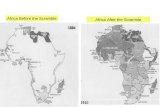
The Scramble For Africa
-
Upload
guest787fe6 -
Category
Education
-
view
5.306 -
download
2
Transcript of The Scramble For Africa

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
1
The Scramble for Africa
Chapter 25 section 2

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
2
Topics
I. The Scramble for Africa
II. The Heart of Africa
III. North Africa
IV. South Africa
V. African resistance

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
3

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
4
I. The Scramble for Africa
A. Why Africa???
B. Exploration to Competition
C. The Belgian Congo
D. The Berlin Conference

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
5

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
6

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
7
A. Why Africa???
• Close to Europe.• Europe valued
African trade.– Long history.– Many established
trading posts.
• African empires did not expect relationship to change.

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
8
B. Exploration to Competition
• Early 1800’s Europeans began limited exploration of interior of Africa.– Malaria– Limited military power– As science and military
power improved, Africa became more vulnerable
• David Livingstone explored Central Africa for 30 years

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
9
C. The Belgian Congo• King Leopold II became
interested in colonies by 1870’s
• Declared Congo region of Africa to be under Belgian control.– Henry Stanley had helped
Leopold to secure treaties with Africans to dominate region.
• This alarmed other European Nations and began a scramble for colonies.

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
10

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
11
D. The Berlin Conference 1884
• European countries feared war from competition.
• European countries could claim African land if they controlled strategic points.– No African rulers were present.
• Europe also agreed to bring “Commerce, Christianity and Civilization” to Africa– end slavery in Africa.

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
12
II. The Heart of Africa
A. King Leopold II
B. Bring civilization to Africa
C. Diplomacy to indirect control
D. Abuses in the Congo

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
13
A. King Leopold II
• Wanted to “civilize” Africa– End the slave trade– Really wanted the resources
• Had Henry Stanley sign 450 Treaties with African leaders to create a trade zone for Belgium
• This became known as the Congo free State

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
14
B. Bring civilization to Africa
• King Leopold advocated the “Commerce, Christianity and Civilization” plan– Adopted at Berlin Conference

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
15
C. Diplomacy to indirect control
• Belgium passed laws claiming unused land as European
• Europe convinced African leaders to pass laws forcing African workers into mines and plantations.– Taxes were used to force Africans into
mines and plantations.

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
16
D. Abuses in the Congo
• Pacification campaigns• Forced taxes on Africans
– To build infrastructure for European business
• Change from food to cash crops– Rubber instead of food– Mass starvations
• Other human atrocities

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
17
III. North Africa
A. France in Algeria
B. The Suez canal
C. Britain and the Suez

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
18
A. France in North Africa
• Took control of Algeria– Large migration of French population– Led to direct control– Also led to brutal revolts in the 1950’s
• France also built Suez Canal
• Britain viewed canal as essential to their interests

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
19
B. The Suez canal

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
20

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
21
C. Britain and the Suez
• Civil fighting broke out in 1882 in Egypt.– Supported by British
• Britain stepped in and established order.– Made Egypt a protectorate– Forced France out
• Britain and Egypt will invade the Sudan and make it into a condominium.– To protect southern access to canal

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
22
IV. South Africa
A. The Boers
B. British Interest
C. The Boer War
D. Second Class Citizens

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
23
A. The Boers• Boers came to South Africa.
– Strict Dutch , Calvinist Settlers.– Believed they were a chosen
people.
• Britain seized control in 1806.– Boers disliked British rule.– Began Great Trek into interior of
Africa.
• Boers create 3 states.– Natal, Transvaal and Orange
Free state.– Defeated Zulu groups to create
them.

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
24
B. British Interest
• Originally interested in ports for trade
• Gained control of coastline and port towns– Content to leave Boers to interior
• Discovery of Diamonds will change this

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
25

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
26
C. The Boer War• Diamonds were discovered in Boer territory.• Cecil Rhodes and other Brits enter interior.• Boers resent this and hostilities increase.• War breaks out.• Britain wins the war but at great cost.
– South Africa will be part of the British empire.– Boers will be able to govern themselves.

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
27
D. Second Class Citizens
• Boers have home rule– Become known as Afrikaners– Despise ad hate local Black population
• African population forced to follow Apartheid– Think Segregation

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
28
V. African Resistance.A. Samouri Toure’ and the Mandingo
Empire
B. Menelik II and Ethiopia
C. Liberia

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
29
A. Samouri Toure’ and the Mandingo Empire
• Purchased weapons from European traders.
• Built his own weapon factory.
• Defended his territory for 6 years.

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
30
B. Menelik II and Ethiopia
• Many European nations attempted treaties with Ethiopia.
• Menelik pitted them against each other.
• Also got European weapons.
• Mountains also protected Ethiopia.

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
31
C. Liberia• Was populated by former American
slaves.
• European nations left it alone.– Feared U.S. involvement in Africa.

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
32
Terms To Know
• Berlin Conference of 1884
• King Leopold II• Suez Canal• Social darwinism
• Menelik II• Liberia • Zulu• Boers• Great Trek

04/12/23
European Imperialism and the Scramble for Africa
33
Summary
• What event started the scramble for Africa?
• Describe King Leopold II’s motivations.
• What were the interests of the French and the British?
• What happened to the rights of Africans?