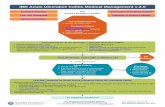
Treatment Algorithms in Ulcerative Colitis Treatment Algorithms in Ulcerative Colitis.
Ulcerative colitis
-
Upload
deepika-vellore-shankar -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
35 -
download
7
Transcript of Ulcerative colitis
ULCERATIVE ULCERATIVE COLITISCOLITIS
BY V.S.DEEPIKA RANIBY V.S.DEEPIKA RANIB.Sc Final yearB.Sc Final year
Erosion in the lining of Erosion in the lining of colon (mucosa and sub colon (mucosa and sub
mucosa)mucosa)
It is characterized by inflammation It is characterized by inflammation and ulceration of colon resulting in and ulceration of colon resulting in frequent passage of stools with frequent passage of stools with blood and mucus.blood and mucus.
It is confined to colon and rectum.It is confined to colon and rectum.
INCIDENCEINCIDENCE unknown cause unknown cause
at any ageat any age
predominates in predominates in middlemiddle
and higher income and higher income
groups.groups.
CAUSESCAUSES
Mental conflicts and emotional stress
Allergy to certain foods
Largely seen in Non smokers and Ex-smokers
Nitric oxide synthesis is increased in Nitric oxide synthesis is increased in U.CU.C
NO is produced from arginine by nitric NO is produced from arginine by nitric oxide synthase.oxide synthase.
U.C is assosiated with increase in U.C is assosiated with increase in mucosal vasodilation.mucosal vasodilation.
CLINICAL FINDINGSCLINICAL FINDINGS
Mucosa becomes fragile.Mucosa becomes fragile. In early stages mucosa is edematous In early stages mucosa is edematous
and hyperemic.and hyperemic. In severe stage, necrosis and frank In severe stage, necrosis and frank
ulceration of mucosa occur.ulceration of mucosa occur.
SymptomsSymptoms
Attack of dysentery.Attack of dysentery. Exacerbations and remissions. Exacerbations and remissions. Loss of water, electrolytes, blood Loss of water, electrolytes, blood
and protein.and protein. Weight lossWeight loss DehydrationDehydration FeverFever AnemiaAnemia Abdominal painsAbdominal pains
AnorexiaAnorexia Metabolic rate is increasedMetabolic rate is increased Liver damageLiver damage Constipation-distal irritability and Constipation-distal irritability and
spasm.spasm.
CAUSES OF NUTRITION CAUSES OF NUTRITION PROBLEMSPROBLEMS
MECHANISMMECHANISM
Decreased nutritional Decreased nutritional intakeintake
Increased nutritional lossesIncreased nutritional losses
Nutritional interference by Nutritional interference by drugsdrugs
CONTRIBUTING CONTRIBUTING FACTORFACTOR
Anorexia, nausea, painAnorexia, nausea, pain, , restrictive/unbalanced restrictive/unbalanced diet.diet.
Malabsorption, intestinal Malabsorption, intestinal
resection, bacterialresection, bacterial over over growth, bile salt growth, bile salt deficiency, drugs.deficiency, drugs.
DiarrheaDiarrhea
BleedingBleeding
Protein-losing enteropathyProtein-losing enteropathy
Intestinal lymphangiectasiaIntestinal lymphangiectasia
Corticosteroids, Corticosteroids, sulfasalazine, sulfasalazine, cholestyraminecholestyramine
NEED FOR NUTRITIONAL NEED FOR NUTRITIONAL CARECARE
MalnutritionMalnutrition insufficient food consumptioninsufficient food consumption excessive nitrogen lossesexcessive nitrogen losses - blood, mucus and necrotic- blood, mucus and necrotic colonic mucosacolonic mucosa -electrolyte loss in feces-electrolyte loss in feces Absorptive areas are destroyedAbsorptive areas are destroyed ulcerations of mucosa and scar tissuesulcerations of mucosa and scar tissues Tissue repair and restore normal Tissue repair and restore normal
functioningfunctioning
DIETARY PRINCIPLESDIETARY PRINCIPLES Individual attentionIndividual attention Diet- highly individualized, nutritionally adequateDiet- highly individualized, nutritionally adequate Small 6 to 8 feedingsSmall 6 to 8 feedings Based up on severity of disease it ranges from Based up on severity of disease it ranges from TPNTPN nasogastric feeding of E.Fnasogastric feeding of E.F oral ingestion of E.Doral ingestion of E.D exclusion of regular foodsexclusion of regular foods fiber supplementationfiber supplementation high fiber diet.high fiber diet.
DIETARY DIETARY RECOMMENDATIONRECOMMENDATION
Chronic U.C Chronic U.C
fistulas, obstruction or fistulas, obstruction or abscesses.abscesses.
TPN TPN
- intestinal atrophy- intestinal atrophy
- invasion of bacteria- invasion of bacteria
Small intestine is not involved.Small intestine is not involved. Oral or Enteral feeding Oral or Enteral feeding
- integrity of intestinal - integrity of intestinal epitheliumepithelium
Prep. – protein concentrate Prep. – protein concentrate
eg. Complan.eg. Complan.
Low residue dietLow residue diet
- high in protein and energy.- high in protein and energy. Exclusion of Irritating foods –nuts, Exclusion of Irritating foods –nuts,
legumes, raw fruits, etc.legumes, raw fruits, etc. In acute U.C – Strict low residue diet In acute U.C – Strict low residue diet
- fecal stasis.- fecal stasis. Fiber content – high fiber diet.Fiber content – high fiber diet. Soluble fibers and pectins Soluble fibers and pectins
Calories : 2000 – 2500 kcalCalories : 2000 – 2500 kcal Proteins : 100 g/dayProteins : 100 g/day
mixed dietmixed diet
high quality protein high quality protein foods foods
eg. tender meats, fish, eg. tender meats, fish, poultry etc.poultry etc.
Carbohydrates : soups, etcCarbohydrates : soups, etc Fats : normalFats : normal
fried foods are not fried foods are not
easily digested.easily digested. Vitamins : commercial prep.Vitamins : commercial prep.
(orally or injections)(orally or injections)
MineralsMinerals
Mineral loss must be marked.Mineral loss must be marked. Unless marked – fatal outcomeUnless marked – fatal outcome Sodium : large volume of fecesSodium : large volume of feces
extra salt in food, saline extra salt in food, saline infusion.infusion.
Potassium : Potassium :
Symptoms- weakness, hypotonia, Symptoms- weakness, hypotonia, abdominal distension, abdominal distension, E.C changes. potassium E.C changes. potassium citrate orallycitrate orally
Iron : 30g/dayIron : 30g/day
oral route if not toleratedoral route if not tolerated
AnemiaAnemia Intra muscular injectionsIntra muscular injections Blood transfusionBlood transfusion Fluids : liberal intakeFluids : liberal intake
1200 – well hydrated 1200 – well hydrated
Calcium : Rapid bone lossCalcium : Rapid bone loss
-milk exclusion -milk exclusion
-steroid therapy-steroid therapy calcium salts – orallycalcium salts – orally
FOODS TO BE AVOIDEDFOODS TO BE AVOIDED
spices, stale foods,spices, stale foods,
irritant foods - legumes, nuts etc.irritant foods - legumes, nuts etc.
Psychological aspects Psychological aspects
They are significantThey are significant Therapy for depression, relaxation Therapy for depression, relaxation
can benefit the patient.can benefit the patient. Exercise is important adjunct.Exercise is important adjunct.
U.C AND CANCERU.C AND CANCER
Constipated patients – lump in right Constipated patients – lump in right colon.colon.
Risk of cancer is increased in cases Risk of cancer is increased in cases lasting more than 7 years.lasting more than 7 years.