Turn in Homework #1 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands · Mt. St. Helens erupted Violently in the...
Transcript of Turn in Homework #1 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands · Mt. St. Helens erupted Violently in the...
-
1
Geology of the Hawaiian IslandsGeology of the Hawaiian IslandsClass 4Class 4
22 January 200422 January 2004
Turn in Homework #1Turn in Homework #1
Any Questions?Any Questions? IMPORTANTIMPORTANTBig Island Field TripBig Island Field Trip
We need aWe need a$162 payment for airfare$162 payment for airfareBEFORE January 29BEFORE January 29thth
Description of logistics, costs, etc., Description of logistics, costs, etc., to be handed out in classto be handed out in class
-
2
Plate Tectonics and the Origin Plate Tectonics and the Origin of the Hawaiian Islandsof the Hawaiian Islands
Hot spots are regions in the Asthenosphere that are hotterthan their surroundings
Molten magma rises to the surface to form volcanoes, similar to what happens at Spreading Centers
Hot spot volcanoes are relatively small, isolated
features.
-
3
Hot spots are believed to be fixedrelative to the mantle.
BUT – this is controversial!
When a plate moves over afixed Hot Spot,
a linear chain of volcanoes is formed.
Our Islands were formed by a Hot Spot
The trail of the Hawaiian Hot Spot goes all the way to the far northwest Pacific
-
4
In addition to the Hawaiian Hot Spot track, there are several others in the Pacific
Note the major bend in theHawaii – Emperor ridge
The bend in the Hawaii-Emperor Ridgewas caused by a change in the
direction of motion of the Pacific Plate relative to the underlying mantle.
The islands (and former islands)of the Hawaii-Emperor Ridgeget progressively older to theNorth. The northern extensionhas been subducted in the Aleutian Trench.
-
5
The Hawaiian Hot Spot is only one of manyHot Spots that are found on the Earth.
Homework #2:Homework #2:How fast does the Pacific PlateHow fast does the Pacific Plate
move over the Hawaiianmove over the HawaiianHot Spot?Hot Spot?
Change Due Date to 29 JanuaryChange Due Date to 29 January
Legend of Legend of PelePele
-
6
Hawaiian Volcanic ActivityHawaiian Volcanic Activity
Each island is the summit of a large Each island is the summit of a large
volcano that rises from the seafloor.volcano that rises from the seafloor.
How deep is the seafloorHow deep is the seafloor
near the islands?near the islands?~ 5000 m (~ 16,000 ft)~ 5000 m (~ 16,000 ft)
How high are the U.S.’sHow high are the U.S.’s
highest mountains?highest mountains?
Mt. Whitney is about 4400 m (~14,500 ft) Mt. Whitney is about 4400 m (~14,500 ft) high. high.
Oahu stands 5000 m above the seafloor Oahu stands 5000 m above the seafloor and is therefore a higher mountain than Mt. and is therefore a higher mountain than Mt. Whitney.Whitney.
How high are the Earth’sHow high are the Earth’s
highest mountains?highest mountains?
The Himalayas are about 8000 m The Himalayas are about 8000 m (~26,000 ft).(~26,000 ft).
-
7
How high are the How high are the Hawai`i’sHawai`i’shighest mountains?highest mountains?
Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea on the Big Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea on the Big Island are about 4000 m above sea Island are about 4000 m above sea level. level.
This makes them about 9000 m above This makes them about 9000 m above the sea floor.the sea floor.
Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea are Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea are 9000 m high. 9000 m high.
The Himalayas are only 8000 m The Himalayas are only 8000 m high.high.
The Hawaiian Islands were built The Hawaiian Islands were built completely by volcanic activitycompletely by volcanic activity
Our study of the Geology of Hawaii Our study of the Geology of Hawaii necessarily deals mostly with volcanism.necessarily deals mostly with volcanism.Other processes are responsible for Other processes are responsible for modifyingmodifyingthe islands, but volcanism is the most the islands, but volcanism is the most important process of important process of formationformation of the islands.of the islands.
Definitions:Definitions:
A A volcanovolcano is a place where is a place where molten rock (molten rock (magmamagma) and/or ) and/or
gas comes to the earth's gas comes to the earth's surface.surface.
-
8
Magma on the surface is often Magma on the surface is often called called lavalava..
The hole through which the The hole through which the magma comes out is called a magma comes out is called a
ventvent..
The term The term volcanovolcano is often is often applied to the mountain built applied to the mountain built
by magma.by magma.
CratersCraters are bowlare bowl-- or funnelor funnel--shaped depressionsshaped depressions
They are often found at the summits of They are often found at the summits of volcanoes, butvolcanoes, butThey can also be found on volcano flanksThey can also be found on volcano flanks
-
9
-
10
Styles of volcanic eruptionsStyles of volcanic eruptions
Some Some volcanoes may erupt only once volcanoes may erupt only once ––Diamond Head is one of this kind of volcano. Diamond Head is one of this kind of volcano. Other volcanoes erupt many times Other volcanoes erupt many times ––Kilauea is one of this kind.Kilauea is one of this kind.
Styles of volcanic eruptionsStyles of volcanic eruptions
Some Some volcanoes are very gentle during volcanoes are very gentle during eruptionseruptions
KilaueaKilauea’’s eruptions are very gentles eruptions are very gentle
-
11
Styles of volcanic eruptionsStyles of volcanic eruptions
Some Some are very violent and explosiveare very violent and explosive
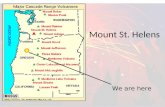
Mt. St. Helens eruptedViolently in the 1980’s
-
12
Mt. St. Helens’ ash cloud went up at least 50,000 ft into the upper atmosphere
-
13
Some people didn’tlisten to warnings aboutthe impending eruption…
-
14
Mt. Pinatubo in the Mt. Pinatubo in the PhilippinesPhilippines
also erupted explosivelyalso erupted explosivelyin the 1980’sin the 1980’s
ExplosivenessExplosiveness of a volcano is a function of of a volcano is a function of the fluidity or the fluidity or viscosityviscosity of the magma.of the magma.The magmas that generate the explosive The magmas that generate the explosive volcanoes are much more volcanoes are much more viscousviscous than than the nonthe non--explosive magmas.explosive magmas.
ViscosityViscosity is controlled by:is controlled by:Chemical composition of the magmaChemical composition of the magmaMagma temperatureMagma temperatureThe amount of gas that it containsThe amount of gas that it contains
The higher the content of silica (SiOThe higher the content of silica (SiO22), ), the more viscous the magma.the more viscous the magma.
Hawaiian magmas:Hawaiian magmas:
Not very explosiveNot very explosiveLow silica contentLow silica content
-
15
Kilauea and Mauna LoaKilauea and Mauna Loa
Very typical of the eruptive style of Very typical of the eruptive style of Hawaiian volcanoesHawaiian volcanoesCalled Called HawaiianHawaiian--typetype eruptionseruptionsThe magmas are very fluid with small The magmas are very fluid with small amounts of gas.amounts of gas.
Kilauea and Mauna LoaKilauea and Mauna Loa
The eruptions are relatively gentle The eruptions are relatively gentle ----explosions are not common. explosions are not common. Although there are often fire fountains, Although there are often fire fountains, these are not explosions.these are not explosions.
Where does the magma come from?
From the Hot Spot in the Asthenosphere
Where does the magma come from?
To magma chambers2-5 km below the volcanoes
-
16
Kilauea and Mauna Loa probablyhave separate magma chambers
How does magma get to the surface?How does magma get to the surface?
Melting at the Hot SpotMelting at the Hot SpotMolten magma less dense, so risesMolten magma less dense, so rises
What happens to the magma?What happens to the magma?
Cools as it risesCools as it risesMineralsMinerals form by form by crystallizationcrystallizationFirst to crystallize is First to crystallize is OlivineOlivineMinerals grow larger and expand into each Minerals grow larger and expand into each other to form a other to form a rockrock when all liquid is used when all liquid is used upup
DefinitionsDefinitions
Rocks that crystallize from magma are Rocks that crystallize from magma are IgneousIgneous rocksrocksVolcanicVolcanic rocks are erupted at the surfacerocks are erupted at the surfacePlutonicPlutonic rocks form when magma rocks form when magma chambers crystallize in placechambers crystallize in place
-
17
DifferencesDifferences
PlutonicPlutonic rocks have large crystals because rocks have large crystals because they cool slowly they cool slowly VolcanicVolcanic rocks have small crystals rocks have small crystals because they cool quicklybecause they cool quickly
DefinitionsDefinitions
Most volcanic rocks have dissolved gasMost volcanic rocks have dissolved gasVesiclesVesicles are the holes left when the gas are the holes left when the gas bubbles out of the rockbubbles out of the rockRocks with lots of vesicles are called Rocks with lots of vesicles are called pumicepumice and are light enough to float on and are light enough to float on waterwater
When a magma has lots of dissolved gas, lava shoots into the air carrying lots of bits and pieces of lava
This is called a pyroclasticeruption
pyro=fireclastic=fragments
-
18
The rocks formed are pyroclasticrocks, also known as tephra
Cinder cones and spatter cones are built by fragments falling around the vents.
-
19
DefinitionsDefinitionsAsh Cones and Tuff Cones form when hot magma erupts into cold sea water
This is an eruption of the volcano Surtseyoff the coast of Iceland
Resulting tuff cone is asymmetric due to ash particles being blown by the wind.
-
20
Compare Surseyto Diamond Head
Questions?Questions?
Homework #2Homework #2Due 27 JanuaryDue 27 January
Don’t forget to go to the web Don’t forget to go to the web site and fill out the “Student site and fill out the “Student
Information” form!Information” form!
-
21
Next TimeNext Time
Please read Chapter 5 in the textPlease read Chapter 5 in the text