The human skeleton
-
Upload
lola-caravaca -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
1.112 -
download
1
Transcript of The human skeleton

MUSCLES AND BONESMUSCLES AND BONES
►BY ÁLVARO BY ÁLVARO GONZÁLEZ GONZÁLEZ SÁNCHEZSÁNCHEZ

MUSCLES AND BONESMUSCLES AND BONES The musculoskeletalm system is The musculoskeletalm system is
composes of many muscles and bonescomposes of many muscles and bones Humans have got an internal skeleton. Humans have got an internal skeleton.
It is made of 206 different bonesIt is made of 206 different bones The functions of the skeleton:The functions of the skeleton:► It suports the body and helps to keep ist It suports the body and helps to keep ist
shape.shape.► It protects the body’s soft, internal It protects the body’s soft, internal
organs.organs.► It is connected to muscles that move the It is connected to muscles that move the
different bones.different bones. Bones are made of bone cels that form Bones are made of bone cels that form
bone tissue.bone tissue.
JointsJoints are parts of the skeleton where are parts of the skeleton where two or more bones are connected.two or more bones are connected.
In some joints there are elastic tissues In some joints there are elastic tissues
called called ligamentsligaments that keep the that keep the bones togetherbones together

MUSCLESMUSCLES► Muscles are made of many muscle Muscles are made of many muscle
cells.cells.► These cells can contrac and These cells can contrac and
become shorter.become shorter.► They can also relax and become They can also relax and become
longer again.longer again.► Muscles contrac and relax to move Muscles contrac and relax to move
different parts of the body.different parts of the body.► Some muscles are conected to Some muscles are conected to
bones by long, non-elastic fibres bones by long, non-elastic fibres called called tendonstendons..
► When the muscles contract, they When the muscles contract, they pull on the tendons and move the pull on the tendons and move the bonesbones

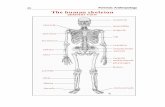
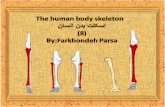
THE HUMAN SKELETONTHE HUMAN SKELETON WE CAN PUT THE BONES OF THE WE CAN PUT THE BONES OF THE
HUMAN SKELETON INTO THREE HUMAN SKELETON INTO THREE GROUPS:GROUPS:
► The bones of the head.The bones of the head.► The bones of the trunk.The bones of the trunk.► The bones of the extremities.The bones of the extremities.
BONES CAN BE DIFFERENT SHAPES BONES CAN BE DIFFERENT SHAPES AND SIZES.AND SIZES.
► Long bones.Long bones.► Short bones.Short bones.► Flat bones.Flat bones.► Cylindrical bones.Cylindrical bones.

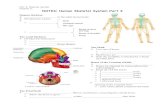
THE CRANIUMTHE CRANIUM
► The bones of the head The bones of the head form the skull (or form the skull (or cranium).cranium).
► These bones protect These bones protect the brain and they also the brain and they also form the face.form the face.

SHAPES OF THE BONESSHAPES OF THE BONES
► THE FEMUR IS A LONG BONE. THE CARPALS ARE SHORT THE FEMUR IS A LONG BONE. THE CARPALS ARE SHORT BONES. THE SCAPULA IS A FLAT BONEBONES. THE SCAPULA IS A FLAT BONE

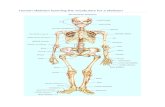
BONES OF THE TRUNK AND BONES OF THE TRUNK AND EXTREMITIESEXTREMITIES
► The bones of the trunk include the spinal The bones of the trunk include the spinal column, the sternum and the ribs.column, the sternum and the ribs.
The spinal column is made of vertebrae. The spinal column is made of vertebrae. The spinal column supports the head The spinal column supports the head and protecs the spinal cord. and protecs the spinal cord.
The sternum and the ribs form the rib The sternum and the ribs form the rib cage. This protects the heart and the cage. This protects the heart and the lungs.lungs.
Upper extremities is connected to the Upper extremities is connected to the trunk by two bones: the clavicle and the trunk by two bones: the clavicle and the scapula.scapula.
Each hand has got 27 bones: carpals, Each hand has got 27 bones: carpals, metacarpals and phalages .metacarpals and phalages .
The lower extremities are connected to The lower extremities are connected to the trunk by the pelvis.the trunk by the pelvis.
Each foot has got 26 bones: tarsals, Each foot has got 26 bones: tarsals, metatarsals and phalangesmetatarsals and phalanges

MUSCULAR SYSTEMMUSCULAR SYSTEM All the muscles of the body form the All the muscles of the body form the
muscular system.muscular system.
Muscles can move and apply force. Muscles can move and apply force. They have got different shapes. They have got different shapes. There are long muscles, flat There are long muscles, flat muscles and cicular muscles.muscles and cicular muscles.
We can also classify muscles by the We can also classify muscles by the way they function:way they function:
Some muscles are voluntary: you Some muscles are voluntary: you can control them whenever you can control them whenever you want.want.
Some muscles are involuntary: they Some muscles are involuntary: they work automatically. Your heart is an work automatically. Your heart is an involuntary muscle. The muscles in involuntary muscle. The muscles in your intestines are also involuntary your intestines are also involuntary

MUSCLES OF THE FACEMUSCLES OF THE FACE
The The FRONTALFRONTAL muscle muscle pulls the eyebrows up. pulls the eyebrows up. It also moves the It also moves the forehead.forehead.
The The ORBICULARORBICULAR eye eye muscles close the muscles close the eyelids.eyelids.
The The STERNOCLEIDOMASTOISTERNOCLEIDOMASTOID muscles turn the D muscles turn the head.head.

JOINTSJOINTS
► Joints are places where two Joints are places where two or more bones are or more bones are connected.connected.
We can classify joints by We can classify joints by how much they move:how much they move:
FIXED joints can´t move.FIXED joints can´t move. SEMI-MOVEABLE joints can´t SEMI-MOVEABLE joints can´t
move very much. move very much. MOVEABLE joints can move MOVEABLE joints can move
a lot. Inside these joints, a lot. Inside these joints, there is a tough, flexible there is a tough, flexible tissue called CARTILAGE to tissue called CARTILAGE to protect them from friction.protect them from friction.

GOOD HABITS FOR YOUR GOOD HABITS FOR YOUR MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEMMUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
Eat foodEat food with lots of with lots of calcium, phosphorus, calcium, phosphorus, vitamin C and vitamin D.vitamin C and vitamin D.
Do different types of sport Do different types of sport and exercise.and exercise.
Try to sleep on your back or Try to sleep on your back or on your side.on your side.
Sit up straight.Sit up straight. Bend your knees when you Bend your knees when you
pick up heavy things.pick up heavy things. Wear your rucksack Wear your rucksack
properly. Use both straps.properly. Use both straps.