Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
description
Transcript of Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands

Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
Patrick Ji, Kevin Samuel, Anthony LeePeriod 1
HAP

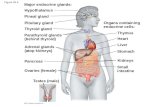
Function & Importance of Endocrine system
Endocrine system - a collection of glands that secrete different hormones for the various functions and chemical reactions occurring within the body
Maintain a stable environment within the body (homeostasis)

Thyroid and Parathyroid

Location
Thyroid glands located in neck◦Close to first part of trachea
Parathyroid glands protrude from the surface of thyroid glands

Function
Thyroid glands:◦Controls rate which body produces energy from
nutrients◦Secretes hormones that regulate energy
high production can causes weight loss, nervousness Low production can cause slowing of bodily function
Parathyroid glands:◦Control the level of calcium in blood◦Produces hormone PTH which raises blood calcium level
Animation: http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp42/4202003.html

Thyroxin and Triiodothyronine

Thyroxin
Thyroxin is the main hormone secreted into the blood stream by the thyroid gland.
It is inactive most of the time in the body until it become its active form of Triiodothyronine.
Animation: http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/9834092339/student_view0/chapter46/mechanism_of_thyroxine_action.html

Triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine is the active form of the thyroid hormone thyroxin.
Approximately 20% of triiodothyronine is secreted into the bloodstream directly by the thyroid gland. The remaining 80% is produced from conversion of thyroxin by organs such as the liver and kidneys.

Thyroxin and Triiodothyronine
Thyroxin plays a vital role in regulating the body’s metabolic rate, heart and digestive functions, muscle control, brain development and maintenance of bones.
Too much thyroxin results in a tumor and goiter in the neck.
Too little thyroxin results in autoimmune diseases and a decrease in metabolic rate.

Diseases
Goiters ~ A thyroid goiter is a dramatic enlargement of the thyroid gland. Goiters are often removed because of cosmetic reasons or, more commonly, because they compress other vital structures of the neck including the trachea and the esophagus making breathing and swallowing difficult.
Hyperparathyroidism- No symptoms at allConfusion, foggy thinkingMuscle cramps. A tingling sensation in the hands and feet.Loss of energy, always tiredTrouble sleeping, waking up at night.Heredity. If other family members had hyperparathyroidism, you are at greater risk to develop the disease.

Interesting Facts
The thyroid is a small gland about the size of two joined cherries. It is situated at the front of your neck, just below the larynx.
The thyroid secretes (releases) three importanthormones – tri-iodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4) and calcitonin.
ParathyroidAll patients with hyperparathyroidism will develop
osteoporosisThere are no drugs that will make parathyroid
disease better….None

Concept Check
1. What is a symptom of Hyperparathyroidism?SweatingMuscle atrophyFatigueLoss of appetite
2. What trouble can a goiter cause?HeadachesMuscle painsHair thinningDifficulty breathing

Concept Check
3. What happens when too little T3 and T4 comes out? SweatingHyperactivityWeight gainWeight loss4. What is the function and importance of the Thyroid gland?The thyroid plays an important role in regulating the
body's metabolism and calcium balance. The T4 and T3 hormones stimulate every tissue in the body to produce proteins and increase the amount of oxygen used by cells.

Bibliography
Works Cited "Endocrine System Function." Buzzle. Buzzle, n.d. Web. 2013.
<http://www.buzzle.com/articles/endocrine-system-function.html>.
"Parathyroid Disease." Cedars-Sinal. Cedars-Sinal, n.d. Web. 2013. <http://www.cedars-sinai.edu/Patients/Health-Conditions/Parathyroid-Disease.aspx>.
"Parathyroid Glands: Function." The American Association of Endocrine Surgeons. The American Association of Endocrine Surgeons, n.d. Web. 2013. <http://endocrinediseases.org/parathyroid/parathyroid_background.shtml>.
"Thyroid Gland Facts." House and Home. House and Home, n.d. Web. 2013. <http://www.houseandhome.org/thyroid-gland-facts>.


















![[PPT]Lab 10 Special Senses and Endocrine System · Web viewLab 11 THE SPECIAL SENSES AND THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS Thyroid & Parathyroid, 100x Thyroid & Parathyroid, 400x Parathyroid Hormone](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5aee361c7f8b9a3b2e91b2bd/pptlab-10-special-senses-and-endocrine-viewlab-11-the-special-senses-and-the-endocrine.jpg)