The Human Nervous System: Cerebrum & Diencephalon€¦ · Cerebrum Parts & Location ⦿ largest...
Transcript of The Human Nervous System: Cerebrum & Diencephalon€¦ · Cerebrum Parts & Location ⦿ largest...

The Human Nervous System: Cerebrum & Diencephalon
By: Shannon Ament, Katie Kelley, and Candice Ellis

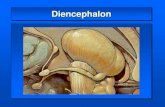
Location of Diencephalon
⦿ between cerebrum’s hemispheres ⦿ encompasses the third ventricle between
the hemispheres of the cerebrum ⦿ part of limbic system

Functions of the Diencephalon
⦿ interprets sensory information ⦿ emotions ⦿ works in coordination with the cerebrum

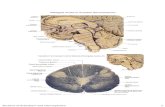
Parts of the Diencephalon
⦿ thalamus ⦿ hypothalamus ⦿ optic tract/optic chiasma ⦿ infundibulum ⦿ posterior pituitary gland ⦿ mammillary bodies ⦿ pineal gland

Cerebrum Parts & Location ⦿ largest part of the brain ⦿ divided into L/R cerebral hemispheres
⦿ corpus callosum (“nerve fiber bridge”) connects the two hemispheres
⦿ separated by dura matter ⦿ cerebral cortex is a layer of “gray matter” on the outside of the
cerebrum has 75% of the nervous system’s neurons ⦿ surface covered with many convolutions (gyri, aka ridges)
⦿ shallow ridges = sulcus ⦿ deep ridges = fissure
⦿ the two lobes are connected by corpus callosum ⦿ main lobes:
⦿ frontal ⦿ parietal ⦿ temporal ⦿ occipital ⦿ insula

Cerebrum Functions
⦿ has several different areas that control different functions
⦿ motor ⦿ frontal lobes ⦿ motor speech (Broca’s) area ⦿ frontal eye field ⦿ another region just in front of primary
motor area controls hands/fingers

Cerebrum Functions (continued)
!⦿ sensory
⦿ cutaneous (sensation / touch) ⦿ visual (sight) ⦿ auditory (hearing) ⦿ taste ⦿ smell ⦿ sensory fibers, like motor fibers, cross over
also

Cerebrum Functions (continued)
!⦿ association
⦿ analyze / interpret sensory experiences ⦿ memory, reasoning, verbalizing, judgement, emotion ⦿ frontal lobes ⦿ parietal ⦿ temporal (and posterior ends of lateral fissures) ⦿ occipital
⦿ general interpretative area: temporal, parietal and occipital association areas meet near posterior end of lateral sulcus; plays primary role in overall complex thought processing

Alzheimer’s Disease
⦿ form of dementia ⦿ impact ability to think, perform normal tasks, and memory ⦿ progresses and gets worsens over time ⦿ the neurons eventually die, disabling the person’s mental
abilities ⦿ defined by the build-up of plaques (irregular protein
molecules) and tangles (proteins that twisted and attach onto the neurons) within the brain
⦿ these proteins make it difficult for the neurons to send messages to one another
⦿ causes ⦿ genetic factors ⦿ age

Alzheimer’s Disease (Continued)
⦿ symptoms ⦿ memory loss ⦿ difficulty in performing typical daily functions or problems ⦿ confusion ⦿ decreased judgement ⦿ mood change
⦿ treatment ⦿ incurable ⦿ medications slow down or stop the progression of the
disease for a short amount of time ⦿ other non-medicinal treatments may be used
⦿ i.e: exercise or diet regimens