Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
Transcript of Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
1/18
Unit 3 Ch. 9
The Human Population
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
2/18
How do we study the humanpopulation?
Demography study of humanpopulations
Study of historical size andmakeup of populations ofcountries in order to makecomparisons and predictions
2 categories for countries Developed higher average
income, slower birthrate, diverseindustrial economies
Developing lower avg. income,agriculture based economies, rapidpopulation growth
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
3/18
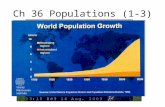
Human population over time
Grew slowly up until 1800
1800s went throughexponential growth
Population growthincreases every decade
Due to increases in foodproduction, betterhygeine, industrial and
scientific revolution Not likely the earth can
sustain this growth
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
4/18
Human population over time
Section 1 Studying Human
PopulationsChapter 9
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
5/18
Forecasting population size
Age structure distribution of ages in a pop shown ina pop pyramid
Survivorship % of members of a group that are likelyto live to a certain age shown with line curves
Fertility rates - # of babies born each year per 1,000women Replacement level avg # of children a parent must
have to replace themselves
Migration movement of individuals between areas
Immigration into Emmigration out of
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
6/18
Population pyramid / Age structure
Chapter 9Section 1 Studying Human
Populations
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
7/18
Declining death rates
Dramatic increase in population in last200 years due to drop in death rates
More access to adequate food, cleanwater, and safe sewage disposal
Life expectancy average number ofyears a member of a population is
likely to live Infant mortality death rate of infants
under 1 year old
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
8/18
The Demographic Transition
Model that describes how economic andsocial changes affect population growthrates (within a country)
Process takes 3 4 generations Stages
1 preindustrial birth rate and death rate arehigh
2 transitional population explosion, death ratelowers due to education, hygiene, nutrition
3 industrial birth rate declines, pop stabilizes Postindustrial birth rate below replacement
level so pop decreases
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
9/18
Demographic Transition
Chapter 9Section 1 Studying Human
Populations
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
10/18
9.2 Changing Population Trends
EQ: How is the world populationchanging? What are problemsassociated with rapid populationgrowth?
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
11/18
Problems of rapid population growth
Overwhelm the infrastructure Infrastructure basic services and facilities that
support a community (water supplies, roads,
sewer lines, schools, etc. ) Symptoms:
Suburban sprawl
Overcrowded schools
Polluted rivers Barren land
Inadequate housing
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
12/18
Problems of pop growth
Resources used faster thanthey can be replenished(vegetation, land andwater)
Fuelwood shortage woodgathered from fallen limbsto burn as fuel - whenpopulation rises trees arecut down for fuel Fuel allows people to boil
water and cook No fuel leads to malnutrition
and disease
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
13/18
Problems of pop growth
Unsafe water in cities where there is noinfrastructure local water source may be usedfor drinking, washing, bathing and sewagedisposal
Water becomes breeding ground fororganisms that cause diseases like cholera,typhoid, and dysentery
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
14/18
Problems cont.
Impacts on land different uses for landare in competition with each other(agriculture, housing, natural habitats)
Arable land used for growing crops Urbanization movement of people from
rural areas to cities for work Suburban sprawl leads to traffic jams,
inadequate infrastructure, and reduction of landfor farms and wildlife
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
15/18
Demographic Diversity in the world
Countries can bedeveloped, developing,more developed, lessdeveloped
Least developedcountries indentified by
UN given priority forforeign aid anddevelopment programs
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
16/18
Managing Development andpopulation growth
Government focus on reducingbirth rates Public advertising Family planning programs
Economic incentives Legal punishments
UN Conference on Populationand Development 1994 pg246 Debates on how to stabilize
population growth A lot of focus on improving
womens status
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
17/18
Growth is slowing
Population is now 6 billion andincreasing
Fertility rates are declining in both
developed and less developed regions Most countries predicted to have
replacement level fertility rates by
2050 UN project med growth rate to a popof 9 billion by 2050
-
8/2/2019 Unit 3 Ch 9 Human Populations
18/18
Closure
How has population growth effectedwest Cobb county?