytosis injecting

Bacteria
Bacterial make up two kingdoms, the
____________ and ____________. In this
unit, we will focus on the kingdom that has
the greater impact on our lives, the
________.
• _______________&_________________
Archaebacteria Eubacteria
Eubacteria
prokaryotic unicellular

Cell Structures
• Cell wall composed of ________________
– __________________________
• ____________________
– ________________________
– Found in region known as ___________
• ____________________
• ____________________
• ____________________
peptidoglycan
Eubacteria only
DNA
Single, circular chromosome
nucleoid
Cell membrane
ribosomes
Cytosol — “cell gel” or fluid

• Most bacteria are motile and have one or
more ______________.
• Many have hair-like appendages called
_________ that allow bacteria to
________ to surfaces or other _________
• Some bacteria have an outer _________;
helps bacterial cells attach to a substrate
or deter the host’s infection-fighting cells.
flagella
fimbriae
adhere bacteria
capsule

Eukaryotic cell structures

What’s inside a cell?
Cell organelles which means “little organs”
1st a little clarification of a couple of terms:
_______________- includes the
___________ or “cell gel” and the ________
cytoplasm
cytosol organelles

Nucleus
• _____________ of
the cell. Genetic
information stored as
____________, which
is _______wrapped in
________________.
Control center
chromatin
DNA
protein
Found in Both Plants & Animals

Nucleolus
• Small, dense region
in the nucleus. Site of
________________
production
ribosome
Found in Both Plants & Animals

Nuclear Envelope
• Double
_________________
membrane. Has
nuclear ___________
which allow _______
to leave the nucleus
phospholipid
pores
RNA
Found in Both Plants & Animals

Ribosomes
• Tiny, granular
organelles located on
_________________
or suspended in
_________. Site of
_________________.
All cells (pro & euk)
have ribosomes.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
cytosol
protein production
Found in Both Plants & Animals

Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
• Extensive network continuous
with _________________.
Called “rough” because it has
________________ all along
the membrane. Function of the
rough ER is to
_____________________.
Most of these proteins are
packaged into _____________
(like bubbles or sacs) and
shuttled to the ____________
nuclear envelope
ribosomes
modify & transport proteins
vesicles
Golgi apparatus
Found in Both Plants & Animals

Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
• Similar to rough ER in structure, except that it lacks ___________. The smooth ER:
1. manufactures ______, 2. breaks down _______,
3. detoxifies ________, and 4. _____________.
ribosomes
lipidsglycogen
poisons
stores calcium
Found in Both Plants & Animals

Golgi Apparatus• Flattened, round sacs that look like a sack
of ________________. Receives, modifies,
and ships products by way of ___________
into the ____________________________
pancakes
vesicles
cytosol → cell membrane_
Found in Both Plants & Animals

Lysosome
• Found in __________
cells only. Round sacs
containing __________
that _______________
and ______________
used cell components.
Also used as defense
against _______ and
_______________
animal
enzymes
break down
recycle
bacteria
viruses

Vacuole
• Sacs that may be
used as storage for
_______, _________,
_________________,
or wastes. Plants
have a large central
vacuole.
water Salts, proteins
carbohydrates

Mitochondria
• Double-walled
organelle with inner
folds ____________.
____________Uses
_______ to
manufacture energy
in the form of ______.
Mitochondria have
their own _______.
to increase
surface area
glucose
ATP
DNA

Chloroplast
• Found in ______
cells. Contain
__________ (green
pigment) and their
own ______.
Chloroplasts harvest
energy from the ____
to produce ____
through __________.
plant
chlorophyll
DNA
sun
ATP
photosynthesis

Centrioles
• Found in _________
cells only. Bundles of
_________________
that play a role in
_________________
animal
microtubules
cell division

Cytoskeleton• Composed of protein fibers known as _______________
and ______________. Anchor _______________ and
provide ______________. Also provide motility for some
cells in the form of ___________ or ____________. More
extensive cytoskeleton found in __________ cells.
microtubules
microfilaments organelles
structurecilia flagella
animal

Cell walls are the outermost boundary in __________, _______, and ___________.
They are not found in _____________________. The primary function of the cell wall is to provide ___________________________. The cell wall does not regulate what _________________________ the cell.
1. Cell walls of plants are composed of ____________
2. Cell walls of fungi are composed of _____________
Cell Wall
bacteria fungi plants
Animal cells
Structure and support
Enters and leaves
cellulose
chitin

Cell MembraneEvery cell is surrounded by a cell membrane made of
___________________. The cell membrane is
selectively permeable which means
____________________________________________.
This characteristic is critical in helping the cell maintain
_______________. The cell membrane is also called
the ____________________ membrane
Phospholipid bilayer
It only allows certain substances in and certain out.
homeostasis
Plasma