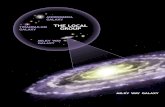
The Size and Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy We live in a new class of astronomical object.
-
Upload
veronica-byrd -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of The Size and Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy We live in a new class of astronomical object.
Structure of the Milky Way
• Disk
• Bulge
• Galactic center
• Galactic halo
Question: what simple observationIs consistent with a part of this picture?
Next topic: the motion of the Sun in the Milky Way (leads to something extremely
interesting)
How does the Sun move in the Milky Way?
Next topic: the motion of the Sun in the Milky Way (leads to something extremely
interesting)
How does the Sun move in the Milky Way?
V=220 km/sec
The sun moves in response to the gravitational force of All the rest of the mass in the galaxy
Mass distributions like 1,2, and 3 give circular orbits with
V(R)
A plot of V versus R is called a rotation curve
Significance of the Rotation Curve for the Milky Way
• Rotation curve stays high outside the bulk of the stars
• Mass indicated by the rotation curve exceeds that in stars
• Most of the mass of the Milky Way is in an unknown form of “Dark Matter”
Dark Matter: A Major Problem for Contemporary Physics and
Astronomy• Stars are a small fraction of the mass of
major galaxies• The dark matter problem becomes more
pronounced as you go out in the universe• The form of the dark matter is unknown;
probably not what you studied in chemistry• Possibly/probably an unknown form of
elementary particle
What do we see at the galactic center (radio and
infrared wavelengths?
• Strong radio source (synchrotron radiation)
• At infrared wavelengths, can see stars orbiting very vast around Sgr A
• http://antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov/apod/ap001220.html
• Ten years of observations speeded up