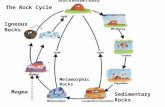
The Rock Cycle- Minerals form rocks All rocks can be transformed into other rock types Rocks are...
-
Upload
leslie-williamson -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of The Rock Cycle- Minerals form rocks All rocks can be transformed into other rock types Rocks are...
The Rock Cycle-Minerals form rocks
All rocks can be transformed into other rock types
Rocks are divided into 3 categories
Igneous- crystalline- forms as liquid cools
Metamorphic- crystalline-forms as rocks are
heated and squeezed
Sedimentary- non-crystalline- smaller pieces
or chemicals from other rocks
The Rock Cycle-Minerals form rocks
All rocks can be transformed into other rock types
Rocks are divided into 3 categories
Igneous- crystalline- forms as liquid cools
Metamorphic- crystalline-forms as rocks are
heated and squeezed
Sedimentary- non-crystalline- smaller pieces
or chemicals from other rocks
QuickTime™ and a decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
(Heat & Pressure)
Eruption or near surface cooling & crystallization
Erosion
MagmaMagma•• molten rock below Earth's molten rock below Earth'ssurface.surface.
LLava ava •• magma on the Earth's surface. magma on the Earth's surface.
Pyroclastic materialPyroclastic material•• ( (pyro pyro = fire, = fire, clastic clastic = debris)= debris)•• Airborne lava Airborne lava
—— cools as it falls cools as it falls
Igneous formed from Magma and LavaIgneous formed from Magma and Lava
Composition of the magmaComposition of the magma• • Analogous to what makes up the “stew"Analogous to what makes up the “stew"
• • What chemical elements are presentWhat chemical elements are present• • What material has the magma moved
throughWhat material has the magma moved through
Temperature of the meltTemperature of the melt• • Not only how hot, but how long it stays that hot Not only how hot, but how long it stays that hot
• • also relates to pressure of the molten rockalso relates to pressure of the molten rock
Cooling environmentCooling environment• • fast fast vsvs slow slow• • Internal vs ExternalInternal vs External
Water contentWater content
Bowen's Reaction Series- Important !
Olivine
Plagioclase(Na-feldspar)BiotiteBiotite
Quartz
PyroxenePyroxene
AmphiboleAmphibole
Muscovite
Plagioclase(Ca-feldspar)
Orthoclase(K-feldspar)
Discontinuous C
ontin
uous
What things might you describe when looking at an igneous rock?
What things might you describe when looking at an igneous rock?
••
Composition of Igneous rocksComposition of Igneous rocksFelsic or Sialic Felsic or Sialic magmamagma
•• Si-rich (> 65%) Si-rich (> 65%) •• rich in K, and Al rich in K, and Al•• little Ca, Fe, and Mg. little Ca, Fe, and Mg.
Intermediate magma Intermediate magma •• between the two extremes in Si between the two extremes in Si content and other atoms. content and other atoms.Mafic Mafic magma magma •• Si - poor (< 35%) Si - poor (< 35%) richer in Ca, Fe, and Mg. richer in Ca, Fe, and Mg.
QuickTime™ and aPhoto - JPEG decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
magmamagma
AssimilationAssimilation
QuickTime™ and aPhoto - JPEG decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
Crystal SettlingCrystal Settling
QuickTime™ and aPhoto - JPEG decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
Magma MixingMagma Mixing
Ways of Changing Magma Composition
Viscosity of Magma/ LavaViscosity of Magma/ Lava
• the resistance of a liquid to flow— —
Viscosity- important for volcanic activity Viscosity- important for volcanic activity
• the resistance of a liquid to flow— high viscosity = thick and stiffhigh viscosity = thick and stiff
— low viscosity = thin and "runny".low viscosity = thin and "runny".
Related to:• • • Mafic
— • Felsic
—
Related to:• amount of water (H2O) in magma• amount of silica (Si) in magma• Mafic
— thin, low viscositythin, low viscosity
• Felsic— thick, high viscosity thick, high viscosity
Igneous Rock Textures- how big are the minerals?
Igneous Rock Textures- how big are the minerals?Phaneritic TexturePhaneritic Texture
•• Visible Mineral Grains Visible Mineral Grains distinguishable as different colored interlockingdistinguishable as different colored interlocking
shapesshapes
Aphanitic TextureAphanitic Texture•• Mineral grains too small to be seen Mineral grains too small to be seen
—— microscopic microscopic
Porphyritic TexturePorphyritic Texture•• Two distinct sizes of mineral grains Two distinct sizes of mineral grains•• Large and Small Large and Small
—— Large = Phenocrysts Large = Phenocrysts—— Small = Groundmass or Matrix Small = Groundmass or Matrix
•• Groundmass Groundmass—— Grains may be either visible or not Grains may be either visible or not
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
Aphanitic basalt (mafic composition) constitutes the groundmass
Aphanitic basalt (mafic composition) constitutes the groundmass
Porphyritic texturePorphyritic texture
Large white crystals are phenocryts
Large white crystals are phenocryts
Cooling HistoriesCooling HistoriesMinerals need time and space to growMinerals need time and space to grow
•• More time = Bigger crystals More time = Bigger crystals —— visible mineral grains visible mineral grains
P & T control cooling rates of magmaP & T control cooling rates of magma•• Temp Temp
—— Earth is a good insulator Earth is a good insulator»» holds in heat holds in heat»» keeps out cool keeps out cool
—— Atmosphere is a relatively bad insulator Atmosphere is a relatively bad insulator»» transfers heat easily transfers heat easily
•• Earth has pressure Earth has pressure—— Weight of overlying rocks Weight of overlying rocks—— Magma trying to push up (density) Magma trying to push up (density)—— water vapor (steam), wants to expand water vapor (steam), wants to expand
Intrusive rocksIntrusive rocks•• cool beneath Earth's surface cool beneath Earth's surface•• cool very slowly cool very slowly•• higher P & T higher P & T
—— Phaneritic textures Phaneritic textures
Extrusive rocksExtrusive rocks•• cool on the Earth's Surface cool on the Earth's Surface•• cool relatively fast cool relatively fast•• lower T & P lower T & P
—— Aphanitic textures Aphanitic textures—— Pyroclastic textures Pyroclastic textures
ComplexComplex••
—— Porphyritic textures Porphyritic textures
Categories of Igneous EOFCategories of Igneous EOF
Partially cools below and above Partially cools below and above
GraniteGranite
Basalt porphyryBasalt porphyry
RhyoliteRhyolite
Igneous rock namesIgneous rock names• • determined by texturedetermined by texture
— — size and arrangement of mineral grainssize and arrangement of mineral grains• • AND by mineral compositionAND by mineral composition
— — minerals affect rock color and indicate temperature of creationminerals affect rock color and indicate temperature of creation
A Pegmatite is a very coarse-grained igneous rock.A Pegmatite is a very coarse-grained igneous rock.Crystals are >2 cm, often larger.Crystals are >2 cm, often larger.
Most are granitic, although mafic pegmatites can form.Most are granitic, although mafic pegmatites can form.
PegmatitePegmatite
Feldspar Feldspar mineral mineral graingrain
Quartz mineral Quartz mineral graingrain
Biotite mineralgrainBiotite mineralgrain
Granite & RhyoliteGranite & Rhyolite
RhyoliteRhyolite
GraniteGranite
Phaneritic TexturePhaneritic TextureFelsic magmaFelsic magma
Aphanitic TextureAphanitic TextureFelsic magmaFelsic magma
What are the textures in these two rocks ?What are the textures in these two rocks ?
Andesite & DioriteAndesite & Diorite Phaneritic texture Phaneritic texture-forms from intermediate composition magma-forms from intermediate composition magma
Aphanitic texture Aphanitic texture forms from intermediate composition magma forms from intermediate composition magma
What are the textures in these two rocks ?What are the textures in these two rocks ?
Basalt & Gabbro
»
aphanitic texture aphanitic texture forms from mafic magma forms from mafic magma
phaneritic texture phaneritic texture forms from mafic magma forms from mafic magma
BasaltBasalt
GabbroGabbro
Peridotite- the abundance (more than 40%) of Olivine crystals makes the rock take on a green appearance
VolcanicGlass
Obsidian- conchoidal fracture And association with volcanic rocksObsidian- conchoidal fracture And association with volcanic rocks
Tuffs & BrecciasTuffs & Breccias- look like sedimentary rock
But they are not….it is volcanic ash that is lithifiedBut they are not….it is volcanic ash that is lithified
Tuffs - may be welded or not
Always consists of fragments smaller than 2mm in diameter
Welded means they were still hot enough that they partially recrystallized they were emplaced and consolidated.
If they are not welded, it means they were not hot enough to partially recrystallize when they settled on the landscape
Breccias - have a tuffaceous matrix but have a large percentage of coarse-grained angular fragment. They may be welded or not too.
Tuffs - may be welded or not
Always consists of fragments smaller than 2mm in diameter
Welded means they were still hot enough that they partially recrystallized they were emplaced and consolidated.
If they are not welded, it means they were not hot enough to partially recrystallize when they settled on the landscape
Breccias - have a tuffaceous matrix but have a large percentage of coarse-grained angular fragment. They may be welded or not too.
How do we tell where the igneous rocks formed?
What can we derive from the rocks about the conditions of formation?
How do we tell where the igneous rocks formed?
What can we derive from the rocks about the conditions of formation?
BatholithBatholith
Volcanic neckVolcanic neck
Igneous dikeIgneous dike
Igneous SillIgneous Sill
Lava flow
Pyroclastics
Areal extent of the Idaho Batholith- a huge (15,400 square miles) intrusive body of primarily felsic composition (granites) igneous rocks
An igneous dike-
Discordant with surrounding rock
It cuts across other rocks
An igneous dike-
Discordant with surrounding rock
It cuts across other rocks
An igneous sill-
Concordant with surrounding rock
It runs parallel to other rocks
An igneous sill-
Concordant with surrounding rock
It runs parallel to other rocks