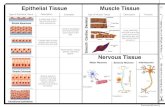
Tissue
-
Upload
guestdcb8f5 -
Category
Technology
-
view
1.372 -
download
2
Transcript of Tissue

Tissue• There are 4 types of
function that has similar structures in human tissue– Epithelia tissue – Connective tissue– Muscular tissue– Nervous tissue

Epithelia tissue• Cellularity- composed almost
entirely of cells
• Polarity-apical and basal surfaces
• Special contacts
• Support by connective tissue
• Types of Epithelia– Simple
– Stratified
• Shapes of cells– Squamous
– Cuboidal or columnar

Simple epithelia • Single Layer
• There are 4 classifications
– Simple Squamous
– Simple Cuboidal
– Simple Columnar
– Psuedostratified Columnar

Simple squamous• Single Layer of flattened cells
• Functions
• Diffusion
• Filtration
• Provide a slick
• Location
• Present in the kidney glomeruli, lining heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and serosae

Simple cuboidal• Single Layer of cube-like cells
with large, spherical central nuclei
• Functions
• Secretion
• Aborption
• Location
• Kidney tubules
• Ducts
• Secretary portions

Simple columnar• Single layer of tall cells with
oval nuclei, and contain many cilia
• Goblet cells are often find in this layer
• Functions
– Absorption, and Secretion
– Cilia help move substances through internal passageways
– Ciliated type line
• Small Bronchi, Uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus

• Single layer of cells with different heights
– Some don’t reach the free surface
• Nuclei are seen at different layers
• Function
– Secretion, and propulsion of mucus
• Present in the male sperm- carrying ducts (non-ciliated), and trachea (ciliated).

• Quite rare in the body
• Found in some sweat and mammary glands
• Typically 2 cell layers thick

• Limited distribution in the body
• Location
– Pharynx, male urethra, and lining some glandular ducts
– Occurs at transition areas between 2 other types of epithelia.

• Several cell layers, basal cells are cuboidal, surface cells are dome shaped
• Stretches to permit the distension of the urinary bladder
• Lines the urinary bladder, ureters, and part of the urethra.

• Thick membrane
• Functions
– Protection of underlying arcas subjected to abrasion

Connective tissue• Abundant and widely distributed tissue
proper
• Types of connective tissue
– Connective tissue proper
– Connective tissue cartilage
– Connective tissue Bone
– Connective tissue Blood
• Function
– Binding and support
– Protection
– Insulation
– Transportation
• Types of cells of connective tissue– Fibroblasts
– Chondroblasts
– Osteoblasts
– Hematopoietic stem cells

Connective tissue proper
• Just one cell– Fibroblasts
• 2 types of connective tissue proper– Loose
– Dense

Connective tissue bone
• Hard, calcified matrix
• Osteocytes can be found in Lacume, and vas cularized
• Stores calcium, minerals and fats

Connective tissue blood• Red and white cells in a matrix
• Function
– Transport of respiratory
• Gases
• Nutrients
• wastes

Nervous tissue• Branched neurons with long
cellular processes and support cells
• Location
– Brain
– Spinal cord
– Peripheral nerves

Connective tissue proper: Loose
• 3 types of connective tissue proper: Loose– Areolar
– Adipose
– Reticular

Loose Connective tissue proper: Areolar
• Gel-like matrix with all 3 connective tissue fibers
• Wraps and eushions organs
• Widely distributed throughout the body
• There are fibroblasts, maerophages, mast cells, and some white blood cells

Loose Connective tissue proper: Adipose
• Matrix similar to areolar connective tissue with closely packed adipocytes
• Reserved food stores
• Local fat deposits serve nutrients needs of highly active organs

Loose Connective tissue proper: reticular
• Loose ground substance with reticular fibers
• They form a soft internal skeleton
• They found in lymph nodes, and the spleen

Connective tissue proper: Dense
• 2 types of connective tissue proper: Dense
– Dense regular
– Dense irregular

Connective tissue proper: Dense regular
• Fibroblasts
• Found in tendons, ligaments, and aponearoses
• Parallel collagen fibers with a few elastic fibers

Connective tissue proper: Dense irregular
• Irregularly arranged collagens fibers with imperceptible network of collagen fibers
• Forms the costal cartilage
• In embryonic skeleton, the end of long bones, nose, trachea, and larynx

Hyaline cartilage
• Chondrocyte lie in lacunae
• Supports, reinforces, cushions, and resists compression
• Forms the costal cartilage

Connective tissue cartilage
• 3 types
– Hyaline cartilage
– Elastic cartilage
– Fibro cartilage
• Ground substance
• Chondrocyte

Elastic cartilage
• Similar to hyaline cartilage but has more elastic
• Maintain shape structure while allowing flexibility

Fibrocartilage
• Matrix similar to hyaline cartilage
• Provides tensile strength and absorbs compression shock

Muscle tissue• 3 types of muscle tissue
– Skeletal
– Cardiac
– Smooth
• Common in body
• Has contractions

Muscle skeletal tissue
• Long, cylindrical, multi nucleate cells with obvious striations
• Initiates and controls voluntary movement

Muscle cardiac tissue
• Branching, striated, uni nucleate cells interlocking at intercalated discs
• Found in the walls of the heart

Muscle smooth tissue• Sheets of spindle-shaped cells
with central nuclei
• Found in the walls of hollow organs

Credits
• Pictures by Andrew Green, Nikki Caros, David Na
• Information by David Na
• By David Na