THE SKIN B&S CHAPTER 6. Purpose of the skin Its the largest organ in the body Used for protection...
-
Upload
megan-hensley -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of THE SKIN B&S CHAPTER 6. Purpose of the skin Its the largest organ in the body Used for protection...

THE SKINB&S CHAPTER 6

Purpose of the skin
• It’s the largest organ in the body
• Used for protection against drying (dehydration) and pathogens
• Regulates temperature
• Sensory – nerve-endings
• Absorption and excretion

The skin includes…
• Skin is associated with structures known as appendages which include glands, hair and nails
• An appendage is anything attached, like the nails, hair and glands

Other names for skin
• Covering
• Cutaneous
• Skin sheds, when it sheds, it’s ridding the body of pathogens that are on it

Facts about skin
• Skin DOES NOT BREATHE
• The pores of the epidermis only serve as an outlet for perspiration from the sweat glands and sebum (oil) from the sebaceous glands
• THEY ARE NOT USED FOR EXCHANGE OF GASES

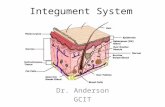
Skin consists of 2 layers:
• 1) Epidermis
• 2) Dermis

Epidermis
• Outer most portion, it’s the surface layer of the skin
• Epidermis is made up of epithelial cells and contain NO blood vessels
• These epidermal cells are constantly lost through wear and tear

Is the epidermis living or non-living?
• Non-living, but because there are no living blood vessels in the epidermis, THE ONLY LIVING CELLS ARE LOCATED IN THE DEEPEST LAYER OF THE EPIDERMIS CALLED:
• STRATUM GERMINATIVUM

Stratum germinativum
• Deepest layer of the epidermis where nourishment is provided by capillaries
• It’s known as the “growing layer”
• Cells in the stratum germinativum are constantly dividing, producing daughter cells which get pushed upward to the surface

Stratum germinativum

What happens when these cells get pushed up to the surface?
• The surface cells die from the gradual loss of nourishment and they undergo changes
• What changes you ask?

• These cells develop keratin which serves to thicken and protect skin
• By the time the epithelial cells reach the surface, they change in character

• They become flat and horny, forming the uppermost layer of the epidermis called the…
• Stratum Corneum – Does NOT contain blood vessels. But does contain nerves, hair follicles, sebaceous and sudoriferous glands

MELANIN
• These are the cells that are formed in the deepest layer of the epidermis
• Melanin is a dark pigment that colors the skin

MelaninMelanin
Slide 4.12Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Pigment (melanin) produced by melanocytes
Color is yellow to brown to black
Amount of melanin produced depends upon genetic and exposure to sunlight

Freckles
• Irregular patches of melanin

THE DERMIS, 2nd layer of skin
• Also called the corium or the true skin
• Is make up of elastic connective tissue
• Is well-supplied with blood vessels and nerves
• Stretches dramatically like in pregnancy

Appendages in the dermis
• Most of the appendages of the skin incl. sweat glands (sudoriferous) , oil glands (sebaceuos) and hair, are located in the dermis, they may extend down into the SQ layer too

Thickness of dermis
• Varies in different areas
• Sole of feet and palms of hands are covered in thick layers of skin
• Eyelids are covered with thin delicate layers

Fingerprints
• Are formed by papillae which are extensions that form a distinct pattern of ridges on the surface of thick skin. They extend upward allowing blood vessels to get closer to the surface cells
• These papillae help to prevent from slipping when grasping an object
• These are your fingerprints, they are determined by heredity

Subcutaneous Layer
• The dermis rests on the sub-Q layer• This layer connects the skin to the surface muscles• It consists of loose conn. Tissue and lrg. Amts of
adipose tissue, the fat serves as insulation
• Continuous bundles of elastic fibers connect the sub-Q tissue with the dermis, there's no clear boundary between the two

Subcutaneous layer

• There are major blood vessels that supply the skin in this layer
• This layer is rich in nerve endings
• Thickness varies, thicker in abd than in eye lid
• Sebaceous glands and hair roots extend here

APPENDAGES
• Sudoriferous glands – or sweat glands are coiled, tubelike structures located in the dermis and sub-Q tissue
• These glands function to regulate body temp through evaporation of sweat from the body surface

A 2nd Sudoriferous gland…
• Is located in the armpits and groin area
• When there is stress or sexual stimulation, these glands release their secretions through the hair folicles
• This secretion, broken down by bacteria, produces body odor…peee-u

Modified Sweat Gland
• The ceruminous glands in the ear canal produce ear wax or cerumen

Another appendage…
• Sebaceous Glands – are sac-like in structure, their oily secretions called sebum, lubricates the skin and hair to prevent drying. The ducts of these glands, open to hair follicles

Vernix caseosa
• Produced by the sebaceous glands, it’s a covering that resembles cream cheese to protect newborns at birth

Blackheads
• Are a combo of keratin and dried sebum or oil that collect at the opening of the sebaceous gland
• If these glands become infected, pimples result

Sebaceous Cysts
• When sebaceous glands become blocked by accumulated sebum or oil, a sac of the secretion forms and grows in size, surgery may be needed to remove these

Hair
• Is made of keratin and is NOT living
• Each hair develops within a sheath called a follicle and new hair is formed from cells at the bottom of the follicles

Goosebumps
• Are what they are…attached to hair follicles, muscles contract, raising the hair on the body
• This response is not import. To humans but in animals, it helps animals with furry coats to conserve heat

Nails
• Protective structure made of hard keratin
• Nails are affected by general health. Changes including abnormal color, thickness, shape or texture occur in chronic diseases such as heart, peripheral vasc diseases, malnutrition and anemia.
• Nailbeds should BE PINK, not blue

Skin can absorb and excrete
• Substances such as medication can be absorbed through the skin through a dermal patch
• Minimal amt of excretion through the skin occurs. H2O and electrolytes are perspired out of the skin

Vitamin D
• Vit. D is needed for the development and maintenance of bone tissue
• Vit D is manufactured in the skin under the effects of ultra violet rays from the sun

Skin Homeostatic ImbalancesSkin Homeostatic Imbalances
Slide 4.25Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Burns
Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat, electricity, UV radiation, or chemicals
Associated dangers
Dehydration
Electrolyte imbalance
Circulatory shock

Burns to the skin…
• 1st degree – involves the epidermis, it becomes red and painful, like sun burn
• Treatment: bathing the wound in cold water


• 2nd degree burn – penetrates into deeper layers and often causes a blister to form
• Examples: severe sunburns or scalding with hot water
• Silvadene cream

2nd degree burn

• 3rd degree – is full thickness burn, is the most serious. Usually involved underlying tissues such as muscle and connective tissue

3rd degree burn

• HOW TO CLASSIFY A BURN
• “RULE OF NINE’S”

RULE OF NINE’S
• rule of nines - a method of estimating the extent of body surface that has been burned in an adult, dividing the body into sections of 9 per cent or multiples of 9 per cent.
• Rule of nines.

Color of skin
• Melanin gives skin it’s color, skin should be pink

Pallor
• Pallor – is pale colored skin often caused by reduced blood flow
• Most easily noted in lips, nail beds, and mucous membranes

Flushing
• Redness of the skin related to fever
• Most noticeable in the face or neck

Cyanosis
• Bluish discoloration in skin
• Due to not enough oxygen circulating in the blood
• This is a symptom of heart failure or of breathing problems such as asthma or respiratory obstruction

Jaundice
• Yellow discoloration of the skin
• May be due to the presence of excessive quantities of bile pigment called bilirubin, in the blood

Lesion
• Is any wound or local damage to tissue
• A surface lesion is called a rash
• A raised lesion is called an eruption

Terms used to describe surface skin lesions:
• Macules – spots that are neither raised nor depressed. They are typical of measles and descriptive of freckles
• Papules – firm raised areas as in some stages of chicken pox. Pimples are papules
• Nodule – a large firm papule

• Vesicle – blisters or small sacs full of fluid like chicken pox
• Pustules – vesicles filled with pus, can develop in chicken pox

Deeper lesions
• Deeper lesions may develop from surface lesions or may be caused by trauma

Deep injuries to the skin
• Excoriation – scratch of the skin surface
• Laceration – rough, jagged wound made by the tearing of the skin
• Ulcer – a sore associated with disintegration and death of tissues
• Fissure – a crack in the skin, like in athletes foot

• Excoriation • Laceration

• Ulceration • Fissure

Dermatitis
• Inflammation of the skin
• May be d/t irritants such as poison oak or ivy, detergents, strong acids or other chemicals

Treatment of dermatitis
• Prompt removal of the irritant is most effective
• Washing thoroughly with soap and water to wash away the plant oil

Atopic Dermatitis or eczema
• Intense itching and skin inflammation
• Redness (erythema)• Blisters (vesicles)• Pimple-like lesions
(papules)• Scaling and crusting of
skin

When does eczema start?
• Occurs first in childhood and recurs throughout life
• Skin may be sensitive to soaps or detergents
• Person may be subject to allergic disorders like asthma, hayfever and food allergies

Impetigo
• Acute, contagious disease of staphylococcal or streptococcal origin
• Can cause death in newborn infants• It’s a blister-like lesion filled with pus that
contain millions of virulent bacteria• One can infect and re-infect himself and
others..need antibiotics


Alopecia
• baldness

Other disorders of the skin…
• Carbuncle – a pus producing lesion formed from an infected boil. These involve skin and sub-Q tissues and have numerous drainage channels that extend to the skin surface

Herpes Simplex Virus
• Characterized by formation of watery vesicles (cold sores, fever blisters) on the skin and mucous membranes including the genital area

Shingles (herpes zoster virus)
• Virus is seen in adults and is caused by same virus that causes chicken pox
• Infection follows nerve pathways producing small lesions on the skin
• Pain, increased sensitivity and itching are common symptoms that usually last longer than a year

What to treat herpes virus with?
• Antivirals like acyclovir or Zovirax
• P.O. takes away itching, sensitivity and lesions
• IS NOT A CURE OF THE VIRUS, only helps with symptoms

Decubitis
• Bed sore d/t decreased circulation
• Treatment: frequent position changes, adequate nutrition and
if sore is present, aggressive skin treatment

Affects of aging on skin
• Loss of fat and collagen=wrinkles• Skin becomes transparent and can tear
easily• Decreased pigment esp. in hair (grey hair)
and in skin, except in some areas such as hands
• Decreased sweat glands• Hardening of nails





Jaundice

Jaundice

Cyanosis

Macule

Terms used to describe surface skin lesions:
• Macules – spots that are neither raised nor depressed. They are typical of measles and descriptive of freckles
• Papules – firm raised areas as in some stages of chicken pox. Pimples are papules
• Nodule – a large firm papule

Papule

Vesicle

Pustule

Excoriation

Laceration

Ulcer

Fissure on Heel

Boils- Furuncle
Cold Sores Herpes Simplex

Basal Cell Carcinoma

Malignant Melanoma

ABCD Rule for moles or nevusABCD Rule for moles or nevus
Slide 4.32Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
A = Asymmetry Two sides of pigmented mole do not match
B = Border irregularity Borders of mole are not smooth
C = Color Different colors in pigmented area
D = Diameter Spot is larger then 6 mm in diameter

Impetigo
Psoriasis

Shingles- Herpes Zoster

Athlete’s Foot

THE END